Rigid-flex printed circuit boards (PCBs) combine rigid and flexible circuitry into a single, integrated assembly. They provide solutions for complex and space-constrained electronics by enabling three-dimensional routing and embedding components. However, the unique benefits of rigid-flex come at a cost. This article will take an in-depth look at the factors that influence rigid flex PCB pricing.
What is Rigid Flex?
A rigid-flex PCB consists of rigid sections interconnected by flexible circuits. The rigid portions provide mechanical support and mounting surfaces for components and connectors. The flexible sections allow the PCB to conform to different shapes and enable dynamic flexing during use.
Rigid-flex allows:
- Three-dimensional layouts by folding and bending the flex circuits
- Component mounting on both sides of a PCB
- Dynamic flexing and vibration absorption
- Miniaturization and weight reduction
- Reduced connector requirements
Common applications include aerospace systems, medical devices, consumer electronics, robotics, test & measurement equipment, and more.
Rigid Flex Construction
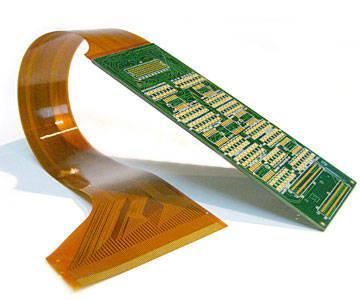
There are two main types of rigid-flex construction:
Discrete Flex
This method joins individual rigid and flex PCBs using mechanical fasteners or adhesives. The rigid sections act as “islands”, with the flexible circuits in between. Simpler to manufacture than multilayer, but limited in routing options.
Multilayer Flex
This builds up rigid and flexible layers into a single integrated multilayer assembly. Enables complex routing between sections and minimizes interconnections. More challenging to manufacture. 2+ layer count typical.
Factors That Influence Rigid Flex PCB Cost
The costs of rigid-flex PCBs are driven by the following key factors:
Layer Count
Adding more conductive layers increases cost through additional material, processing, inspection, and testing requirements. 2-12 layers are common.
Board Complexity
Design characteristics like high density interconnects (HDI), blind/buried vias, and small holes/traces. The more complex the PCB layout and stackup, the higher the fabrication cost.
Board Size
Larger rigid-flex PCBs require more raw materials and processing to manufacture. They also lead to lower panel utilization during fabrication. Standard sizes range from under 50mm x 50mm up to 610mm x 610mm panels.
Flex Layer Thickness
Thicker flexible circuits (>400 micron) are inherently less expensive than thinner flex materials. Thin flex down to 25 microns is possible, but adds cost.
Stiffener Material
The rigid sections require stiffening materials. More expensive options like FR4 and polyimide are higher performance while cheaper materials like paper and textile composites reduce costs.
Quantity Ordered
Economies of scale apply to PCB production. Manufacturing large order volumes lowers the cost per board. Prototyping or low volume production increases per unit pricing.
Lead Time
Standard lead times range from 2-8+ weeks. Rush turnaround times under 1 week cost extra due to increased processing expenses and production disruption.
Special Factors
Unusual board shapes, non-standard materials, and special processes (coating, bonding, etc) also increase manufacturing costs.
Rigid Flex Cost Drivers Summary
Here is a summary of the major rigid flex PCB cost drivers:
| Cost Driver | More Expensive | Less Expensive |
|---|---|---|
| Layer Count | 8+ Layers | 2-6 Layers |
| Design Complexity | HDI, Blind/Buried Vias | Standard Density |
| Board Size | 460mm x 610mm | Under 100mm x 100mm |
| Flex Thickness | 25-100 Microns | 200+ Microns |
| Stiffener Material | FR4 and Polyimide | Paper and Fabric |
| Quantity | Prototyping (1-50 boards) | High Volume (1,000+ boards) |
| Lead Time | 1-4 Day Rush | 8+ Week Standard |
| Special Factors | Non-Standard Shapes/Materials | Standard Offerings |
Rigid Flex PCB Cost Estimates
Based on the factors above, here are some typical base costs for rigid-flex PCB production (per board pricing):
Prototype and Low Volume
| Layer Count | Board Size | Quantity | Lead Time | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-4 | 50mm x 50mm | 10 boards | 2 weeks | $300-$800 |
| 6-8 | 100mm x 100mm | 25 boards | 2 weeks | $350-$1200 |
| 8-12 | 200mm x 150mm | 50 boards | 4 weeks | $800-$2000 |
Medium Volume
| Layer Count | Board Size | Quantity | Lead Time | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-4 | 100mm x 100mm | 250 boards | 4 weeks | $60-$150 |
| 4-6 | 200mm x 150mm | 500 boards | 6 weeks | $100-$250 |
| 6-8 | 300mm x 250mm | 1,000 boards | 8 weeks | $150-$400 |
High Volume
| Layer Count | Board Size | Quantity | Lead Time | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-6 | 250mm x 250mm | 3,000 boards | 8+ weeks | $15-$50 |
| 6-8 | 460mm x 300mm | 5,000 boards | 12+ weeks | $25-$100 |
These rough estimates demonstrate how factors like complexity, volume, size, and lead time impact per unit pricing. Lower complexity and higher quantities bring down cost.
