What is PCB Prepreg?
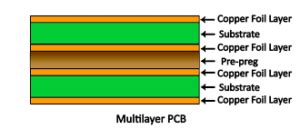
PCB prepreg is a composite material that is used as an insulating layer between the conductive copper layers in a Multilayer PCB. The prepreg material is made by impregnating a reinforcement fabric, usually fiberglass, with a thermoset resin, such as epoxy or polyimide. The resin is partially cured, or “B-staged,” which allows it to flow and bond the layers together during the lamination process.
Composition of PCB Prepreg
PCB prepreg typically consists of two main components:
-
Reinforcement fabric: The most common reinforcement fabric used in PCB prepreg is fiberglass, which provides mechanical strength and dimensional stability to the multilayer PCB. Other reinforcement materials, such as aramid or polyimide, may be used for high-performance applications.
-
Thermoset resin: The resin used in PCB prepreg is typically a thermoset polymer, such as epoxy or polyimide. The resin is responsible for bonding the layers together and providing electrical insulation between the conductive layers. The choice of resin depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as temperature resistance, dielectric properties, and chemical resistance.
Key Performance Indicators of PCB Prepreg
Several key performance indicators are used to evaluate the quality and suitability of PCB prepreg for Multilayer PCB Manufacturing. These indicators are critical for ensuring the reliability and functionality of the final PCB Assembly.
1. Glass Transition Temperature (Tg)
The glass transition temperature (Tg) is the temperature at which the prepreg resin transitions from a rigid, glassy state to a soft, rubbery state. This temperature is critical for determining the maximum operating temperature of the multilayer PCB, as well as its dimensional stability and mechanical properties.
Typical Tg values for common PCB prepreg resins are:
| Resin Type | Tg Range (°C) |
|---|---|
| Epoxy | 120 – 180 |
| Polyimide | 220 – 260 |
| BT | 170 – 220 |
A higher Tg value indicates better thermal stability and performance at elevated temperatures. The choice of prepreg resin should be based on the specific temperature requirements of the application.
2. Dielectric Constant (Dk) and Dissipation Factor (Df)
The dielectric constant (Dk) and dissipation factor (Df) are critical properties that determine the electrical performance of the PCB prepreg. The dielectric constant is a measure of the material’s ability to store electrical energy, while the dissipation factor is a measure of the material’s loss of electrical energy as heat.
Typical Dk and Df values for common PCB prepreg materials are:
| Material | Dk @ 1 GHz | Df @ 1 GHz |
|---|---|---|
| FR-4 | 4.2 – 4.5 | 0.02 |
| Polyimide | 3.5 – 3.7 | 0.007 |
| PTFE | 2.1 – 2.3 | 0.001 |
Lower Dk and Df values are desirable for high-speed and high-frequency applications, as they result in lower signal loss and distortion. The choice of prepreg material should be based on the specific electrical performance requirements of the application.
3. Resin Flow and Gel Time
Resin flow and gel time are important properties that determine the processability and handling of the PCB prepreg during the lamination process. Resin flow refers to the ability of the partially cured resin to flow and fill the spaces between the layers during lamination, while gel time refers to the time required for the resin to reach a specific degree of cure at a given temperature.
Typical resin flow and gel time values for PCB prepreg are:
| Property | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Resin Flow | 10 – 30% |
| Gel Time | 90 – 120 s |
A higher resin flow value indicates better flow properties and improved bonding between the layers, while a longer gel time allows for better control and uniformity of the lamination process. The choice of prepreg with specific resin flow and gel time properties depends on the complexity of the multilayer PCB design and the lamination process parameters.
4. Peel Strength and Bond Strength
Peel strength and bond strength are mechanical properties that determine the integrity and reliability of the multilayer PCB. Peel strength refers to the force required to separate the copper foil from the prepreg substrate, while bond strength refers to the force required to separate two bonded prepreg layers.
Typical peel strength and bond strength values for PCB prepreg are:
| Property | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Peel Strength | 8 – 12 N/cm |
| Bond Strength | 1,200 – 1,500 N/cm² |
Higher peel strength and bond strength values indicate better adhesion between the layers and improved mechanical reliability of the multilayer PCB. The choice of prepreg with specific peel strength and bond strength properties depends on the mechanical requirements of the application and the manufacturing process.
