Polyimide film, often referred to by the DuPont tradename Kapton, is an incredibly versatile material known for its outstanding thermal, mechanical, and chemical properties. Polyimide films are used in a wide variety of industries and applications including flexible printed circuits (flex PCBs), wire and cable insulation, automotive engine components, aerospace composites, and more.
What is Polyimide?
Polyimide is a polymer material composed of multiple imide group monomers. The monomer chains are linked together through imide bonds (-CO-NR-CO-) to form the long-chain polyimide polymer. Polyimide is considered a high performance plastic due to its:
- High heat resistance
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Low coefficient of thermal expansion
- High tensile strength
Polyimide films are manufactured through a chemical process where a polyamic acid solution is cast onto a belt or drum, then thermally cured at high temperatures into the final polyimide film. The resulting film can have thicknesses ranging from 25 microns up to 125 microns.
Kapton brand polyimide films were first developed by DuPont in the 1960’s and offered improved properties over other insulating films like Mylar. Today Kapton HN is the most widely used polyimide film, offering a balance of electrical, mechanical, chemical, and thermal properties.
Key Properties of Polyimide Films
Thermal Properties
One of the most valued attributes of polyimide films is the ability to maintain its properties across a wide temperature range.
- Glass transition temperature above 360°C
- Can withstand continuous use temperatures up to 260°C
- Withstands short term exposures up to 400°C
This high level of thermal endurance makes polyimide films ideal for applications in extreme temperature environments. The Kapton brand has a UL 94 V-0 flammability rating up to 400°C.
Mechanical Properties
In addition to heat resistance, polyimide films offer excellent mechanical strength and flexibility properties:
- Tensile Strength: 231 MPa
- Elongation at Break: 80%
- Tensile Modulus: 2.5 GPa
The combination of high tensile strength and good elongation leads to tough and durable films that resist tearing or puncturing. The modulus indicates the films have relatively high rigidity and low elasticity.
Chemical Resistance
Polyimide has broad chemical compatibility and can withstand exposure to most solvents and acids. The imide bonds that form the polymer backbone provide solid resistance to alcohols, ketones, esters, aromatics, chlorinated solvents, and dilute acids and bases. This makes polyimide a good insulator choice for applications prone to chemical exposure.
Applications of Polyimide Films
The unique properties of polyimide films lead to widespread use across industries like aerospace, electronics, automotive, and medical. Some common applications include:
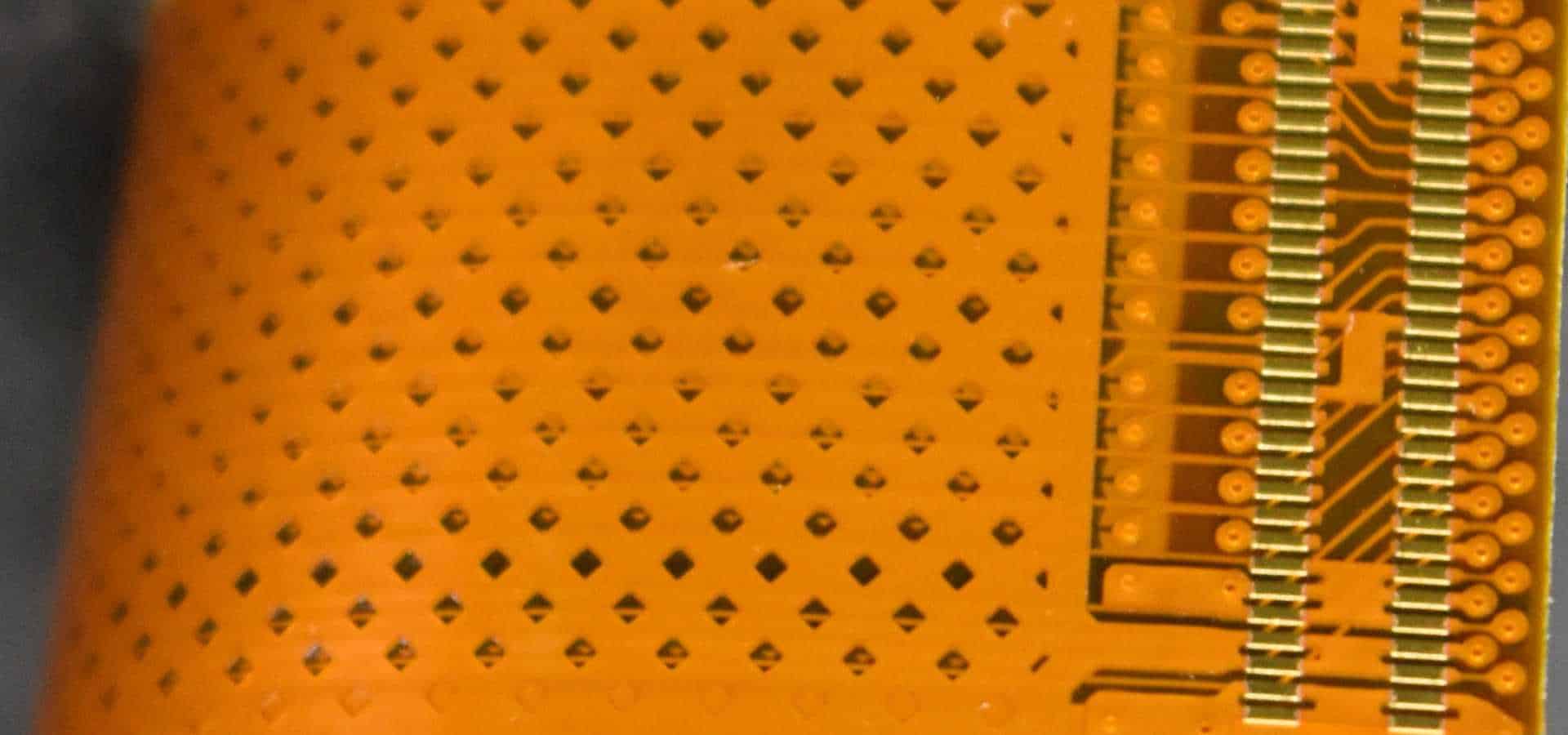
Flexible Printed Circuits
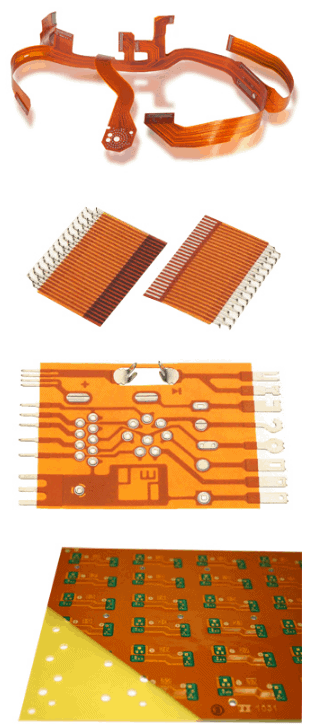
Also known as flex PCBs, flexible printed circuits use polyimide as a robust yet flexible substrate material for etching copper traces. Polyimide flex circuits can be bent and flexed repeatedly without damage, making them perfect for interconnects in small electronic devices. They are found in consumer devices, medical equipment, industrial controls, and more.
| Flex Stackup | Description |
|---|---|
| Polyimide Substrate | Thin polyimide film forms a durable, flexible foundation |
| Copper Foil | Thin rolled annealed copper laminated to substrate |
| Copper Traces | Circuits etched from copper foil using photolithographic process |
| Coverlay | Additional layer of polyimide film laminated over traces for protection |
Wire and Cable Insulation
The heat and chemical resistance of polyimide films make them an ideal choice for insulating wires and cables. Polyimide insulated magnet wire enables coil windings to withstand varnish impregnation at elevated temperatures during manufacture. Polyimide can also replace other polymers like PTFE in high temperature hook-up wire applications.
