Introduction to SEMI-FLEX PCBs
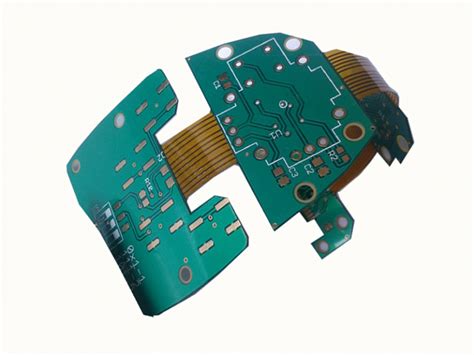
SEMI-FLEX PCBs, also known as semi-flexible printed circuit boards, are a unique type of PCB that combines the benefits of both rigid and flexible PCBs. These boards consist of a flexible substrate with rigid areas strategically placed where components need to be mounted. This hybrid design allows for greater design flexibility, improved reliability, and enhanced performance in applications that require both stability and flexibility.
Advantages of SEMI-FLEX PCBs
-
Flexibility and Durability: SEMI-FLEX PCBs offer the flexibility of a flexible PCB while maintaining the durability and stability of a rigid PCB in the areas where components are mounted. This makes them ideal for applications that require the PCB to bend or flex without compromising the integrity of the mounted components.
-
Space Savings: By combining rigid and flexible sections, SEMI-FLEX PCBs can be designed to fit into tight spaces and conform to unique product shapes. This space-saving feature is particularly valuable in compact electronic devices and Wearable Technology.
-
Reduced Assembly Costs: SEMI-FLEX PCBs can reduce assembly costs by eliminating the need for connectors and cables between rigid and flexible sections. This simplifies the assembly process and minimizes the risk of connection failures.
-
Improved Signal Integrity: The seamless transition between rigid and flexible areas in SEMI-FLEX PCBs reduces signal loss and interference compared to using separate rigid and flexible PCBs connected by cables or connectors. This improves overall signal integrity and system performance.
SEMI-FLEX PCB Design Considerations
When designing SEMI-FLEX PCBs, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Material Selection
Choosing the right materials for your SEMI-FLEX PCB is crucial. The flexible substrate should be selected based on the required flexibility, durability, and environmental resistance. Common flexible substrate materials include polyimide, polyester, and PTFE. The rigid areas are typically made of FR-4 or other standard rigid PCB materials.
Bend Radius and Flexibility
The bend radius is a critical design parameter for SEMI-FLEX PCBs. It refers to the minimum radius that the flexible portion of the PCB can be bent without causing damage or affecting performance. The bend radius is determined by the thickness and material properties of the flexible substrate and the copper traces. Designers must ensure that the bend radius is appropriate for the intended application and does not exceed the maximum allowable value.
Copper Thickness and Trace Width
The thickness of the copper traces and their width play a significant role in the flexibility and current-carrying capacity of SEMI-FLEX PCBs. Thinner copper traces are more flexible but have lower current-carrying capacity, while thicker traces are less flexible but can handle higher currents. Designers must strike a balance between flexibility and current-carrying requirements based on the specific application.
Stiffener Placement
Stiffeners are used in SEMI-FLEX PCBs to provide additional support and stability to the rigid areas where components are mounted. The placement of stiffeners is critical to ensure proper component alignment and prevent damage to the flexible substrate during bending. Stiffeners are typically made of materials such as FR-4, aluminum, or stainless steel.
SEMI-FLEX PCB Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process for SEMI-FLEX PCBs involves several steps that combine the fabrication techniques used for both rigid and flexible PCBs.
Substrate Preparation
The first step in the SEMI-FLEX PCB manufacturing process is to prepare the flexible substrate. This involves cleaning the substrate material and applying a copper layer to one or both sides of the substrate using techniques such as electroless plating or sputtering.
Rigid Area Lamination
Next, the rigid areas of the SEMI-FLEX PCB are laminated onto the flexible substrate. This is typically done using a pre-preg material that is placed between the flexible substrate and the rigid material. The stack-up is then subjected to heat and pressure to bond the layers together.
Circuit Patterning
Once the rigid and flexible layers are laminated, the circuit pattern is created on the copper layer using photolithography and etching processes. This involves applying a photoresist layer, exposing it to UV light through a patterned mask, and then developing and etching the copper to create the desired Circuit Traces.
Coverlay Application
After the circuit pattern is created, a coverlay is applied to the flexible areas of the SEMI-FLEX PCB to protect the copper traces and provide electrical insulation. The coverlay is typically made of a flexible material such as polyimide or polyester and is laminated onto the PCB using heat and pressure.
Component Assembly
Finally, the components are assembled onto the rigid areas of the SEMI-FLEX PCB using standard SMT (Surface Mount Technology) or THT (Through-Hole Technology) processes. The assembled PCB is then tested and inspected to ensure proper functionality and quality.

Applications of SEMI-FLEX PCBs
SEMI-FLEX PCBs find applications in a wide range of industries and products where both flexibility and stability are required.
Automotive Electronics
In the automotive industry, SEMI-FLEX PCBs are used in various applications such as instrument clusters, infotainment systems, and vehicle sensors. These PCBs can withstand the harsh environmental conditions and vibrations encountered in automotive applications while providing the necessary flexibility for packaging and installation.
Medical Devices
SEMI-FLEX PCBs are widely used in medical devices such as wearable monitors, implantable devices, and diagnostic equipment. The flexibility of these PCBs allows them to conform to the human body and fit into compact medical devices, while the rigid areas provide stable mounting points for components.
