Introduction
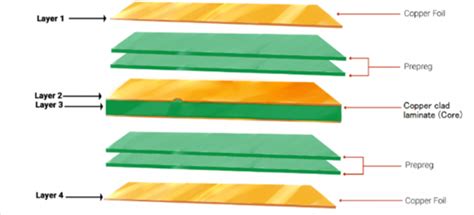
In the world of printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing, two essential components play a crucial role in determining the quality and performance of the final product: prepreg and core. Both prepreg and core are used in the construction of multi-layer PCBs, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. Understanding the differences between prepreg and core is crucial for designers, engineers, and manufacturers to make informed decisions when creating high-quality PCBs.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of prepreg and core, exploring their definitions, properties, manufacturing processes, and applications. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of the key differences between prepreg and core, and how they contribute to the overall performance of a PCB.
What is Prepreg?
Definition and Composition
Prepreg, short for “pre-impregnated,” is a composite material consisting of a reinforcement fabric, typically fiberglass, that is pre-impregnated with a partially cured thermoset resin. The resin is usually an epoxy, but other types, such as polyimide or bismaleimide, can also be used depending on the specific requirements of the PCB.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of prepreg involves several steps:
-
The reinforcement fabric is carefully selected based on the desired properties of the final product, such as strength, flexibility, and electrical performance.
-
The fabric is then impregnated with the chosen thermoset resin using a specialized machine called a treater.
-
The impregnated fabric is partially cured, usually through a heating process, to a specific stage known as the “B-stage.” At this stage, the resin is not fully cured, allowing it to remain flexible and tacky.
-
The B-stage prepreg is then cut to the desired size and shape, and stored in a controlled environment to maintain its properties until it is ready for use in PCB manufacturing.
Properties and Advantages
Prepreg offers several key properties and advantages that make it an essential component in PCB manufacturing:
-
Adhesion: The partially cured resin in prepreg provides excellent adhesion between the layers of a multi-layer PCB, ensuring a strong and reliable bond.
-
Insulation: Prepreg acts as an insulating layer between the conductive layers of a PCB, preventing short circuits and signal interference.
-
Dimensional Stability: The combination of the reinforcement fabric and the thermoset resin in prepreg provides excellent dimensional stability, minimizing warping and twisting during the PCB manufacturing process.
-
Customizability: Prepreg can be customized to meet specific requirements by selecting different reinforcement fabrics, resin systems, and thicknesses.
What is PCB Core?
Definition and Composition
PCB core, also known as the substrate or base material, is the foundation upon which the conductive layers and components of a PCB are built. It is a rigid, flat sheet of insulating material, typically made from a composite of fiberglass and epoxy resin. The most common type of PCB core is FR-4, which is a flame-retardant grade of glass-reinforced epoxy laminate.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of PCB core involves the following steps:
-
The raw materials, usually fiberglass and epoxy resin, are mixed together in a carefully controlled ratio to ensure the desired properties of the final product.
-
The mixture is then formed into a sheet using a process called calendering, which involves passing the material through a series of heated rollers to achieve a uniform thickness and smooth surface.
-
The sheet is then cured under high temperature and pressure to fully crosslink the epoxy resin, resulting in a rigid and stable PCB core.
-
The cured PCB core is then cut to the desired size and shape, and the surface is prepared for the application of conductive layers and components.
Properties and Advantages
PCB core offers several key properties and advantages that make it the foundation of a high-quality PCB:
-
Rigidity: The fully cured epoxy resin in PCB core provides excellent rigidity, ensuring that the PCB maintains its shape and stability throughout its lifetime.
-
Electrical Insulation: PCB core acts as an excellent electrical insulator, preventing short circuits and signal interference between the conductive layers of the PCB.
-
Thermal Stability: The glass-reinforced epoxy laminate in PCB core provides good thermal stability, allowing the PCB to withstand the heat generated by the components and the manufacturing process.
-
Mechanical Strength: PCB core offers excellent mechanical strength, protecting the delicate conductive layers and components from physical damage.

Differences Between Prepreg and Core
Now that we have a clear understanding of what prepreg and core are, let’s examine the key differences between these two essential PCB components.
