Introduction to PCB Manufacturing
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) manufacturing is a crucial process in the electronics industry. It involves the creation of electronic circuits on a non-conductive substrate, typically made of fiberglass or other composite materials. The quality of PCB manufacturing directly impacts the performance, reliability, and longevity of electronic devices.
In this article, we will explore the key factors that determine the best PCB manufacturing practices and how to assess whether your PCB manufacturer meets these standards.
Understanding the PCB Manufacturing Process
The Basic Steps of PCB Manufacturing
- Design and Layout
- Substrate Selection
- Copper Lamination
- Drilling
- Plating
- Etching
- Solder Mask Application
- Silkscreen Printing
- Surface Finish Application
- Testing and Inspection
Design and Layout Considerations
- Schematic design
- Component placement
- Routing and trace width
- Clearance and creepage distances
- Manufacturability and design for manufacturing (DFM)
Substrate Selection
- FR-4 (Flame Retardant 4)
- High-frequency materials (Rogers, Teflon, etc.)
- Flexible substrates (Polyimide, PET, etc.)
- Thermal management substrates (Aluminum, Copper, etc.)
Copper Lamination and Thickness
- Standard copper weights (0.5 oz, 1 oz, 2 oz)
- Heavy copper (3 oz, 4 oz, 6 oz)
- Copper foil types (Electrodeposited, Rolled Annealed)
Drilling Techniques
- Mechanical drilling
- Laser drilling
- Controlled depth drilling
Plating Methods
- Electroless plating
- Electrolytic plating
- Direct metallization
Etching Processes
- Subtractive etching
- Additive etching
- Semi-additive etching
Solder Mask Application
- Liquid photoimageable solder mask
- Dry film solder mask
- Solder mask colors and finishes
Silkscreen Printing
- Legend printing
- Ink types and colors
- Silkscreen resolution
Surface Finish Options
- Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL)
- Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG)
- Immersion Silver
- Immersion Tin
- Organic Solderability Preservative (OSP)
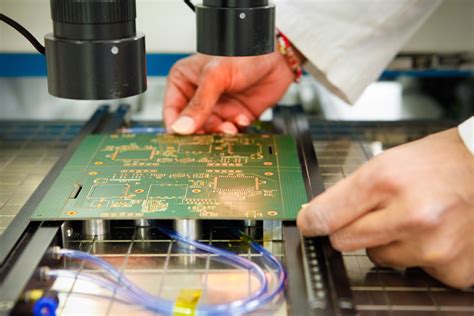
Testing and Inspection
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
- X-ray inspection
- Electrical testing
- Functional testing
Key Factors in Determining the Best PCB Manufacturing
Quality Management System
- ISO 9001 certification
- Total Quality Management (TQM)
- Continuous improvement processes
Capability and Capacity
- PCB complexity (layer count, HDI, etc.)
- Production volume
- Lead time and turnaround
Technology and Equipment
- State-of-the-art machinery
- Automation and robotics
- Advanced software tools
Material Selection and Sourcing
- Reliable material suppliers
- Traceability and lot control
- Compliance with industry standards (RoHS, REACH, UL, etc.)
Skilled Workforce
- Experienced engineers and technicians
- Ongoing training and development
- Cross-functional teams
Customer Support and Communication
- Responsive and knowledgeable support team
- Clear and timely communication
- Collaborative approach to problem-solving
Certifications and Standards Compliance
- ISO 9001 (Quality Management)
- ISO 14001 (Environmental Management)
- IATF 16949 (Automotive Quality Management)
- IPC Standards (IPC-A-600, IPC-6012, IPC-6013, etc.)
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories)
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances)
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals)
Continuous Improvement and Innovation
- Lean manufacturing principles
- Six Sigma methodology
- Regular process audits and reviews
- Investment in research and development

Assessing Your PCB Manufacturer’s Performance
Quality Metrics
- First-pass yield
- Defect rate
- On-time delivery
- Customer satisfaction
Communication and Responsiveness
- Ease of contact
- Response time
- Problem resolution
Technical Support
- Engineering expertise
- Design for manufacturability (DFM) feedback
- Prototype support
Flexibility and Adaptability
- Ability to handle design changes
- Rapid prototyping capabilities
- Customization options
Cost and Value
- Competitive pricing
- Cost reduction initiatives
- Value-added services
The Benefits of Working with the Best PCB Manufacturer
Improved Product Quality
- Fewer defects and failures
- Increased reliability and durability
- Enhanced performance
Faster Time-to-Market
- Efficient production processes
- Rapid prototyping and iteration
- Streamlined supply chain
Cost Savings
- Reduced scrap and rework
- Optimized material usage
- Economies of scale
Competitive Advantage
- Differentiated products
- Improved customer satisfaction
- Greater market share
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between a PCB Prototype and a production PCB?
A PCB prototype is a small batch of boards used for testing and validation purposes before mass production. Production PCBs are manufactured in large quantities for use in the final product.
2. What is the typical lead time for PCB manufacturing?
Lead times vary depending on the complexity of the PCB, the manufacturer’s capacity, and the order volume. Typical lead times range from a few days for simple prototypes to several weeks for large production runs.
3. How do I choose the right surface finish for my PCB?
The choice of surface finish depends on factors such as the intended application, the components used, the assembly process, and the environmental conditions. Consult with your PCB manufacturer to determine the most suitable surface finish for your specific needs.
4. What is the minimum feature size that can be achieved in PCB manufacturing?
The minimum feature size depends on the capabilities of the PCB manufacturer and the specific manufacturing process used. Advanced PCB manufacturing techniques can achieve feature sizes as small as 25 microns (0.025mm) or less.
5. How can I ensure the reliability and longevity of my PCBs?
To ensure the reliability and longevity of your PCBs, consider the following:
– Design for manufacturability (DFM) and design for reliability (DFR)
– Use high-quality materials and components
– Adhere to industry standards and best practices
– Perform thorough testing and inspection
– Work with a reputable and experienced PCB manufacturer
Conclusion
Choosing the best PCB manufacturer is essential for ensuring the quality, reliability, and performance of your electronic products. By understanding the key factors that determine the best PCB manufacturing practices and assessing your manufacturer’s capabilities and performance, you can make informed decisions and achieve a competitive advantage in the market.
Remember to consider factors such as quality management, technological capabilities, material selection, skilled workforce, customer support, certifications and standards compliance, and continuous improvement when evaluating your PCB manufacturer. By partnering with the best PCB manufacturer, you can improve product quality, reduce time-to-market, save costs, and gain a competitive edge in the industry.





Leave a Reply