Diode Overview
The 1N4002 is a popular general-purpose rectifier diode widely used in various electronic applications. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the 1N4002 diode, including its characteristics, applications, and frequently asked questions.
What is a 1N4002 Diode?
A 1N4002 diode is a silicon rectifier diode that allows current to flow in only one direction, from anode to cathode, when forward biased. It is part of the 1N400x series of diodes, which includes 1N4001, 1N4002, 1N4003, 1N4004, 1N4005, 1N4006, and 1N4007. The main difference between these diodes is their maximum reverse voltage rating, with the 1N4002 having a reverse voltage rating of 100 volts.
1N4002 Diode Specifications
The following table summarizes the key specifications of the 1N4002 diode:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum Repetitive Peak Reverse Voltage (VRRM) | 100 V |
| Maximum RMS Voltage (VRMS) | 70 V |
| Maximum DC Blocking Voltage (VDC) | 100 V |
| Maximum Average Forward Rectified Current (IF(AV)) | 1 A |
| Maximum Peak Forward Surge Current (IFSM) | 30 A |
| Maximum Instantaneous Forward Voltage Drop (VF) | 1.1 V |
| Maximum Reverse Current (IR) at Rated DC Blocking Voltage | 5 µA |
| Operating Junction Temperature Range (TJ) | -65°C to +175°C |
These specifications make the 1N4002 diode suitable for a wide range of applications, including power supply rectification, signal conditioning, and overvoltage protection.
1N4002 Diode Construction
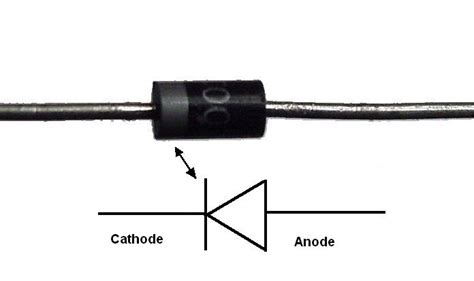
The 1N4002 diode is constructed using a silicon PN junction. The anode is the P-type region, while the cathode is the N-type region. The diode is encapsulated in a plastic package with a black band on the cathode end for easy identification.
Forward and Reverse Bias Characteristics
When the anode is connected to a positive voltage with respect to the cathode, the diode is said to be forward biased. In this state, the diode conducts current with a small forward voltage drop, typically around 0.7 volts for silicon diodes like the 1N4002.
When the cathode is connected to a positive voltage with respect to the anode, the diode is reverse biased. In this state, the diode blocks current flow, allowing only a small leakage current to pass through. If the reverse voltage exceeds the diode’s maximum reverse voltage rating, the diode may break down and conduct large currents, potentially damaging the device.
1N4002 Diode Applications
The 1N4002 diode finds use in various electronic applications, including:
-
Power Supply Rectification: The 1N4002 can be used in bridge rectifier circuits to convert AC to DC power. It is suitable for low-voltage, low-current applications.
-
Reverse Polarity Protection: The 1N4002 can be placed in series with a power supply to protect sensitive electronic components from damage due to accidental reverse polarity connections.
-
Overvoltage Protection: The 1N4002 can be used as a clamping diode to limit voltage spikes in circuits, protecting components from overvoltage damage.
-
Signal Conditioning: The 1N4002 can be used to clip or limit signals in analog circuits, such as in waveform generators or audio processing applications.
-
Flyback Diodes: In inductive circuits, such as relay coils or motor drives, the 1N4002 can be used as a flyback diode to suppress voltage spikes generated when the inductive load is switched off.
Choosing the Right Diode
When selecting a diode for a specific application, consider the following factors:
-
Reverse Voltage Rating: Ensure the diode’s reverse voltage rating is sufficient for the application. The 1N4002 has a 100 V rating, which is suitable for many low-voltage applications.
-
Forward Current Rating: The diode must be able to handle the expected forward current in the application. The 1N4002 has a maximum average forward current rating of 1 A.
-
Switching Speed: For high-frequency applications, consider using a fast-switching diode, such as a Schottky diode, instead of the 1N4002, which is a standard recovery diode.
-
Package Type: The 1N4002 is available in various package types, including through-hole (DO-41) and surface-mount (SMD) options. Choose the package that best suits your circuit design and assembly requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the difference between a 1N4001 and a 1N4002 diode?
The main difference is the maximum reverse voltage rating. The 1N4001 has a 50 V rating, while the 1N4002 has a 100 V rating. Otherwise, their specifications are similar. -
Can I use a 1N4002 diode for high-frequency applications?
The 1N4002 is a standard recovery diode and may not be suitable for high-frequency applications. For such applications, consider using a fast-switching diode, such as a Schottky diode. -
What is the maximum current a 1N4002 diode can handle?
The 1N4002 has a maximum average forward current rating of 1 A. However, it can handle peak forward surge currents up to 30 A for a short duration. -
Can I use a 1N4002 diode for reverse polarity protection?
Yes, the 1N4002 can be placed in series with a power supply to protect sensitive electronic components from damage due to accidental reverse polarity connections. -
What is the forward voltage drop of a 1N4002 diode?
The maximum instantaneous forward voltage drop of a 1N4002 diode is 1.1 V. However, in practice, the forward voltage drop is typically around 0.7 V for silicon diodes.
In conclusion, the 1N4002 diode is a versatile, general-purpose rectifier diode suitable for a wide range of low-voltage, low-current applications. Its 100 V reverse voltage rating and 1 A forward current rating make it a popular choice for power supply rectification, reverse polarity protection, overvoltage protection, signal conditioning, and flyback diode applications. When selecting a diode, consider the reverse voltage rating, forward current rating, switching speed, and package type to ensure it meets the requirements of your specific application.





Leave a Reply