Introduction
Flexible printed circuit boards (flex PCBs) have become increasingly popular in modern electronic devices due to their ability to bend and flex to fit into tight spaces. As flex PCBs grow in popularity, designers are pushing the limits on their maximum size capabilities. But what determines the maximum size of a flex PCB? In this article, we will examine the factors that limit the size of flex PCBs and discuss techniques to optimize size in your flex PCB design.
What Are Flex PCBs?
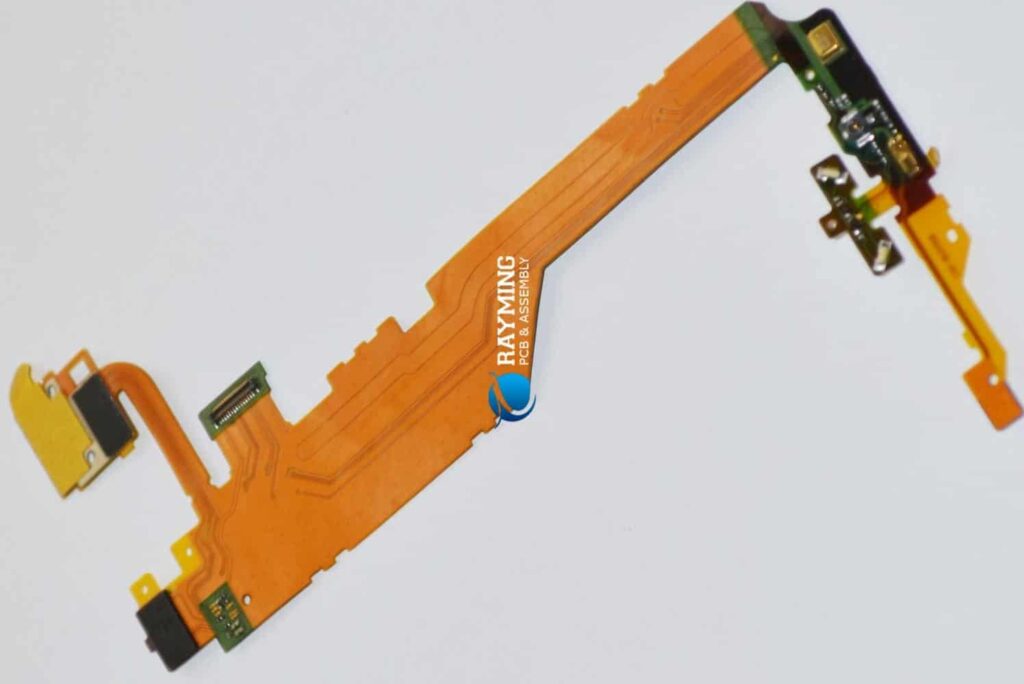

Before diving into size limitations, let’s review what exactly flex PCBs are. Flex PCBs are printed circuit boards made from flexible polymer substrates like polyimide or polyester. The circuits are printed using conductive inks, allowing the PCB to bend and twist. Components are surface mounted onto the flex PCB, which connects them electronically.
Flex PCBs provide several key advantages:
- Flexibility – Can bend, fold and twist to fit constrained spaces
- Thin and lightweight – Excellent for compact devices
- Dynamic flexing – Withstand repeated bending cycles
- High reliability – Polymer substrates withstand vibration and shock
Common applications of flex PCBs include wearables, medical devices, cameras, consumer electronics and automotive dashboards. Now let’s look at what factors limit how big flex PCBs can be manufactured.
Flex PCB Size Limiting Factors
There are several technical factors that constrain the maximum size of flex PCBs:
Substrate Material Properties
The flexible polymer material that makes up the PCB substrate limits size in a few key ways:
- Flexibility – The larger the PCB, the less flexible it becomes. For very large boards, the flex forces required can exceed the substrate’s capabilities.
- Dimensional stability – Larger boards can warp or change shape over time and temperature due to coefficient of thermal expansion differences.
- Dielectric strength – Larger surface area reduces the dielectric withstand voltage, increasing risk of shorts and insulation breakdown.
Fabrication Challenges
The challenges of fabricating large flex PCBs also restricts maximum size:
- Photolithography – Resolution limits of photomasks and photoresists constrain fine line/space patterning needed for interconnects.
- Registration – Aligning layers becomes more difficult across larger panels during lamination.
- Stress control – Internal stresses in layers can distort large boards during fabrication.
- Handling – Large thin flex boards are tricky to maneuver during assembly without damage.
Application Constraints
The application’s product requirements and assembly process also limit flex PCB sizes:
- Enclosure limits – Flex PCB length and width ultimately constrained by product housing dimensions.
- Dynamic flexing – Applications requiring tight dynamic bends restrict board size.
