CPU Socket
The CPU socket is one of the most critical components on a motherboard. It determines the type of processor the motherboard supports. Modern motherboards typically feature LGA (Land Grid Array) or PGA (Pin Grid Array) sockets for Intel and AMD processors, respectively.
| Socket | Compatible Processors |
|---|---|
| LGA 1700 | Intel 12th & 13th Generation Core |
| LGA 1200 | Intel 10th & 11th Generation Core |
| AM5 | AMD Ryzen 7000 Series |
| AM4 | AMD Ryzen 1000 to 5000 Series |
It’s essential to choose a motherboard with a socket that matches your desired processor.
Chipset
The chipset is a set of chips on the motherboard that controls the communication between the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and other peripherals. It determines the features and capabilities of the motherboard. Modern chipsets offer support for faster memory, more USB ports, advanced storage interfaces, and enhanced power management.
Examples of Modern Chipsets
- Intel Z790, H770, B760 (600 Series)
- Intel Z690, H670, B660 (600 Series)
- AMD X670, B650 (AM5 Socket)
- AMD X570, B550, A520 (AM4 Socket)
The chipset you choose will impact your motherboard’s overall functionality and performance.
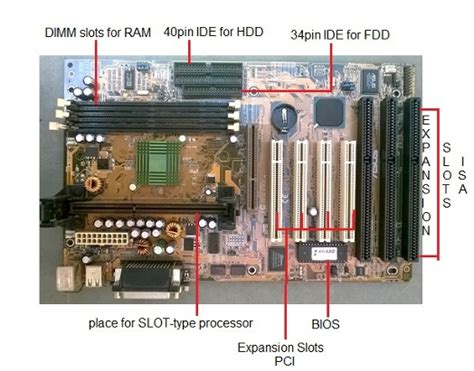
Memory Slots
Memory slots, also known as DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) slots, are where you install the RAM modules. Modern motherboards usually have four memory slots, supporting dual-channel or quad-channel memory configurations. The number of slots and the maximum supported memory capacity vary depending on the motherboard.
| DIMM Slots | Max Memory Capacity | Memory Type |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | Up to 128GB | DDR4, DDR5 |
| 2 | Up to 64GB | DDR4, DDR5 |
Modern motherboards support DDR4 or the newer DDR5 memory standard, offering faster speeds and higher capacities.

Expansion Slots
Expansion slots allow you to add various components to your motherboard, such as graphics cards, sound cards, network cards, and more. The most common expansion slots on modern motherboards are PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots.
PCIe Slot Configurations
- PCIe x16: Used for graphics cards and high-performance peripherals
- PCIe x8: Used for high-speed devices like NVMe SSDs or dual graphics cards
- PCIe x4: Used for devices like Wi-Fi cards, capture cards, or NVMe SSDs
- PCIe x1: Used for low-bandwidth devices like sound cards or USB expansion cards
Modern motherboards often include multiple PCIe slots to support various configurations and expandability options.
Storage Interfaces
Storage interfaces on modern motherboards allow you to connect various storage devices, such as hard drives, SSDs, and NVMe drives. The most common storage interfaces are SATA and M.2.
SATA (Serial ATA)
SATA is the standard interface for connecting hard drives and SSDs. Modern motherboards typically include 4-8 SATA ports, supporting SATA 3.0 (6 Gbps) speeds.
M.2
M.2 is a newer interface designed for small form factor SSDs. It offers faster speeds and lower latency compared to SATA. Modern motherboards often have 1-3 M.2 slots, supporting PCIe 3.0, PCIe 4.0, or PCIe 5.0 speeds.
| Interface | Max Speed | Compatible Devices |
|---|---|---|
| SATA 3.0 | 6 Gbps | Hard Drives, SATA SSDs |
| M.2 PCIe 3.0 | 32 Gbps | NVMe SSDs |
| M.2 PCIe 4.0 | 64 Gbps | NVMe SSDs |
| M.2 PCIe 5.0 | 128 Gbps | NVMe SSDs |
USB Ports
USB (Universal Serial Bus) ports are essential for connecting various peripherals, such as keyboards, mice, external storage devices, and more. Modern motherboards include a mix of USB 2.0, USB 3.2 Gen 1, USB 3.2 Gen 2, and USB 4 ports.
USB Port Types and Speeds
- USB 2.0: Up to 480 Mbps
- USB 3.2 Gen 1 (USB 3.0): Up to 5 Gbps
- USB 3.2 Gen 2: Up to 10 Gbps
- USB 3.2 Gen 2×2: Up to 20 Gbps
- USB 4: Up to 40 Gbps
Modern motherboards often include a combination of USB port types to support a wide range of devices and speeds.
