Introduction to Flex-Rigid PCB
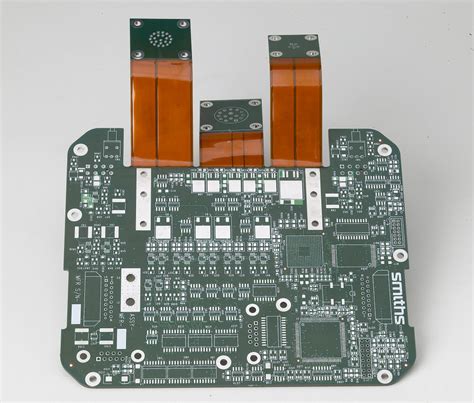
Flex-Rigid PCBs, also known as Rigid-Flex PCBs, are a unique combination of flexible and rigid printed circuit boards. These PCBs offer the best of both worlds by providing the flexibility of a flex PCB and the stability of a rigid PCB. RAYPCB, a leading PCB manufacturer, has mastered the art of designing and manufacturing high-quality flex-rigid PCBs for various applications.
What is a Flex-Rigid PCB?
A flex-rigid PCB is a hybrid printed circuit board that combines flexible and rigid substrates. The flexible part of the PCB allows for bending and folding, while the rigid part provides structural support and stability. This combination enables the creation of complex, three-dimensional designs that are not possible with traditional rigid PCBs.
Advantages of Flex-Rigid PCBs
Flex-rigid PCBs offer several advantages over traditional rigid PCBs:
- Space-saving: Flex-rigid PCBs can be folded and bent to fit into tight spaces, reducing the overall size of the device.
- Reduced weight: By eliminating the need for connectors and cables, flex-rigid PCBs can significantly reduce the weight of the device.
- Improved reliability: Flex-rigid PCBs minimize the number of interconnects, which reduces the risk of connection failures and improves overall reliability.
- Enhanced signal integrity: The reduced number of interconnects also minimizes signal loss and interference, resulting in better signal integrity.
- Design flexibility: Flex-rigid PCBs allow for creative and complex designs that are not possible with rigid PCBs alone.
RAYPCB’s Capabilities in Flex-Rigid PCB Manufacturing
RAYPCB has invested heavily in state-of-the-art equipment and skilled personnel to provide top-notch flex-rigid PCB manufacturing services. Some of the key capabilities include:
Advanced Materials
RAYPCB uses a variety of advanced materials to manufacture flex-rigid PCBs, including:
- Polyimide (PI) for the flexible layers
- FR-4, high-Tg FR-4, and Rogers materials for the rigid layers
- Copper-clad laminates (CCLs) for the conductive layers
These materials are carefully selected based on the specific requirements of each project to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Multilayer Flex-Rigid PCBs
RAYPCB can manufacture flex-rigid PCBs with multiple layers, combining flexible and rigid layers as needed. The company has the capability to produce PCBs with up to 30 layers, including:
- 1-6 layer flex
- 4-14 layer rigid
- 6-20 layer rigid-flex
This allows for the creation of complex, high-density designs that meet the demands of modern electronic devices.
Controlled Impedance
RAYPCB offers controlled impedance flex-rigid PCBs to ensure proper signal integrity and minimize signal distortion. The company can maintain impedance control within ±10% tolerance, which is essential for high-speed applications such as:
- High-speed digital circuits
- RF and microwave circuits
- Telecommunications equipment
Fine-Pitch Routing
RAYPCB has the capability to produce flex-rigid PCBs with fine-pitch routing, enabling the creation of high-density designs. The company can achieve trace widths and spacings as low as 50 µm (2 mil), which is suitable for a wide range of applications, including:
- Miniaturized devices
- Wearable electronics
- Medical implants
Blind and Buried Vias
To further enhance the design flexibility and space-saving properties of flex-rigid PCBs, RAYPCB offers blind and buried via technology. This allows for the creation of vias that do not extend through the entire thickness of the PCB, enabling more compact and efficient designs.
Impedance Control
RAYPCB can fabricate flex-rigid PCBs with controlled impedance to ensure proper signal integrity and minimize signal distortion. The company can maintain impedance control within ±10% tolerance, which is essential for high-speed applications such as:
- High-speed digital circuits
- RF and microwave circuits
- Telecommunications equipment
IPC Class 3 Standards
RAYPCB manufactures flex-rigid PCBs in accordance with IPC Class 3 standards, ensuring the highest level of quality and reliability. This is particularly important for applications that require superior performance and durability, such as:
- Aerospace and defense
- Medical devices
- Automotive electronics
Applications of Flex-Rigid PCBs
Flex-rigid PCBs are used in a wide range of industries and applications due to their unique properties and benefits. Some of the most common applications include:
Aerospace and Defense
Flex-rigid PCBs are widely used in aerospace and defense applications, where space, weight, and reliability are critical factors. Examples include:
- Satellites
- Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)
- Missile guidance systems
Medical Devices
The compact size, reliability, and design flexibility of flex-rigid PCBs make them ideal for medical devices, such as:
- Implantable devices (e.g., pacemakers, neurostimulators)
- Wearable health monitors
- Surgical instruments
Automotive Electronics
Flex-rigid PCBs are increasingly used in automotive electronics, where they help reduce weight, save space, and improve reliability. Applications include:
- Engine control units (ECUs)
- Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS)
- Infotainment systems
Consumer Electronics
The demand for smaller, lighter, and more feature-rich consumer electronics has driven the adoption of flex-rigid PCBs in this sector. Examples include:
- Smartphones
- Wearable devices (e.g., smartwatches, fitness trackers)
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) headsets
Industrial Equipment
Flex-rigid PCBs are also used in various industrial equipment, where they provide reliable performance in harsh environments. Applications include:
- Robotics
- Machine vision systems
- Process control equipment

Flex-Rigid PCB Design Considerations
Designing a flex-rigid PCB requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure optimal performance and manufacturability. Some key design considerations include:
Bend Radius
The bend radius is a critical factor in flex-rigid PCB design, as it determines the minimum radius at which the flexible portion of the PCB can be bent without causing damage. The bend radius is typically specified by the manufacturer and depends on factors such as the thickness of the flexible layers and the materials used.