Consumer Electronics
Many consumer electronic products, such as smartphones, smartwatches, and VR/AR headsets, utilize SEMI-FLEX PCBs to achieve compact and flexible designs. The ability to bend and fold the PCB enables designers to create innovative product form factors and maximize space utilization.
Industrial Equipment
In industrial applications, SEMI-FLEX PCBs are used in equipment such as robotics, automation systems, and machine vision cameras. The flexibility of these PCBs allows for easy routing of the board through tight spaces and around moving parts, while the rigid areas provide a stable platform for mounting sensors, controllers, and other components.
SEMI-FLEX PCB Assembly Services
To ensure the successful fabrication and assembly of SEMI-FLEX PCBs, it is essential to partner with experienced and reliable PCB assembly services providers.
Choosing a SEMI-FLEX PCB Assembly Partner
When selecting a SEMI-FLEX PCB assembly partner, consider the following factors:
-
Experience and Expertise: Look for a partner with a proven track record in fabricating and assembling SEMI-FLEX PCBs. They should have the necessary knowledge, skills, and equipment to handle the unique challenges associated with these PCBs.
-
Quality Control and Testing: Ensure that the assembly partner has robust quality control processes and testing procedures in place to guarantee the reliability and performance of the assembled PCBs. This may include automated optical inspection (AOI), X-ray inspection, and functional testing.
-
Design Support: A good SEMI-FLEX PCB assembly partner should offer design support services to help optimize your PCB layout for manufacturability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. They should be able to provide guidance on material selection, bend radius, stiffener placement, and other critical design aspects.
-
Prototyping and Low-Volume Production: If you require prototypes or low-volume production runs, choose a partner that can accommodate these needs with fast turnaround times and flexible manufacturing processes.
Benefits of Outsourcing SEMI-FLEX PCB Assembly
Outsourcing your SEMI-FLEX PCB assembly to a specialized service provider offers several benefits:
-
Cost Savings: Outsourcing eliminates the need to invest in expensive manufacturing equipment and facilities, as well as the cost of hiring and training skilled personnel. This can result in significant cost savings, especially for low-volume production runs.
-
Access to Expertise: SEMI-FLEX PCB assembly service providers have the necessary expertise and experience to handle the complexities of fabricating and assembling these PCBs. They can provide valuable insights and recommendations to optimize your design and ensure the best possible results.
-
Faster Time-to-Market: By outsourcing your SEMI-FLEX PCB assembly, you can leverage the service provider’s streamlined processes and capacity to achieve faster production times and shorter time-to-market for your products.
-
Focus on Core Competencies: Outsourcing allows you to focus on your core competencies, such as product design and marketing, while leaving the manufacturing and assembly tasks to the experts. This can lead to improved overall efficiency and competitiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the difference between a SEMI-FLEX PCB and a Rigid-Flex PCB?
A SEMI-FLEX PCB consists of a flexible substrate with rigid areas laminated onto it, while a rigid-flex PCB is made by laminating multiple layers of flexible and rigid substrates together. Rigid-flex PCBs offer more design flexibility but are typically more expensive and complex to manufacture. -
Can SEMI-FLEX PCBs be used for high-frequency applications?
Yes, SEMI-FLEX PCBs can be designed for high-frequency applications by using low-loss dielectric materials and optimizing the circuit layout to minimize signal integrity issues. However, careful design considerations and material selection are essential to ensure optimal performance. -
How do I determine the appropriate bend radius for my SEMI-FLEX PCB?
The bend radius for a SEMI-FLEX PCB depends on several factors, including the thickness and material properties of the flexible substrate, the copper trace thickness, and the number of layers. As a general rule, the bend radius should be at least 6-10 times the total thickness of the flexible portion of the PCB. Consult with your PCB manufacturer for specific recommendations based on your design. -
What are the common challenges in assembling SEMI-FLEX PCBs?
Some of the common challenges in assembling SEMI-FLEX PCBs include maintaining the proper alignment of components on the rigid areas during the bending process, preventing damage to the flexible substrate during handling and assembly, and ensuring reliable solder joint formation on the flexible areas. Working with an experienced SEMI-FLEX PCB assembly partner can help mitigate these challenges. -
How do I choose the right coverlay material for my SEMI-FLEX PCB?
The choice of coverlay material depends on factors such as the required flexibility, durability, and environmental resistance. Common coverlay materials include polyimide, polyester, and epoxy-based laminates. Polyimide is known for its excellent thermal and chemical resistance, while polyester offers good flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Consult with your PCB manufacturer to select the most suitable coverlay material for your application.
Conclusion
SEMI-FLEX PCBs offer a unique combination of flexibility and stability, making them an attractive option for a wide range of applications across various industries. By understanding the key design considerations, manufacturing processes, and assembly challenges associated with SEMI-FLEX PCBs, product designers and engineers can leverage the benefits of this technology to create innovative and reliable electronic products.
Partnering with an experienced and reliable SEMI-FLEX PCB assembly service provider is crucial to ensure the success of your project. By outsourcing your PCB assembly needs to a specialized partner, you can benefit from their expertise, access to advanced manufacturing capabilities, and ability to deliver high-quality results while saving time and costs.
As the demand for compact, flexible, and high-performance electronic devices continues to grow, SEMI-FLEX PCBs are poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of the electronics industry. By staying informed about the latest developments and best practices in SEMI-FLEX PCB design and assembly, you can position your organization to capitalize on the opportunities presented by this exciting technology.





Leave a Reply