How to Get an Accurate Rigid Flex Quote

To receive an accurate rigid flex PCB quote tailored to your specific requirements, provide as much of the following information as possible to manufacturers:
- Layer count
- Board dimensions (length x width)
- Stiffener material type
- Flexible layer thickness
- Minimum bend radius
- Dielectric materials used
- Copper thickness and finished copper weight
- Board thickness
- Line width/spacing
- Hole sizes
- Pad sizes
- Finishing type (ENIG, immersion silver, OSP, etc)
- Surface finish (matte, glossy, scratch, etc)
- Panelization requirements
- Stencil requirements
- Testing and inspection needs
- Special considerations like controlled impedance
- Quantity required
- Target lead time
With these PCB design specifications, manufacturers can provide a custom rigid flex quotation with expected costs for your particular project. Always get quotes from multiple fabricators to compare pricing.
Tips for Reducing Rigid Flex PCB Costs
Here are some tips to lower your rigid-flex PCB costs:
- Use the least number of layers possible
- Design with standard materials and processes in mind
- Reduce board size as much as possible
- Use lower cost stiffener materials where feasible
- Build panels efficiently to maximize material utilization
- Adjust layer stackup to standard thicknesses when possible
- Consider longer lead times for best pricing
- Order larger quantities to benefit from volume discounts
- Design for ease of manufacture and assembly where practical
- Engage with your PCB partner early in design process
- Request design reviews to identify cost reduction opportunities
Rigid-Flex PCB Cost vs Flexible Circuits Cost
Comparing rigid-flex boards with flexible PCBs is not apples-to-apples. Flex circuits essentially only have the flexible component layers without rigid sections.
In general, flex PCBs have lower material costs without the stiffeners. But they present their own unique fabrication challenges. Small features, thin dielectric layers, and high layer counts make flex PCB production more complex in some ways.
When considering flex circuit vs rigid-flex PCB pricing, you need to weigh up:
- Layer count difference
- Stiffener layer cost
- Relative production volumes
- Design complexity factors
- Whether you need true rigid-flex integration
Rigid-flex provides a complete 3D interconnect solution. Flexible circuits enable dynamic cabling. Evaluate your application requirements before deciding which approach is most cost effective.
Factors That Reduce Cost Effectiveness of Rigid-Flex
While rigid-flex PCBs provide unique advantages, they may not be the most cost-effective choice in certain situations:
- Very high layer counts (12+) drive costs exponentially higher
- Small production volumes under 100 boards do not benefit from economy of scale
- Large board sizes over 300mm x 500mm impact material utilization
- Extremely tight bend radii increase fabrication difficulty
- Aggressive lead time requirements lead to price premiums
In these cases, traditional PCB technologies or alternative solutions like wire harnesses may provide better value depending on performance requirements. Work with your PCB partner to review options.
Conclusion
Rigid-flex PCBs enable innovative and compact product designs, but come at a cost premium versus standard PCB technologies. Layer count, board complexity, size, flex thickness, stiffener materials, order volume, lead time, and special processing requirements are key pricing factors.
Understanding these cost drivers helps set expectations and identify opportunities to optimize rigid-flex PCB designs for efficiency. While exact costs depend on specific project details, target the lowest cost structure that meets your product needs. Partnering early with a quality rigid-flex PCB manufacturer gives the greatest chance to reduce costs while fulfilling performance requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical cost per square inch for a rigid flex PCB?
For a medium complexity, medium volume 4-6 layer rigid flex PCB, typical costs range from $30-60 per square inch depending on the design specifics. In higher volumes above 5000 boards, cost can be as low as $10-25 per square inch. On lower volume complex boards, cost per square inch could exceed $100.
What are the main advantages of rigid flex PCBs vs standard PCBs?
Rigid flex provides benefits like dynamic flexing cabling, three-dimensional layouts, vibration resistance, reduced connectors, and part integration. This enables miniaturization, weight savings, improved reliability, and higher product performance.
How can I estimate the cost savings of switching a design to rigid flex PCBs?
Work with a rigid flex PCB manufacturer to provide current design files and requirements. Ask them to provide an initial quotation along with an estimated cost reduction or avoidance versus your current approach. They can help quantify savings from part integration, reduced connectors, lower assembly costs, etc.
Can flex-to-install rigid sections help lower costs vs full rigid layers?
Yes, flex-to-install is a lower cost option than full rigid board layers. Discrete rigid sections are added in assembly after board fabrication. This saves on material costs but may have performance or assembly tradeoffs to consider.
What design and fabrication factors should I avoid to prevent excessive rigid flex costs?
Avoid very high layer counts over 12 layers unless essential. Minimize board sizes under 500mm x 500mm if possible. Keep rigid layer counts to 2-4 if feasible. Use standard dielectric materials and copper weights. Allow at least 4-6 week lead times. Review design with your PCB partner early.rigid flex pcb cost





Leave a Reply