Introduction to Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W
The Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W are both compact and affordable single-board computers designed for projects, hobbyists, and educators. Despite their small size, they pack a punch in terms of functionality and versatility.
What is Raspberry Pi Zero?
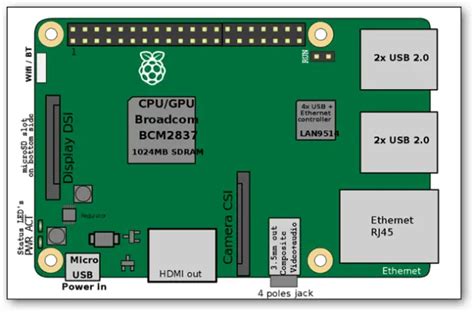
The Raspberry Pi Zero is a tiny, low-cost computer released in 2015. It measures just 65mm x 30mm x 5mm and weighs only 9 grams. Despite its diminutive size, it offers a surprising amount of computing power, making it ideal for various projects and applications.
What is Raspberry Pi Zero W?
The Raspberry Pi Zero W, released in 2017, is an enhanced version of the original Zero. It shares the same compact form factor but adds built-in wireless connectivity, including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. This addition makes the Zero W even more versatile and convenient for projects that require wireless communication.
Specifications Comparison
Let’s take a closer look at the technical specifications of both the Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W:
| Specification | Raspberry Pi Zero | Raspberry Pi Zero W |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | 1GHz single-core ARM11 | 1GHz single-core ARM11 |
| RAM | 512MB | 512MB |
| Storage | MicroSD card slot | MicroSD card slot |
| USB | 1 x Micro USB OTG | 1 x Micro USB OTG |
| Video Output | Mini HDMI | Mini HDMI |
| GPIO Pins | 40-pin header | 40-pin header |
| Wi-Fi | No | 802.11b/g/n |
| Bluetooth | No | Bluetooth 4.1 |
| Power | 5V via Micro USB | 5V via Micro USB |
| Dimensions | 65mm x 30mm x 5mm | 65mm x 30mm x 5mm |
| Weight | 9g | 9g |
As you can see, the main difference between the two models lies in the wireless connectivity. The Raspberry Pi Zero W includes built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, while the Zero does not.
Performance
Both the Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W are powered by a 1GHz single-core ARM11 processor and have 512MB of RAM. While they may not be as powerful as some of the more advanced Raspberry Pi models, they still offer sufficient performance for a wide range of projects and applications.
The single-core processor is capable of handling tasks such as running lightweight operating systems, executing Python scripts, and controlling hardware components. The 512MB of RAM provides enough memory for most basic projects and allows for smooth multitasking.
It’s important to note that the performance of the Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W may be limited compared to more powerful models like the Raspberry Pi 4. However, their compact size and low power consumption make them ideal for projects where space and energy efficiency are crucial factors.

Connectivity
One of the key differences between the Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W is their connectivity options. Let’s explore how they differ:
Raspberry Pi Zero
The Raspberry Pi Zero comes with a single Micro USB OTG (On-The-Go) port, which serves multiple purposes. It can be used for power input, data transfer, and even as a USB device mode. However, due to the single port, you may need to use a USB hub if you want to connect multiple peripherals simultaneously.
For video output, the Zero features a Mini HDMI port, allowing you to connect it to a display or monitor. It supports resolutions up to 1080p at 60fps, making it suitable for projects that require a visual interface.
The Raspberry Pi Zero lacks built-in wireless connectivity, which means you’ll need to use a USB Wi-Fi dongle or Ethernet adapter if you want to connect it to a network.
Raspberry Pi Zero W
The Raspberry Pi Zero W, on the other hand, comes with built-in wireless connectivity. It includes both Wi-Fi (802.11b/g/n) and Bluetooth 4.1, making it incredibly convenient for projects that require wireless communication.
With Wi-Fi, you can easily connect the Zero W to your home network or create an access point. This enables remote access, wireless file transfers, and the ability to control the device wirelessly. The Bluetooth functionality allows you to connect peripherals such as keyboards, mice, and sensors without the need for additional cables.
Like the Zero, the Zero W also features a single Micro USB OTG port and a Mini HDMI port for power, data, and video output.
GPIO and Expansion
Both the Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W come with a 40-pin GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) header, which is compatible with the larger Raspberry Pi models. This header allows you to connect various sensors, actuators, and other hardware components to interact with the physical world.
The GPIO pins can be programmed using languages like Python to control LEDs, motors, and other electronic devices. They also support communication protocols such as I2C, SPI, and UART, enabling you to connect a wide range of peripherals and modules.
It’s worth noting that the Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W have unpopulated GPIO headers, meaning the pins are not soldered. You’ll need to solder the header yourself or use a solderless hammer header if you want to access the GPIO functionality.
Power and Efficiency
One of the standout features of the Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W is their low power consumption. Both models can be powered using a 5V power supply through the Micro USB port.
The Zero and Zero W typically consume around 100-150mA of current, making them extremely energy-efficient. This low power consumption makes them ideal for battery-powered projects or applications where power efficiency is crucial.