Stiffener Placement
Stiffeners are used to provide support and stability to the flexible portions of the PCB. Proper placement of stiffeners is essential to ensure that the PCB can be bent as intended without causing damage or affecting performance.
Layer Stack-up
The layer stack-up of a flex-rigid PCB must be carefully designed to ensure proper signal integrity, impedance control, and mechanical stability. This involves selecting the appropriate materials, thicknesses, and arrangement of the flexible and rigid layers.
Trace Routing
Trace routing on a flex-rigid PCB must take into account the unique properties of the flexible and rigid portions of the board. This includes considering factors such as bend radius, impedance control, and signal integrity when routing traces between the flexible and rigid layers.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process for flex-rigid PCBs is more complex than that of traditional rigid PCBs, and designers must work closely with the manufacturer to ensure that the design is optimized for manufacturability. This may involve making design adjustments to accommodate the specific capabilities and limitations of the manufacturer’s equipment and processes.
RAYPCB’s Flex-Rigid PCB Manufacturing Process
RAYPCB follows a comprehensive manufacturing process to ensure the highest quality and reliability of its flex-rigid PCBs. The process includes the following steps:
- Material selection and preparation
- Inner layer processing
- Lamination
- Drilling
- Plating
- Outer layer processing
- Solder mask application
- Surface finish application
- Electrical testing
- Final inspection and packaging
Throughout the manufacturing process, RAYPCB employs strict quality control measures to ensure that each PCB meets the specified requirements and standards.
Flex-Rigid PCB Testing and Quality Control
To ensure the highest level of quality and reliability, RAYPCB conducts rigorous testing and quality control throughout the manufacturing process. Some of the key testing and quality control measures include:
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
AOI is used to inspect the PCBs for defects such as shorts, opens, and misalignments. This automated process allows for fast and accurate inspection of large numbers of PCBs.
X-ray inspection
X-ray inspection is used to detect internal defects that cannot be seen by visual inspection, such as voids in vias and delamination.
Flying Probe Testing
Flying probe testing is used to check the electrical continuity and isolation of the PCB. This test can detect opens, shorts, and other electrical defects.
Functional Testing
Functional testing is used to verify that the PCB operates as intended in its final application. This may involve testing the PCB under various environmental conditions and loads.
Cross-Sectioning
Cross-sectioning is used to examine the internal structure of the PCB, including the layer stack-up, via formation, and plating thickness. This destructive test is typically performed on a sample basis to ensure that the PCB meets the specified requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the minimum bend radius for a flex-rigid PCB?
A1: The minimum bend radius depends on several factors, including the thickness of the flexible layers, the materials used, and the number of layers. RAYPCB can help determine the appropriate bend radius for your specific application.
Q2: How many layers can a flex-rigid PCB have?
A2: RAYPCB can manufacture flex-rigid PCBs with up to 30 layers, including 1-6 layer flex, 4-14 layer rigid, and 6-20 layer rigid-flex.
Q3: What materials are used in flex-rigid PCBs?
A3: Flex-rigid PCBs typically use polyimide (PI) for the flexible layers, FR-4, high-Tg FR-4, or Rogers materials for the rigid layers, and copper-clad laminates (CCLs) for the conductive layers.
Q4: Can flex-rigid PCBs be used in high-speed applications?
A4: Yes, flex-rigid PCBs can be designed with controlled impedance to ensure proper signal integrity and minimize signal distortion, making them suitable for high-speed applications such as high-speed digital circuits, RF and microwave circuits, and telecommunications equipment.
Q5: What industries commonly use flex-rigid PCBs?
A5: Flex-rigid PCBs are used in a wide range of industries, including aerospace and defense, medical devices, automotive electronics, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment.
Conclusion
Flex-rigid PCBs offer a unique combination of flexibility and stability, enabling the creation of complex, three-dimensional designs that are not possible with traditional rigid PCBs. RAYPCB has the capability and expertise to manufacture high-quality flex-rigid PCBs for a wide range of applications, using advanced materials, multilayer construction, fine-pitch routing, and blind and buried vias.
By working closely with RAYPCB’s experienced engineers and following best practices for flex-rigid PCB design, you can take advantage of the many benefits of this innovative technology, including space savings, weight reduction, improved reliability, and enhanced signal integrity.





Leave a Reply