Introduction to Reflow Soldering
Reflow soldering is a crucial process in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs). It is a technique used to attach surface mount components to the PCB by melting solder paste, which forms a strong electrical and mechanical connection between the components and the board. Reflow soldering has become the preferred method for PCB Assembly due to its efficiency, reliability, and ability to handle high-volume production.
In this article, we will dive into the details of reflow soldering, exploring its advantages, the process itself, and the key factors that influence the success of the reflow soldering process. We will also discuss the role of RAYPCB, a leading PCB manufacturer, in providing high-quality reflow soldering services for PCB assembly.
Advantages of Reflow Soldering
Reflow soldering offers several advantages over other soldering techniques, such as Wave Soldering or hand soldering. Some of the key benefits include:
-
Efficiency: Reflow soldering allows for the simultaneous soldering of multiple components on a PCB, making it a highly efficient process for high-volume production.
-
Consistency: The automated nature of reflow soldering ensures consistent and repeatable results, reducing the chances of human error.
-
Compatibility with Surface Mount Technology (SMT): Reflow soldering is well-suited for SMT components, which are widely used in modern electronics due to their small size and high performance.
-
Improved joint quality: Reflow soldering produces strong and reliable solder joints, enhancing the overall quality and durability of the PCB assembly.
The Reflow Soldering Process
The reflow soldering process involves several stages, each playing a critical role in achieving a successful PCB assembly. Let’s take a closer look at each stage:
1. Solder Paste Application
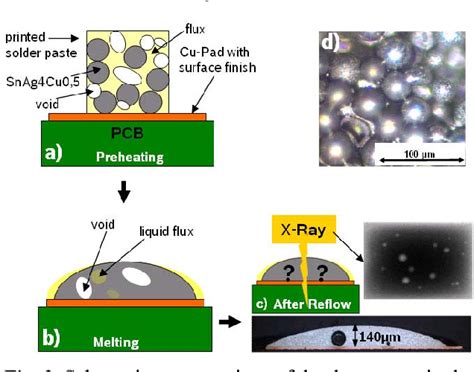
The first step in reflow soldering is applying solder paste to the PCB. Solder paste is a mixture of tiny solder particles suspended in a flux medium. The paste is applied to the PCB using a stencil printing process, where a thin metal stencil with apertures corresponding to the PCB’s solder pads is placed over the board. The solder paste is then spread across the stencil using a squeegee, filling the apertures and depositing the paste onto the solder pads.
2. Component Placement
After the solder paste is applied, the surface mount components are placed onto the PCB using a pick-and-place machine. This automated machine uses a vacuum nozzle to pick up the components from a feeder and accurately place them onto the corresponding solder pads on the PCB. The placement process is guided by fiducial markers on the PCB, ensuring precise alignment of the components.
3. Reflow Soldering
Once the components are placed, the PCB enters the reflow oven for the actual soldering process. The reflow oven consists of several temperature-controlled zones that gradually heat the PCB and the components to the desired temperature profile. The temperature profile is carefully designed to ensure proper melting and solidification of the solder paste without damaging the components or the PCB.
The reflow soldering process can be divided into four main stages:
-
Preheat: The PCB is slowly heated to a temperature just below the melting point of the solder paste. This stage activates the flux and prepares the components and the PCB for soldering.
-
Soak: The temperature is maintained at a stable level for a specified duration to ensure even heat distribution and to allow the flux to remove any oxides from the surfaces to be soldered.
-
Reflow: The temperature is rapidly increased to a peak temperature above the melting point of the solder paste. At this stage, the solder particles melt and form a strong bond between the components and the PCB.
-
Cooling: The PCB is cooled down gradually to allow the molten solder to solidify, forming a strong and reliable solder joint.
4. Inspection and Testing
After the reflow soldering process is complete, the PCB undergoes visual inspection and automated optical inspection (AOI) to ensure the quality of the solder joints and the overall assembly. Any defects or issues detected during the inspection process are addressed and rectified before the PCB moves on to the next stage of the manufacturing process.

Key Factors Influencing Reflow Soldering
Several factors play a critical role in achieving successful reflow soldering results. These include:
1. Temperature Profile
The temperature profile is one of the most crucial factors in reflow soldering. It defines the time-temperature relationship throughout the soldering process and must be carefully optimized for each specific PCB and component combination. The ideal temperature profile ensures that the solder paste melts and solidifies correctly without causing thermal stress or damage to the components.
