Introduction to Fiducial PCBs
Fiducial PCBs, also known as fiducial markers or fiducials, are essential components in the manufacturing process of printed circuit boards (PCBs). These small, circular copper pads serve as reference points for automated assembly equipment, ensuring precise and accurate placement of components on the PCB. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the design, function, and importance of fiducial PCBs in the electronics industry.
What are Fiducial PCBs?
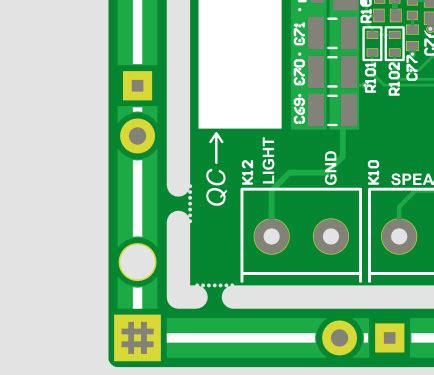
Fiducial PCBs are non-functional copper pads strategically placed on a PCB to provide a reference point for automated assembly machines. These pads are typically circular in shape and have a diameter ranging from 1mm to 3mm. Fiducials are placed in specific locations on the PCB, usually in the corners or along the edges, to create a coordinate system for the assembly equipment to follow.
The Importance of Fiducial PCBs in PCB Assembly
Accurate Component Placement
One of the primary functions of fiducial PCBs is to ensure the accurate placement of components on the PCB. Automated assembly machines, such as pick-and-place machines and solder paste printers, rely on fiducials to determine the exact position and orientation of the PCB. By using fiducials as reference points, these machines can place components with high precision, reducing the risk of misalignment and improving the overall quality of the assembled PCB.
Faster Assembly Process
Fiducial PCBs also contribute to a faster assembly process. By providing clear reference points for the automated equipment, fiducials eliminate the need for manual alignment and positioning of the PCB. This automation not only speeds up the assembly process but also reduces the likelihood of human error, resulting in higher production efficiency and lower manufacturing costs.
Improved Reliability and Yield
The use of fiducial PCBs in the assembly process leads to improved reliability and yield of the final product. With accurate component placement and reduced risk of misalignment, the assembled PCBs are less likely to suffer from defects or malfunctions. This, in turn, results in fewer rejected boards, lower rework costs, and higher overall yield, benefiting both the manufacturer and the end-user.
Designing Fiducial PCBs
Fiducial Size and Shape
When designing fiducial PCBs, it is essential to consider the size and shape of the pads. The most common shape for fiducials is circular, as it provides a clear and easily recognizable target for the automated assembly equipment. The size of the fiducial should be large enough to be easily detected by the machine vision systems but not so large that it interferes with the placement of other components or traces on the PCB.
| Fiducial Diameter | Recommended PCB Size |
|---|---|
| 1mm | Small to medium PCBs |
| 1.5mm | Medium to large PCBs |
| 2mm | Large PCBs |
| 3mm | Very large PCBs |
Fiducial Placement
The placement of fiducials on the PCB is another critical aspect of their design. Fiducials should be positioned in a way that provides a clear line of sight for the automated assembly equipment, avoiding obstruction by tall components or other features on the board. It is recommended to place fiducials in the corners of the PCB, as this provides the most stable reference points for the assembly machines.
| Number of Fiducials | Recommended Placement |
|---|---|
| 2 | Opposite corners of the PCB |
| 3 | Corners of the PCB forming a triangle |
| 4 | All four corners of the PCB |
Fiducial Material and Finish
Fiducial PCBs are typically made of the same copper material as the rest of the PCB traces and pads. However, the finish applied to the fiducials can vary depending on the specific requirements of the assembly process. The most common finishes for fiducials are:
- HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling): A tin-lead alloy is applied to the copper pads, providing a flat, solderable surface.
- ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold): A layer of nickel is plated onto the copper, followed by a thin layer of gold, resulting in a flat, corrosion-resistant surface.
- OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative): A thin, organic coating is applied to the copper, protecting it from oxidation and ensuring good solderability.
The choice of finish for fiducials depends on factors such as the overall PCB finish, the assembly process requirements, and the environmental conditions the PCB will be exposed to.

Fiducial Recognition and Machine Vision Systems
How Fiducial Recognition Works
Fiducial recognition is a crucial part of the automated PCB assembly process. Machine vision systems, integrated into pick-and-place machines and solder paste printers, use cameras and image processing algorithms to locate and identify the fiducials on the PCB. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Image Acquisition: The machine vision system captures an image of the PCB using a high-resolution camera.