Networking
Modern motherboards include built-in networking capabilities, allowing you to connect your computer to a local network or the internet. The most common networking features are Ethernet and Wi-Fi.
Ethernet
Ethernet ports on modern motherboards support Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) or 2.5 Gigabit Ethernet speeds. Some high-end motherboards even offer 5 Gbps or 10 Gbps Ethernet for faster wired networking.
Wi-Fi
Many modern motherboards come with built-in Wi-Fi, supporting the latest wireless standards like Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) or Wi-Fi 6E. This allows for fast and convenient wireless networking without the need for an additional Wi-Fi card.
Audio
Audio is an essential component of modern motherboards, providing high-quality sound output for music, movies, and games. Most motherboards include a built-in audio codec, supporting multi-channel audio and various audio connectors.
Common Audio Features
- Realtek ALC1200 or ALC1220 audio codec
- Support for 7.1 or 5.1 Surround Sound
- Optical S/PDIF output for digital audio
- Audio capacitors and shielding for improved sound quality
Some high-end motherboards even offer dedicated audio components and software enhancements for an immersive audio experience.
Power Delivery
Power delivery is a crucial aspect of modern motherboards, ensuring stable and reliable Power Supply to the CPU, RAM, and other components. The power delivery system consists of the VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) and power connectors.
VRM
The VRM is responsible for converting the 12V power from the power supply to the appropriate voltage levels required by the CPU and other components. Modern motherboards often feature robust VRMs with multiple power phases for stable power delivery and better overclocking potential.
Power Connectors
Modern motherboards include various power connectors to supply power to different components:
- 24-pin ATX main power connector
- 8-pin or 4-pin CPU power connector
- 6-pin or 8-pin PCIe power connectors for graphics cards
- SATA power connectors for storage devices
- 4-pin Molex connectors for additional power
A high-quality power delivery system is essential for system stability and performance, especially when overclocking or using power-hungry components.
BIOS and UEFI
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is the firmware that runs on the motherboard, initializing hardware components and loading the operating system. Modern motherboards use UEFI, which offers advanced features and a more user-friendly interface compared to the legacy BIOS.
UEFI Features
- Graphical user interface for easy navigation
- Mouse support for convenient input
- Secure Boot to protect against malware and unauthorized firmware
- Fast boot times and improved hardware compatibility
- Support for larger storage devices (over 2TB)
Most modern motherboards offer a feature-rich UEFI with various customization options, allowing users to fine-tune their system settings and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What should I consider when choosing a motherboard?
A: When selecting a motherboard, consider factors such as the CPU socket, chipset, memory support, expansion slots, storage interfaces, networking options, and audio features. Make sure the motherboard is compatible with your desired processor and offers the features and expandability you need. -
Q: Can I mix different types of RAM on a motherboard?
A: It’s generally not recommended to mix different types of RAM (e.g., DDR4 and DDR5) on a motherboard. Stick to using the same type of RAM modules with matching speeds and timings for optimal performance and stability. -
Q: How do I know if a graphics card is compatible with my motherboard?
A: To ensure graphics card compatibility, check the motherboard’s PCIe slot configuration. Make sure the motherboard has a PCIe x16 slot that matches the graphics card’s interface (e.g., PCIe 3.0 or PCIe 4.0). Also, verify that your power supply has the necessary PCIe power connectors to support the graphics card. -
Q: Can I install an NVMe SSD on any modern motherboard?
A: Most modern motherboards include at least one M.2 slot for installing NVMe SSDs. However, make sure to check the motherboard’s specifications to confirm the supported M.2 slot types (e.g., PCIe 3.0, PCIe 4.0, or SATA) and sizes (e.g., 2242, 2260, or 2280). -
Q: How important is the motherboard’s VRM for overclocking?
A: The motherboard’s VRM plays a crucial role in overclocking, as it determines the stability and reliability of the power delivery to the CPU. A high-quality VRM with multiple power phases and efficient cooling is essential for achieving stable overclocks and preventing thermal throttling.
Modern motherboards offer a wide range of components and features to cater to different user needs and preferences. When building a new computer or upgrading an existing one, it’s essential to choose a motherboard that is compatible with your desired components and offers the features and expandability you require. By understanding the key components and their functions, you can make an informed decision and select the best motherboard for your specific use case.





Leave a Reply