2. Solder Paste Properties
The properties of the solder paste, such as its composition, particle size, and flux activity, significantly influence the reflow soldering process. The choice of solder paste depends on the specific requirements of the PCB, including the component sizes, pitch, and the desired soldering performance.
3. PCB Design
The PCB design, including the layout, pad sizes, and spacing, plays a vital role in the success of reflow soldering. Proper PCB design ensures adequate solder paste deposition, reduces the risk of bridging or tombstoning, and facilitates efficient heat transfer during the reflow process.
4. Component Placement Accuracy
Accurate component placement is essential for achieving reliable solder joints. Any misalignment or shifting of components during the placement process can lead to soldering defects, such as open circuits or short circuits. Modern pick-and-place machines offer high precision and repeatability to minimize placement errors.
RAYPCB’s Expertise in Reflow Soldering
RAYPCB, a leading PCB manufacturer, has extensive experience and expertise in reflow soldering for PCB assembly. With state-of-the-art facilities and a team of skilled professionals, RAYPCB delivers high-quality reflow soldering services for a wide range of PCB Applications.
Some of the key advantages of choosing RAYPCB for your reflow soldering needs include:
-
Advanced Equipment: RAYPCB invests in the latest reflow Soldering Equipment, ensuring precise control over the temperature profile and soldering process.
-
Experienced Team: RAYPCB’s team of engineers and technicians have years of experience in reflow soldering and are well-versed in handling complex PCB designs and component packages.
-
Strict Quality Control: RAYPCB follows stringent quality control procedures, including visual inspection, AOI, and electrical testing, to ensure the highest quality of the soldered PCBs.
-
Customization: RAYPCB offers customized reflow soldering solutions tailored to the specific requirements of each client, ensuring optimal results for every PCB assembly project.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the difference between reflow soldering and wave soldering?
Reflow soldering is primarily used for surface mount components and involves applying solder paste, placing components, and melting the solder in a reflow oven. Wave soldering, on the other hand, is used for through-hole components and involves passing the PCB over a wave of molten solder. -
Can reflow soldering be used for through-hole components?
While reflow soldering is primarily used for surface mount components, it can also be used for certain through-hole components with appropriate adaptations, such as using solder paste in the through-holes or using pin-in-paste techniques. -
What is the purpose of the flux in solder paste?
The flux in solder paste serves two main purposes: (1) it removes oxides and contaminants from the surfaces to be soldered, ensuring good wetting and bonding; (2) it helps to prevent oxidation of the molten solder during the reflow process, promoting the formation of strong solder joints. -
What are some common defects that can occur in reflow soldering?
Some common defects in reflow soldering include bridging (unintended connection between adjacent solder pads), tombstoning (one end of a component lifting off the PCB), insufficient or excessive solder, and solder balls (small spheres of solder that can cause short circuits). -
How can I optimize the reflow soldering process for my specific PCB?
To optimize the reflow soldering process for your specific PCB, consider factors such as the PCB design, component sizes and types, solder paste properties, and temperature profile. Work closely with your PCB manufacturer, like RAYPCB, to develop a customized reflow soldering solution that meets your specific requirements and ensures the best possible results.
Conclusion
Reflow soldering is a critical process in PCB assembly, enabling the efficient and reliable attachment of surface mount components to the PCB. By understanding the advantages, process stages, and key factors influencing reflow soldering, you can ensure the success of your PCB assembly projects.
RAYPCB, with its expertise and advanced capabilities in reflow soldering, is well-positioned to support your PCB assembly needs. By partnering with RAYPCB, you can benefit from their experience, state-of-the-art equipment, and commitment to quality, ensuring that your PCBs are soldered to the highest standards.
| Reflow Soldering Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Solder Paste Application | Applying solder paste to the PCB using a stencil printing process |
| Component Placement | Placing surface mount components onto the PCB using a pick-and-place machine |
| Reflow Soldering | Melting the solder paste in a reflow oven to form strong solder joints |
| Inspection and Testing | Conducting visual inspection and automated optical inspection to ensure the quality of the soldered PCB |
By leveraging the power of reflow soldering and partnering with a reliable PCB manufacturer like RAYPCB, you can achieve high-quality, reliable, and efficient PCB assemblies that meet the demands of today’s electronics industry.





Leave a Reply