What is MCPCB and Why is it Important for LEDs?
MCPCB stands for Metal Core Printed Circuit Board. As the name suggests, it is a special type of PCB that has a metal core layer, usually made of aluminum, as its base. This metal core serves as an efficient heat spreader, allowing the PCB to dissipate heat much more effectively than traditional FR-4 PCBs.
In the LED industry, thermal management is a critical factor in ensuring the longevity and performance of LED lights. LEDs generate a significant amount of heat during operation, and if this heat is not dissipated properly, it can lead to a decrease in the LED’s lifespan, luminous efficiency, and color consistency. This is where MCPCB comes into play.
By using MCPCB as the substrate for LED lighting applications, manufacturers can ensure that the heat generated by the LEDs is efficiently transferred to the metal core layer and then dissipated into the surrounding environment. This helps to maintain the LED’s optimal operating temperature, which in turn enhances its performance and prolongs its lifespan.
The Structure and Composition of MCPCB
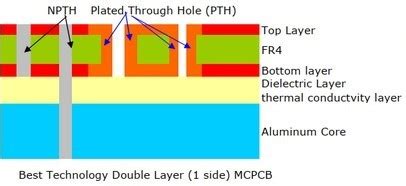
A typical MCPCB consists of three main layers:
-
The Base Layer: This is the metal core layer, usually made of aluminum, which acts as the heat spreader. The thickness of this layer can vary depending on the specific application and the amount of heat that needs to be dissipated.
-
The Dielectric Layer: This layer is placed on top of the metal core and provides electrical insulation between the metal core and the circuit layer. It is typically made of a thermally conductive, but electrically insulating material, such as epoxy or ceramic.
-
The Circuit Layer: This is the top layer of the MCPCB, where the actual electrical circuit is printed. It is made of copper and is etched to create the desired circuit pattern.
Here’s a table summarizing the layers of an MCPCB:
| Layer | Material | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Base Layer | Aluminum | Heat spreader |
| Dielectric Layer | Epoxy or Ceramic | Electrical insulation |
| Circuit Layer | Copper | Electrical circuit |
The specific materials used in each layer can vary depending on the manufacturer and the intended application. For example, some MCPCBs may use a different metal for the base layer, such as copper or steel, depending on the thermal conductivity requirements.
Advantages of Using MCPCB in LED Applications
There are several key advantages to using MCPCB in LED lighting applications:
-
Enhanced Thermal Management: As mentioned earlier, the metal core layer of MCPCB acts as an efficient heat spreader, allowing for better thermal management of LEDs. This helps to maintain the LED’s optimal operating temperature, which is crucial for its performance and longevity.
-
Improved Luminous Efficiency: By keeping the LED’s temperature within the optimal range, MCPCB helps to improve the luminous efficiency of the LED. This means that the LED can produce more light output for the same amount of input power, resulting in energy savings.
-
Extended Lifespan: Proper thermal management is essential for prolonging the lifespan of LEDs. By using MCPCB, manufacturers can ensure that the LEDs operate at a lower temperature, which reduces the rate of degradation and extends their useful life.
-
Better Color Consistency: The color output of an LED can shift if its operating temperature fluctuates. By maintaining a stable temperature through the use of MCPCB, manufacturers can achieve better color consistency across the LED’s lifetime.
-
Compact and Lightweight: MCPCB is thinner and lighter compared to traditional heat sinks and PCBs. This makes it ideal for applications where space and weight are critical factors, such as in automotive lighting or portable LED devices.
Here’s a table comparing the benefits of MCPCB with traditional FR-4 PCBs:
| Feature | MCPCB | FR-4 PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Management | Excellent | Poor |
| Luminous Efficiency | Higher | Lower |
| Lifespan | Longer | Shorter |
| Color Consistency | Better | Worse |
| Weight and Size | Compact and Lightweight | Bulky and Heavy |

Applications of MCPCB in the LED Industry
MCPCB finds applications in various sectors of the LED industry, including:
-
General Lighting: MCPCB is widely used in LED bulbs, tubes, and fixtures for residential, commercial, and industrial lighting applications. Its excellent thermal management properties help to ensure the reliability and performance of these LED lighting products.