However, it’s important to ensure that you use a reliable power supply that can provide sufficient current. A power supply with a minimum capacity of 1A is recommended to ensure stable operation, especially if you have peripherals connected.
Operating System and Software
The Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W are compatible with a wide range of operating systems and software. The most popular choice is the official Raspberry Pi OS (previously known as Raspbian), which is based on Debian Linux.
Raspberry Pi OS is specifically optimized for the Raspberry Pi hardware and offers a user-friendly desktop environment along with a vast collection of pre-installed software and tools. It includes programming languages like Python, educational software like Scratch, and productivity tools like LibreOffice.
In addition to Raspberry Pi OS, you can also use other Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, Fedora, and Arch Linux on the Zero and Zero W. These distributions provide more flexibility and customization options for advanced users.
If you prefer a headless setup (without a graphical user interface), you can install lightweight operating systems like Raspbian Lite or DietPi, which are optimized for minimal resource usage and remote access.
Use Cases and Projects
The Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W are versatile single-board computers that can be used for a wide range of projects and applications. Here are a few popular use cases:
-
Media Center: With the compact size and HDMI output, the Zero and Zero W can be turned into a lightweight media center. You can install software like Kodi or LibreELEC to stream movies, TV shows, and music to your TV or home theater system.
-
Internet of Things (IoT): The low power consumption and wireless connectivity of the Zero W make it an excellent choice for IoT projects. You can use it to build smart home devices, sensor networks, or remote monitoring systems. With the GPIO pins, you can connect various sensors and actuators to interact with the physical world.
-
Robotics: The small form factor of the Zero and Zero W makes them suitable for robotics projects. You can use them as the brain of your robot, controlling motors, sensors, and other components. The GPIO pins allow you to interface with motor drivers, servo controllers, and other robotics modules.
-
Retro Gaming: The Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W can be transformed into retro gaming consoles using software like RetroPie or Lakka. With a USB gamepad and the HDMI output, you can enjoy classic games from various retro gaming systems.
-
Network Appliance: The Zero W’s built-in wireless connectivity makes it an excellent choice for network-related projects. You can use it as a wireless access point, network-attached storage (NAS) server, or a network ad-blocker.
-
Portable Projects: The compact size and low power consumption of the Zero and Zero W make them ideal for portable projects. You can create portable gaming consoles, handheld devices, or even wearable electronics.
These are just a few examples of the countless projects and applications you can build with the Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W. The possibilities are limited only by your imagination and creativity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Can I use the Raspberry Pi Zero or Zero W as a desktop computer?
While it is possible to use the Zero or Zero W as a basic desktop computer, they may not provide the best user experience for general-purpose computing. The single-core processor and limited RAM may result in slower performance compared to more powerful Raspberry Pi models or traditional desktop computers. However, they can still be used for lightweight tasks and specific applications. -
What accessories do I need to get started with the Raspberry Pi Zero or Zero W?
To get started with the Zero or Zero W, you’ll need a few essential accessories: - A microSD card (at least 8GB) for storage and installing the operating system
- A power supply (5V, 1A minimum) with a Micro USB connector
- A Micro USB OTG cable for connecting peripherals or a USB hub
- A Mini HDMI to HDMI cable for connecting to a display
-
A soldering iron and header pins if you want to access the GPIO pins
-
Can I connect a camera module to the Raspberry Pi Zero or Zero W?
Yes, both the Zero and Zero W have a camera connector that is compatible with the official Raspberry Pi Camera Module. You can connect a camera module to capture images or record videos for various projects, such as surveillance systems or computer vision applications. -
How do I set up wireless connectivity on the Raspberry Pi Zero W?
The Raspberry Pi Zero W comes with built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. To set up wireless connectivity, you can use the graphical user interface provided by the operating system or configure it through the command line. The Raspberry Pi OS provides a user-friendly way to connect to Wi-Fi networks using the desktop environment or theraspi-configutility. -
Can I use the Raspberry Pi Zero or Zero W for commercial products?
Yes, you can use the Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W for commercial products. However, it’s important to comply with the terms and conditions set by the Raspberry Pi Foundation. You should also consider factors such as production scalability, reliability, and support when using the Zero or Zero W in commercial applications.
Conclusion
The Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W are remarkable single-board computers that offer a balance of compactness, affordability, and functionality. While they may not be as powerful as some of the larger Raspberry Pi models, they excel in projects where size, power efficiency, and cost are key considerations.
The main difference between the two models lies in the wireless connectivity, with the Zero W offering built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. This feature makes the Zero W more versatile and convenient for projects that require wireless communication.
Whether you’re a beginner exploring the world of electronics and programming or an experienced maker working on advanced projects, the Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W provide a solid foundation to bring your ideas to life. With their extensive community support, abundant resources, and wide range of compatible software and hardware, these tiny computers open up a world of possibilities.
So, which one should you choose? If your project requires wireless connectivity, the Raspberry Pi Zero W is the clear choice. However, if you don’t need wireless functionality and want to save a few dollars, the Raspberry Pi Zero is still a capable option.
Regardless of your choice, both the Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W are powerful tools that empower you to create, innovate, and learn. Happy tinkering!





Leave a Reply