- Image Processing: The captured image is processed to enhance the contrast and remove any noise or artifacts.
- Fiducial Detection: The image processing algorithm searches for circular patterns that match the size and shape of the fiducials.
- Coordinate Calculation: Once the fiducials are detected, the machine vision system calculates their coordinates relative to the PCB’s origin.
- Alignment and Positioning: The calculated coordinates are used to align and position the PCB for component placement or solder paste printing.
Factors Affecting Fiducial Recognition
Several factors can affect the accuracy and reliability of fiducial recognition in automated PCB assembly:
- Fiducial Size and Shape: The size and shape of the fiducials should be consistent and within the specified tolerances to ensure accurate detection by the machine vision system.
- Fiducial Contrast: The contrast between the fiducial and the surrounding PCB surface should be high enough for the machine vision system to distinguish the fiducial from the background.
- PCB Surface Finish: The surface finish of the PCB can impact the visibility and contrast of the fiducials. Matte finishes, such as OSP, may provide better contrast than glossy finishes like HASL.
- Lighting Conditions: Consistent and even lighting is essential for accurate fiducial recognition. Uneven or glaring lighting can cast shadows or create reflections that interfere with the machine vision system’s ability to detect the fiducials.
Best Practices for Implementing Fiducial PCBs
Fiducial Design Guidelines
To ensure the effective use of fiducial PCBs in the assembly process, consider the following design guidelines:
- Use a minimum of two fiducials per PCB, placed in opposite corners.
- Keep the fiducial size consistent throughout the design, typically between 1mm and 3mm in diameter.
- Ensure a minimum clearance of 3mm between the fiducial and any other components or features on the PCB.
- Place fiducials in areas that provide a clear line of sight for the machine vision system, avoiding obstruction by tall components.
- Use a contrasting solder mask color around the fiducial to improve visibility and detection.
Collaboration with Assembly Partners
Effective implementation of fiducial PCBs requires close collaboration between the PCB designer and the assembly partner. It is essential to communicate the specific requirements and guidelines for fiducial placement, size, and finish to ensure compatibility with the assembly partner’s equipment and processes. Regular communication and feedback can help identify and resolve any issues related to fiducial recognition and placement accuracy.
Testing and Validation
Before starting full-scale production, it is crucial to test and validate the fiducial PCB design and assembly process. This can be done by producing a small batch of boards and running them through the automated assembly line to verify the accuracy of fiducial recognition and component placement. Any issues or discrepancies should be addressed and corrected before proceeding with mass production.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the minimum number of fiducials required on a PCB?
A: A minimum of two fiducials, placed in opposite corners of the PCB, is recommended for most applications. However, larger or more complex PCBs may require additional fiducials for improved accuracy and stability. -
Q: Can fiducials be placed on both sides of the PCB?
A: Yes, fiducials can be placed on both sides of the PCB if the assembly process requires component placement on both sides. In such cases, it is essential to ensure that the fiducials on each side are correctly aligned and do not interfere with each other. -
Q: What is the recommended clearance between fiducials and other components?
A: A minimum clearance of 3mm between fiducials and any other components or features on the PCB is recommended to ensure accurate detection by the machine vision system and avoid interference with component placement. -
Q: Can fiducials have different shapes other than circular?
A: While circular fiducials are the most common and widely used, some applications may require different shapes, such as squares or triangles. However, it is essential to consult with the assembly partner to ensure compatibility with their equipment and processes. -
Q: How do I choose the right finish for my fiducial PCBs?
A: The choice of finish for fiducial PCBs depends on factors such as the overall PCB finish, the assembly process requirements, and the environmental conditions the PCB will be exposed to. Consult with your assembly partner to determine the most suitable finish for your specific application.
Conclusion
Fiducial PCBs play a critical role in the accurate and efficient assembly of printed circuit boards. By providing clear reference points for automated assembly equipment, fiducials ensure precise component placement, improve production speed, and enhance the overall reliability and yield of the assembled PCBs. Effective implementation of fiducial PCBs requires careful consideration of design factors, such as size, shape, placement, and finish, as well as close collaboration with assembly partners and thorough testing and validation of the assembly process. By following best practices and guidelines for fiducial PCB design and implementation, manufacturers can optimize their assembly processes and produce high-quality, reliable electronic products.





Leave a Reply