Aerospace Composites
In aerospace structural composites, polyimide films provide a high strength-to-weight ratio reinforcement material. Polyimide laminates and honeycombs offer lightweight constructions with durability across extreme temperatures and vibration. Polyimide composites are found in aircraft engine nacelles, helicopter blades, rocket nozzles, and other critical aerostructures.
Automotive Applications
Polyimide’s stable properties at high temperatures make it suitable for automotive applications like insulation in high voltage wire harness, flex foil circuits, and as a substrate for exhaust gas sensors. Polyimide powder coatings and composites are also used to replace metal parts and reduce vehicle weight.
Medical Devices
For medical devices like patient monitors, IV pumps, and surgical equipment, polyimide provides thin, lightweight circuits that can withstand repeated flexing and cleaning. Polyimide tubing and coatings improve performance of catheters and other devices that contact blood or tissues. Radiation resistance also makes polyimide useful for parts like dosimeter badges.
Polyimide vs. Other High Temperature Films

Polyimide is one of several plastic films capable of retaining its properties at elevated temperatures. How does it compare to other popular high heat films?
| Property | Polyimide | PTFE | Polyester (Mylar) | Polyphenylene Sulfide |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Operating Temperature | 260°C | 260°C | 150°C | 240°C |
| Tensile Strength | High | Medium | Medium | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Moderate | Good |
| Dielectric Strength | Fair | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Cost | Medium | High | Low | High |
Polyimide provides the best overall balance of heat resistance, strength, chemical resistance, and cost. PTFE (Teflon) has better dielectric properties but is more expensive. Mylar polyester is less expensive but limited to lower temperatures. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) has similar heat resistance to polyimide but is more costly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about polyimide films:
What are some key suppliers of polyimide films?
The major global suppliers of polyimide films include DuPont, Kaneka, and Saint Gobain. DuPont’s Kapton brand polyimide film has been produced since the 1960’s and dominates much of the market. UBE and Toray are major suppliers in Asia.
What are some alternatives to polyimide for high temperature applications?
For certain applications, other plastic films can be used in place of polyimide at high temperatures, such as PTFE, FEP, PEEK, ULTEM, and others. Ceramics, fiberglass, mica papers, and other inorganic materials are also used. Polyimide however provides the best balance of properties for many applications.
Is polyimide susceptible to humidity absorption?
Polyimide absorbs very little water, with moisture absorption below 3% relative to most other plastic films. However, humidity can still impact the dielectric properties of polyimide at high temperatures and frequencies, so low moisture conditions may be required for some electrical applications.
What are the main disadvantages of polyimide films?
Polyimide’s disadvantages compared to other plastics include:
- High material cost
- Limited UV/solar radiation resistance
- Can be difficult to laminate or bond without proper surface treatment
- Poor permeation resistance to helium, hydrogen and other small molecules
How are polyimide films attached or bonded to other materials?
Adhesion to polyimide can be improved through chemical or plasma surface treatments. Lamination adhesives like acrylic, epoxy, or silicone adhesives are common. Polyimide can also be bonded directly using heat bonding or welding processes. Mechanical fasteners or thermal spray coatings provide removable attachment methods.






Leave a Reply