-
Automotive Lighting: LED lighting is increasingly being used in the automotive industry for headlights, taillights, and interior lighting. MCPCB’s compact size and efficient heat dissipation make it an ideal choice for these applications, where space is limited, and the lighting is exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
-
Outdoor Lighting: LEDs are popular for outdoor lighting applications, such as street lights, floodlights, and landscape lighting. MCPCB helps to ensure that these LEDs can withstand the high-power demands and extreme temperatures often encountered in outdoor environments.
-
Horticulture Lighting: LEDs are used in horticulture lighting to promote plant growth and development. MCPCB is used in these applications to ensure that the LEDs operate at optimal temperatures, which is critical for the health and yield of the plants.
-
Display Lighting: LEDs are used in various display applications, such as digital signage, video walls, and large-scale displays. MCPCB helps to maintain the brightness and color consistency of these displays by effectively managing the heat generated by the LEDs.
Here’s a table summarizing the key applications of MCPCB in the LED industry:
| Application | Benefits of MCPCB |
|---|---|
| General Lighting | Reliability, performance |
| Automotive Lighting | Compact size, heat dissipation |
| Outdoor Lighting | High-power handling, temperature resistance |
| Horticulture Lighting | Optimal temperature for plant health and yield |
| Display Lighting | Brightness and color consistency |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: What is the difference between MCPCB and traditional FR-4 PCB?
A: The main difference between MCPCB and traditional FR-4 PCB is the presence of a metal core layer in MCPCB. This metal core, usually made of aluminum, acts as a heat spreader, allowing for better thermal management compared to FR-4 PCB. MCPCB is also thinner and lighter than FR-4 PCB.
- Q: Can MCPCB be used for applications other than LED lighting?
A: While MCPCB is primarily used in the LED industry, it can also be used in other applications where efficient heat dissipation is required. This includes power electronics, automotive electronics, and high-power RF applications.
- Q: What are the factors to consider when choosing an MCPCB for an LED application?
A: When choosing an MCPCB for an LED application, you should consider factors such as the thermal conductivity of the metal core layer, the thickness of the dielectric layer, the copper thickness of the circuit layer, and the overall size and shape of the MCPCB. These factors will depend on the specific requirements of your application, such as the power level of the LEDs, the ambient temperature, and the available space.
- Q: How does the thickness of the metal core layer affect the thermal performance of MCPCB?
A: In general, a thicker metal core layer will provide better thermal conductivity and heat spreading capabilities. However, increasing the thickness of the metal core will also increase the overall thickness and weight of the MCPCB. Therefore, the optimal thickness of the metal core layer will depend on the specific requirements of the application and the balance between thermal performance and other factors like size and cost.
- Q: Can MCPCB be customized for specific LED applications?
A: Yes, MCPCB can be customized to meet the specific requirements of different LED applications. This includes customizing the size and shape of the MCPCB, the thickness of the metal core and dielectric layers, and the layout of the copper circuit layer. Many MCPCB manufacturers offer custom design and fabrication services to help customers optimize their MCPCBs for their specific LED applications.
Conclusion
MCPCB plays a crucial role in the LED industry by providing an efficient thermal management solution for LED lighting applications. Its unique structure, with a metal core layer acting as a heat spreader, allows for better heat dissipation compared to traditional PCBs. This, in turn, leads to improved LED performance, luminous efficiency, color consistency, and lifespan.
As the LED industry continues to grow and evolve, the demand for high-quality MCPCBs is expected to increase. Manufacturers who invest in MCPCB technology and expertise will be well-positioned to meet this demand and deliver reliable, high-performance LED lighting solutions for a wide range of applications.





Leave a Reply