Introduction to Micro SD Cards
Micro SD cards are tiny, removable flash memory cards used to store data in portable devices such as smartphones, digital cameras, GPS units, and more. As technology advances and file sizes increase, having reliable, high-capacity storage solutions like micro SD cards is essential.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the fundamentals of micro SD cards, including their Pinout Configuration, types, speed classes, and capacity. We’ll also discuss best practices for using and maintaining these memory cards to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Understanding Micro SD Card Pinout
To effectively use micro SD cards, it’s crucial to understand their pinout configuration. The pinout refers to the arrangement and function of the electrical contacts on the card. Micro SD cards have eight pins, each serving a specific purpose in facilitating communication between the card and the host device.
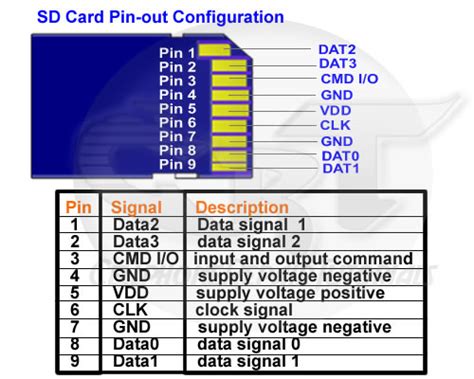
Micro SD Card Pinout Diagram
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | DAT2 | Data Line 2 |
| 2 | CD/DAT3 | Card Detect / Data Line 3 |
| 3 | CMD | Command Line |
| 4 | VDD | Supply Voltage (2.7-3.6V) |
| 5 | CLK | Clock Signal |
| 6 | VSS | Ground |
| 7 | DAT0 | Data Line 0 |
| 8 | DAT1 | Data Line 1 |
Pin Functions Explained
-
DAT2 (Data Line 2): This pin is used for data transfer between the card and the host device. It is part of the 4-bit Data Bus.
-
CD/DAT3 (Card Detect / Data Line 3): This pin serves two functions. In the SPI mode, it acts as the Card Detect signal, indicating whether a card is inserted. In the SD mode, it functions as the fourth data line (DAT3) of the 4-bit data bus.
-
CMD (Command Line): The Command Line is used to send commands from the host device to the micro SD card for various operations such as reading, writing, and erasing data.
-
VDD (Supply Voltage): This pin provides power to the micro SD card. The voltage range is typically between 2.7V and 3.6V.
-
CLK (Clock Signal): The Clock Signal synchronizes data transfer between the host device and the micro SD card.
-
VSS (Ground): This pin serves as the ground reference for the micro SD card.
-
DAT0 (Data Line 0): This pin is used for data transfer and is part of the 4-bit data bus. In the SPI mode, it also functions as the MISO (Master In Slave Out) signal.
-
DAT1 (Data Line 1): This pin is used for data transfer and is part of the 4-bit data bus.
Types of Micro SD Cards
There are several types of micro SD cards available, each with different features and capabilities. Understanding these types will help you choose the right card for your device and storage needs.
Micro SD
The original micro SD card format has a capacity range of 64MB to 2GB. These cards are suitable for storing small files such as contacts, text messages, and low-resolution photos.
Micro SDHC
Micro SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity) cards have a capacity range of 4GB to 32GB. They offer faster read/write speeds compared to standard micro SD cards and are ideal for storing high-resolution photos, HD videos, and larger files.
Micro SDXC
Micro SDXC (Secure Digital eXtended Capacity) cards offer capacities ranging from 64GB to 2TB. These cards are designed for users who require vast amounts of storage, such as professional photographers and videographers. They boast the fastest read/write speeds among micro SD card types.
Micro SDUC
Micro SDUC (Secure Digital Ultra Capacity) is the newest standard in the micro SD card family. These cards have a theoretical maximum capacity of 128TB, although the largest available capacity as of 2021 is 1TB. Micro SDUC cards are designed to meet the growing demands of 4K and 8K video recording, high-resolution photography, and large file storage.

