What is a PCB?
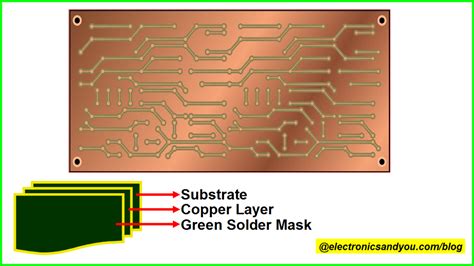
Before diving into the various types of PCBs, let’s first understand what a PCB is. A Printed Circuit Board is a flat insulating board that contains conductive tracks, pads, and other features etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. These boards are used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks, or signal traces.
PCBs have revolutionized the electronics industry by replacing the bulky, complex wiring systems with a more compact, reliable, and cost-effective solution. They have enabled the miniaturization of electronic devices and have made mass production of electronics possible.
Types of PCBs
There are several types of PCBs, each with its own unique features and applications. Let’s explore some of the most common types of PCBs in the electronics industry.
1. Single-sided PCB
Single-sided PCBs, also known as one-layer PCBs, have conductive tracks and components on only one side of the board. The other side of the board is usually left bare or coated with a solder mask to protect the copper traces from oxidation and short-circuiting.
Single-sided PCBs are the simplest and most cost-effective type of PCB. They are commonly used in basic electronic devices such as calculators, radios, and power supplies. However, their simplicity also limits their functionality and density, making them unsuitable for more complex circuits.
2. Double-sided PCB
Double-sided PCBs have conductive tracks and components on both sides of the board. The two sides are connected using through-hole technology, where small holes are drilled through the board, and copper is plated inside the holes to create a conductive path between the two sides.
Double-sided PCBs offer several advantages over single-sided PCBs, such as higher component density, better signal integrity, and improved heat dissipation. They are commonly used in more complex electronic devices such as televisions, computer motherboards, and automotive electronics.
3. Multi-layer PCB
Multi-layer PCBs consist of three or more conductive layers separated by insulating layers. The layers are connected using through-holes or vias, which are small holes drilled through the board and plated with copper to create a conductive path between the layers.
Multi-layer PCBs offer the highest level of complexity and functionality among all types of PCBs. They can accommodate a large number of components and circuits in a small space, making them ideal for high-density applications such as smartphones, medical devices, and aerospace systems.
| PCB Type | Layers | Complexity | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-sided | 1 | Low | Basic electronic devices |
| Double-sided | 2 | Medium | More complex devices |
| Multi-layer | 3+ | High | High-density applications |
4. Flexible PCB
Flexible PCBs, also known as flex circuits, are made from flexible plastic substrates such as polyimide or PEEK. They can be bent, twisted, or folded without damaging the conductive tracks or components.
Flexible PCBs are commonly used in applications that require a high degree of flexibility or where space is limited, such as wearable electronics, medical implants, and aerospace systems. They can also be used to connect rigid PCBs in a three-dimensional configuration, allowing for more complex designs and better use of available space.
5. Rigid-Flex PCB
Rigid-flex PCBs are a combination of rigid and flexible PCBs. They consist of one or more rigid PCBs connected by flexible PCBs, allowing for a three-dimensional configuration that can be folded or bent to fit into tight spaces.
Rigid-flex PCBs offer the best of both worlds, combining the stability and durability of rigid PCBs with the flexibility and space-saving benefits of flexible PCBs. They are commonly used in applications that require high reliability and performance, such as aerospace, military, and medical devices.
6. High-Frequency PCB
High-frequency PCBs are designed to handle high-frequency signals, typically above 1 GHz. They are made from specialized materials such as PTFE or Rogers that have low dielectric loss and high thermal stability to minimize signal loss and distortion.
High-frequency PCBs are commonly used in applications that require high-speed data transmission, such as 5G networks, radar systems, and satellite communications. They require careful design and manufacturing to ensure signal integrity and minimize interference.
7. High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCB
High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCBs are a type of multi-layer PCB that uses advanced manufacturing techniques to achieve higher component density and smaller feature sizes. They typically have smaller vias, narrower traces, and tighter spacing between components compared to traditional PCBs.
HDI PCBs are commonly used in applications that require high performance and miniaturization, such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. They offer several advantages over traditional PCBs, such as better signal integrity, lower power consumption, and reduced size and weight.
FAQ
-
Q: What is the difference between a single-sided and double-sided PCB?
A: Single-sided PCBs have conductive tracks and components on only one side of the board, while double-sided PCBs have them on both sides. Double-sided PCBs offer higher component density and better signal integrity compared to single-sided PCBs. -
Q: What are the advantages of using a multi-layer PCB?
A: Multi-layer PCBs offer several advantages over single-sided and double-sided PCBs, such as higher component density, better signal integrity, and improved heat dissipation. They can accommodate a large number of components and circuits in a small space, making them ideal for high-density applications. -
Q: What are flexible PCBs used for?
A: Flexible PCBs are commonly used in applications that require a high degree of flexibility or where space is limited, such as wearable electronics, medical implants, and aerospace systems. They can also be used to connect rigid PCBs in a three-dimensional configuration, allowing for more complex designs and better use of available space. -
Q: What are high-frequency PCBs made of?
A: High-frequency PCBs are made from specialized materials such as PTFE or Rogers that have low dielectric loss and high thermal stability to minimize signal loss and distortion. -
Q: What are the advantages of using an HDI PCB?
A: HDI PCBs offer several advantages over traditional PCBs, such as better signal integrity, lower power consumption, and reduced size and weight. They are commonly used in applications that require high performance and miniaturization, such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices.

Conclusion
In conclusion, there are several types of PCBs used in the electronics industry, each with its own unique features and applications. Single-sided PCBs are the simplest and most cost-effective, while double-sided PCBs offer higher component density and better signal integrity. Multi-layer PCBs offer the highest level of complexity and functionality, while flexible PCBs are ideal for applications that require flexibility or where space is limited. Rigid-flex PCBs combine the benefits of rigid and flexible PCBs, while high-frequency PCBs are designed to handle high-frequency signals. HDI PCBs use advanced manufacturing techniques to achieve higher component density and smaller feature sizes.
When choosing a PCB for a particular application, it’s important to consider factors such as the complexity of the circuit, the required performance and reliability, the available space, and the budget. By understanding the different types of PCBs and their unique characteristics, engineers and designers can make informed decisions and create high-quality electronic devices that meet the needs of their customers.





Leave a Reply