Composition and Structure
| Characteristic | Prepreg | Core |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Reinforcement fabric (e.g., fiberglass) pre-impregnated with partially cured thermoset resin | Rigid, flat sheet of insulating material, typically made from a composite of fiberglass and fully cured epoxy resin |
| Resin State | Partially cured (B-stage) | Fully cured |
| Flexibility | Flexible and tacky | Rigid and stable |
Manufacturing Process
| Stage | Prepreg | Core |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Reinforcement fabric and thermoset resin | Fiberglass and epoxy resin |
| Impregnation | Fabric is impregnated with resin using a treater | Not applicable |
| Curing | Partially cured to B-stage | Fully cured under high temperature and pressure |
| Cutting | Cut to desired size and shape after partial curing | Cut to desired size and shape after full curing |
Properties and Functions
| Property | Prepreg | Core |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesion | Provides excellent adhesion between layers | Not applicable |
| Insulation | Acts as an insulating layer between conductive layers | Acts as an excellent electrical insulator |
| Dimensional Stability | Provides dimensional stability during PCB manufacturing | Maintains shape and stability throughout PCB lifetime |
| Customizability | Can be customized with different fabrics, resins, and thicknesses | Limited customizability, primarily varies in thickness |
Applications and Use Cases
Prepreg Applications
Prepreg is primarily used in the construction of multi-layer PCBs, where it serves as the insulating and bonding layer between the conductive layers. Some common applications of prepreg include:
- High-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs
- Flexible PCBs
- Rigid-flex PCBs
- High-frequency PCBs
- Aerospace and defense electronics
PCB Core Applications
PCB core is the foundation upon which all types of PCBs are built, providing the necessary rigidity, insulation, and mechanical strength. Some common applications of PCB core include:
- Single-layer and double-layer PCBs
- Multi-layer PCBs (in combination with prepreg)
- High-power electronics
- Automotive electronics
- Industrial control systems
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Can prepreg be used without PCB core?
A: No, prepreg is used in conjunction with PCB core to create multi-layer PCBs. Prepreg serves as the insulating and bonding layer between the conductive layers, while PCB core provides the necessary rigidity and foundation. -
Q: What is the most common type of PCB core material?
A: The most common type of PCB core material is FR-4, which is a flame-retardant grade of glass-reinforced epoxy laminate. FR-4 offers excellent electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and thermal stability. -
Q: Can different types of prepreg be used in the same PCB?
A: Yes, different types of prepreg can be used in the same PCB to achieve specific properties or meet certain requirements. For example, a combination of epoxy and polyimide prepregs can be used to create a PCB with enhanced thermal resistance and flexibility. -
Q: How does the thickness of PCB core affect the performance of a PCB?
A: The thickness of PCB core can affect several aspects of PCB performance, including signal integrity, power handling capacity, and mechanical strength. Thicker PCB cores are generally used for high-power applications or when greater mechanical stability is required, while thinner cores are used for high-density and high-speed designs. -
Q: What are the storage requirements for prepreg?
A: Prepreg should be stored in a controlled environment to maintain its properties until it is ready for use in PCB manufacturing. Ideal storage conditions for prepreg include a temperature between 40-50°F (4-10°C) and a relative humidity between 30-50%. Prepreg should also be protected from direct sunlight and stored in sealed containers to prevent contamination and moisture absorption.
Conclusion
In conclusion, prepreg and PCB core are two essential components in the construction of high-quality printed circuit boards. While both materials serve important functions, they have distinct compositions, manufacturing processes, and properties that set them apart.
Prepreg, with its partially cured thermoset resin and reinforcement fabric, provides excellent adhesion, insulation, and dimensional stability between the layers of a multi-layer PCB. On the other hand, PCB core, typically made from a fully cured composite of fiberglass and epoxy resin, offers the necessary rigidity, electrical insulation, and mechanical strength that form the foundation of a PCB.
Understanding the differences between prepreg and core is crucial for designers, engineers, and manufacturers to make informed decisions when creating PCBs for various applications. By selecting the appropriate materials and leveraging their unique properties, it is possible to create high-performance PCBs that meet the demands of today’s increasingly complex electronic devices.
As technology continues to advance, the importance of prepreg and PCB core in the electronics industry will only continue to grow. By staying informed about these essential components and their evolving properties, manufacturers can remain at the forefront of PCB design and production, creating innovative and reliable electronic solutions for a wide range of industries.





Leave a Reply