Micro SD Card Speed Classes
Micro SD card speed classes indicate the minimum sustained write speed of the card. Higher speed classes are essential for applications that require fast data transfer, such as recording high-resolution video or burst mode photography.
| Speed Class | Minimum Sequential Write Speed |
|---|---|
| Class 2 | 2 MB/s |
| Class 4 | 4 MB/s |
| Class 6 | 6 MB/s |
| Class 10 | 10 MB/s |
In addition to the standard speed classes, there are two newer speed class ratings:
-
UHS (Ultra High Speed) Speed Class: Designed for SDHC and SDXC cards, UHS speed classes are denoted by a number inside the letter U. There are three UHS speed classes: UHS Speed Class 1 (U1) with a minimum write speed of 10 MB/s, UHS Speed Class 3 (U3) with a minimum write speed of 30 MB/s, and UHS Speed Class 2 (U2) with a minimum write speed of 20 MB/s (proposed but not widely adopted).
-
Video Speed Class: Created specifically for video recording, video speed classes ensure a minimum sustained write speed for smooth video capture. There are five video speed classes: V6 (6 MB/s), V10 (10 MB/s), V30 (30 MB/s), V60 (60 MB/s), and V90 (90 MB/s).
To choose the right speed class for your needs, consider the following guidelines:
- For general use, such as storing documents and photos, Class 2 or Class 4 cards are sufficient.
- For recording Full HD (1080p) video, Class 6 or Class 10 cards are recommended.
- For recording 4K video or capturing high-resolution photos in burst mode, UHS Speed Class 3 (U3) or Video Speed Class V30 or higher cards are ideal.
Micro SD Card Capacity
Micro SD card capacities have increased significantly over the years, accommodating the growing storage needs of modern devices and applications. When choosing a micro SD card, consider your storage requirements and the compatibility of your device.
| Capacity | Suitable for |
|---|---|
| 2GB-32GB | – Basic storage needs – Storing documents, music, and photos |
| 64GB-256GB | – High-resolution photos – Full HD (1080p) and 4K video recording – Large app and game storage |
| 512GB-1TB | – Professional photography and videography – Extensive media libraries – Expandable storage for laptops and gaming consoles |
Best Practices for Using Micro SD Cards
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of your micro SD cards, follow these best practices:
-
Format the card in your device: Before using a new micro SD card, format it in the device you intend to use it with. This ensures compatibility and optimal performance.
-
Safely eject the card: Always use the “Safely Remove” or “Eject” option in your device’s settings before physically removing the micro SD card to prevent data corruption.
-
Avoid extreme temperatures: Keep your micro SD cards away from extreme heat or cold, as temperature fluctuations can damage the card and its contents.
-
Use a protective case: When not in use, store your micro SD card in a protective case to shield it from dust, moisture, and physical damage.
-
Create backups: Regularly back up the data on your micro SD card to another storage device or cloud service to protect against data loss due to card failure or accidental deletion.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Can I use a micro SD card from my smartphone in my digital camera?
Yes, micro SD cards are compatible with various devices as long as the device supports the card’s capacity and speed class. However, it’s essential to format the card in the new device before use. -
What happens if I remove a micro SD card without ejecting it first?
Removing a micro SD card without properly ejecting it can lead to data corruption or loss. Always use the “Safely Remove” or “Eject” option in your device’s settings before physically removing the card. -
Can I use a micro SDXC card in a device that only supports micro SDHC?
No, micro SDXC cards are not backward compatible with devices that only support micro SDHC. Always check your device’s specifications to ensure compatibility with the desired card type and capacity. -
How can I recover deleted files from a micro SD card?
There are several data recovery software options available, such as EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, Recuva, and Disk Drill. These tools can help you recover deleted files from a micro SD card, provided the data hasn’t been overwritten. -
What should I do if my micro SD card is not recognized by my device?
First, try reinserting the card to ensure proper contact with the device’s card reader. If the issue persists, try using the card in another device to determine if the problem lies with the card or the original device. If the card is faulty, you may need to replace it.
Conclusion
Micro SD cards are essential storage solutions for a wide range of portable devices. By understanding the pinout configuration, types, speed classes, and capacities of these cards, you can make informed decisions when selecting the right card for your needs.
Remember to follow best practices for using and maintaining your micro SD cards to ensure optimal performance and data safety. With proper care and usage, micro SD cards can provide reliable, high-capacity storage for your digital life.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect micro SD cards to offer even greater capacities and faster speeds, meeting the ever-growing demands of modern devices and applications. By staying informed about the latest developments in micro SD card technology, you can ensure that you’re always equipped with the best storage solutions for your needs.





Leave a Reply