- Component placement – Component layout and spacing requirements influence size.
- Assembly challenges – Populating large flex PCBs with components is difficult.
So in summary, while flex PCBs provide many advantages, their maximum size is limited by material properties, fabrication challenges, and product integration factors. But what exactly is the typical size limit for commercially available flex PCBs?
Typical Maximum Size of Flex PCBs
Most flex PCB manufacturers quote an upper limit of around 18-24 inches (45-60 cm) for the longest dimension of a flex board. However, larger sizes up to 36 inches (90cm) are possible with advanced processes.
Here are typical maximum size capabilities quoted from leading global flex PCB manufacturers:
| Flex PCB Manufacturer | Typical Max Size |
|---|---|
| All Flex | 24 in (61 cm) |
| Flexible Circuit Technologies | 18 in (45.7 cm) |
| DWFritz | 24 in (60 cm) |
| American Standard Circuits | 24 in (60 cm) |
| Minco | 24 in (60 cm) |
| Lenthor Engineering | 36 in (91 cm) |
So while 18-24 inches appears to be the common limit, lengths up to 3 feet (90 cm) are possible with specialized fabrication techniques. For widths, 10-12 inches (25-30 cm) is typical max, but widths up to 15 inches (38 cm) or more are possible.
Anything above these sizes would be considered a very large flex board. Now let’s look at techniques designers can use to optimize flex PCB sizes.
Techniques for Optimizing Flex PCB Size
If your application requires a large flex PCB, here are some tips to optimize your design:
- Panelize – Break up into smaller PCBs joined by flex jumpers.
- Folding/rolling – Design with hinges and folds to pack into 3D space.
- Advanced materials – Use high Tg and thermally stable substrates.
- Stiffener integration – Strategically add rigid sections for support.
- Build sequentially – Assemble components in multiple passes.
- Specialized processes – Utilize advanced fabrication methods.
With smart design choices, the maximum usable size of a flex PCB can be extended beyond typical limits.
Now let’s look at a few examples of large flex PCBs in real-world applications.
Real-World Examples of Large Flex PCBs
Here are some examples of large flex PCBs used in current products:
Wearable Displays
- Flex PCB for a wearable display system with embedded electronics. Requires dynamic folding and rolling.
Automotive Instrument Clusters
- Rigid-flex PCB integrating both rigid and flex sections for an automotive digital instrument cluster. Complex multilayer board.
Medical Radiation Detectors
- Large thin imaging sensor array for medical radiology using a giant flex PCB substrate. Requires high dimensional stability.
Industrial Process Control Panel
- Rigid-flex control panel PCB integrating touchscreen LCD displays, buttons, and processing boards for industrial equipment. Complex multilayer HDI technology.
These examples demonstrate that with careful design and advanced fabrication techniques, flex PCB dimensions of well over 24 inches are achievable for specialty applications.
Now let’s answer some common questions about large flex PCBs.
Large Flex PCB Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about large flex PCB capabilities:
Q: What are the biggest challenges when working with large flex PCBs?
Manufacturing and assembly of large flex PCBs can be challenging. Photolithography, registration, and handling of large thin boards requires specialized processes. Populating components across a large area is also difficult. Careful planning is required to accurately place parts.
Q: How are components assembled onto large flex PCBs?
Given the challenges of populating large PCBAs, components are often assembled sequentially in multiple passes. Components may also be clustered into sections and reinforced with temporary stiffeners during placement to avoid warping the thin flex board.
Q: Can rigid sections be incorporated into large flex PCBs?
Yes, rigid sections and stiffeners can be integrated using rigid-flex PCB technology. This provides important reinforcement to the flex board for component assembly and installation while still maintaining flexibility in critical bending areas.
Q: What are best practices for designing large flex PCBs?
It’s important to design for manufacturability and minimize fabrication challenges. Use panelization or folding techniques to break the board into smaller sections. Include stiffeners and rigid sections where needed. Select the most thermally stable substrates available. Allow adequate spacing for dynamic bending.
Q: What testing is required to validate large flex PCBs?
In addition to standard electrical testing, large flex PCBs require extensive mechanical cycle testing to validate flex performance and longevity for the application. Parameters like bend radius, torque, and cycle life must be thoroughly tested.
Conclusion
While flex PCBs provide many advantages in complex devices, their maximum size is constrained by a variety of technical factors. Typical size limits for commercially available flex PCBs range from 18-24 inches (45-60 cm) in length and 10-12 inches (25-30 cm) in width. However, advanced design techniques like folding and panelization combined with specialized fabrication processes allow somewhat larger flex PCB dimensions in the range of 36 x 15 inches (90 x 38 cm) to be achieved. With careful design and process consideration, flex PCBs can be pushed beyond normal size limits for unique applications.






Leave a Reply