5. Thickness and Tolerance
The thickness and tolerance of the PCB prepreg are critical for ensuring the dimensional accuracy and consistency of the multilayer PCB. The prepreg thickness determines the spacing between the conductive layers, which affects the electrical properties and impedance control of the PCB.
Typical thickness and tolerance values for PCB prepreg are:
| Thickness (mm) | Tolerance (mm) |
|---|---|
| 0.05 – 0.10 | ± 0.005 |
| 0.10 – 0.20 | ± 0.010 |
| 0.20 – 0.30 | ± 0.015 |
Tighter thickness tolerances are required for high-density and high-speed applications, where precise control of the layer spacing is critical for maintaining signal integrity and impedance matching. The choice of prepreg thickness and tolerance depends on the specific design requirements of the multilayer PCB.
Factors Affecting PCB Prepreg Performance
Several factors can affect the performance and quality of PCB prepreg, including:
-
Storage conditions: PCB prepreg should be stored in a cool, dry environment to prevent moisture absorption and premature curing of the resin. Improper storage can lead to degraded performance and reduced shelf life.
-
Handling and processing: Proper handling and processing techniques should be used to prevent contamination, damage, and exposure to excessive heat or humidity during the manufacturing process. Improper handling can result in defects, such as delamination, voids, or poor adhesion.
-
Lamination parameters: The lamination process parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and time, should be optimized for the specific prepreg material and multilayer PCB design. Improper lamination can lead to poor bonding, warpage, or other defects.
-
Compatibility with other materials: The PCB prepreg should be compatible with the other materials used in the multilayer PCB, such as the copper foil, solder mask, and surface finish. Incompatible materials can result in poor adhesion, delamination, or other reliability issues.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the difference between prepreg and core material in a multilayer PCB?
A: Prepreg is the partially cured, B-staged material that is used to bond the layers together during the lamination process, while core material is the fully cured, rigid material that forms the base substrate of the multilayer PCB. -
Q: Can different types of prepreg be used in the same multilayer PCB?
A: Yes, different types of prepreg can be used in the same multilayer PCB to achieve specific performance requirements, such as using a low-loss prepreg for high-speed signal layers and a standard prepreg for power and ground layers. -
Q: How does the choice of prepreg affect the cost of a multilayer PCB?
A: The choice of prepreg can significantly affect the cost of a multilayer PCB, as high-performance materials, such as low-loss or high-temperature prepregs, are typically more expensive than standard materials. The cost impact should be balanced against the performance requirements of the application. -
Q: What are the common defects associated with PCB prepreg, and how can they be prevented?
A: Common defects associated with PCB prepreg include voids, delamination, and poor adhesion. These defects can be prevented by proper storage and handling of the prepreg, optimizing the lamination process parameters, and ensuring compatibility with other materials used in the multilayer PCB. -
Q: How does the choice of prepreg affect the environmental sustainability of a multilayer PCB?
A: The choice of prepreg can affect the environmental sustainability of a multilayer PCB, as some materials, such as halogen-free or bio-based prepregs, are more environmentally friendly than others. However, the performance and cost implications of using eco-friendly prepregs should also be considered.
Conclusion
PCB prepreg is a critical material in the manufacturing of Multilayer PCBs, and its key performance indicators directly impact the quality, reliability, and functionality of the final PCB assembly. Understanding the properties and characteristics of PCB prepreg, such as glass transition temperature, dielectric constant, resin flow, peel strength, and thickness tolerance, is essential for selecting the appropriate material for a given application and ensuring optimal performance.
Proper storage, handling, and processing of PCB prepreg, as well as compatibility with other materials used in the multilayer PCB, are also crucial for preventing defects and achieving consistent, high-quality results. As the demand for high-performance and environmentally sustainable PCBs continues to grow, the development and selection of advanced PCB prepreg materials will play an increasingly important role in meeting these challenges.





Leave a Reply