Introduction to PCB and PCBA
In the world of electronic manufacturing, two terms that are often used interchangeably are PCB and PCBA. However, there is a significant difference between the two, and understanding this difference is crucial for anyone involved in the electronics industry. In this article, we will explore the key differences between PCB and PCBA, their manufacturing processes, and their applications.
What is a PCB?
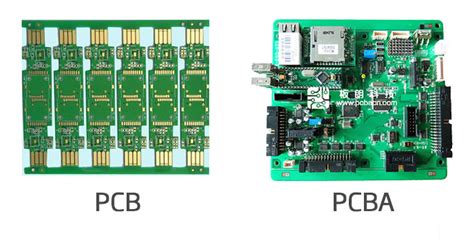
A PCB, or Printed Circuit Board, is a flat board made of insulating material, such as fiberglass, with conductive pathways printed on its surface. These pathways, also known as traces, are used to connect electronic components and allow them to communicate with each other. PCBs are the foundation of modern electronics and are used in a wide range of applications, from simple consumer devices to complex industrial equipment.
What is a PCBA?
A PCBA, or Printed Circuit Board Assembly, is a PCB that has been populated with electronic components. In other words, a PCBA is a completed circuit board that is ready to be installed in an electronic device. The process of assembling a PCBA involves soldering components onto the PCB, testing the board for functionality, and packaging it for shipment.
The PCB Manufacturing Process
The PCB manufacturing process involves several steps, each of which is critical to the overall quality and reliability of the finished board. Here is a brief overview of the PCB manufacturing process:
-
Design: The first step in the PCB manufacturing process is to design the board using specialized software. The design includes the placement of components, the routing of traces, and the creation of any necessary mechanical features, such as holes and cutouts.
-
Printing: Once the design is complete, the next step is to print the conductive pathways onto the insulating material. This is typically done using a silk-screen printing process, which involves applying a conductive ink to the surface of the board through a fine mesh screen.
-
Etching: After the conductive pathways have been printed, the board is etched to remove any unwanted copper. This is typically done using a chemical etching process, which involves immersing the board in a solution that dissolves the unwanted copper.
-
Drilling: Once the board has been etched, any necessary holes are drilled to allow for the installation of components and connectors.
-
Plating: After drilling, the board is plated with a thin layer of copper to improve the conductivity of the traces and to protect them from corrosion.
-
Solder Mask: A solder mask is then applied to the board to protect the copper traces from oxidation and to prevent solder from bridging between adjacent traces during the assembly process.
-
Silkscreen: Finally, a silkscreen layer is applied to the board to add labels, logos, and other identifying marks.
The PCBA Manufacturing Process
The PCBA manufacturing process involves several additional steps beyond those required for PCB manufacturing. Here is a brief overview of the PCBA manufacturing process:
-
Component Placement: The first step in the PCBA manufacturing process is to place the electronic components onto the PCB. This is typically done using automated Pick-and-Place machines, which can place components with high speed and accuracy.
-
Soldering: Once the components have been placed, they are soldered to the board using either through-hole or Surface-mount technology. Through-hole soldering involves inserting the component leads through holes in the board and soldering them in place, while surface-mount soldering involves placing the components directly onto pads on the surface of the board and soldering them in place.
-
Inspection: After soldering, the board is inspected for any defects or errors. This is typically done using automated optical inspection (AOI) equipment, which can quickly identify any problems with the placement or soldering of components.
-
Testing: Once the board has passed inspection, it is tested for functionality using a variety of methods, such as in-circuit testing (ICT), Functional Testing, and boundary scan testing.
-
Coating: After testing, the board may be coated with a protective layer to improve its durability and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and dust.
-
Packaging: Finally, the completed PCBA is packaged for shipment to the customer.

Key Differences between PCB and PCBA
Now that we have a basic understanding of the PCB and PCBA manufacturing processes, let’s take a closer look at the key differences between the two:
| PCB | PCBA |
|---|---|
| A bare board with no components | A board populated with components |
| Used as a foundation for electronic circuits | A complete, functional electronic circuit |
| Manufactured using printing, etching, drilling, and plating processes | Manufactured using component placement, soldering, inspection, testing, and packaging processes |
| Can be single-sided, double-sided, or multi-layered | Can be single-sided, double-sided, or multi-layered |
| Typically less expensive than PCBA | Typically more expensive than PCB |
As you can see, the main difference between PCB and PCBA is that a PCB is a bare board with no components, while a PCBA is a board that has been populated with components and is ready to be installed in an electronic device. PCBs are the foundation of electronic circuits, while PCBAs are complete, functional electronic circuits.
Applications of PCB and PCBA
PCBs and PCBAs are used in a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial equipment. Here are a few examples:
Consumer Electronics
PCBs and PCBAs are used in virtually every consumer electronic device, including:
- Smartphones
- Tablets
- Laptops
- Televisions
- Gaming consoles
- Wearable devices
Industrial Equipment
PCBs and PCBAs are also used in a variety of industrial equipment, such as:
- Medical devices
- Aerospace equipment
- Automotive electronics
- Industrial automation systems
- Power generation and distribution equipment
Military and Defense
PCBs and PCBAs are used in a range of military and defense applications, including:
- Communication systems
- Navigation equipment
- Surveillance and reconnaissance systems
- Weapon systems
Advantages of Using PCBs and PCBAs
There are many advantages to using PCBs and PCBAs in electronic manufacturing, including:
-
Miniaturization: PCBs and PCBAs allow for the miniaturization of electronic devices, as they can be designed to fit into small spaces and can be populated with tiny components.
-
Reliability: PCBs and PCBAs are highly reliable, as they are manufactured using precise processes and can be thoroughly tested for functionality before being installed in a device.
-
Cost-effective: PCBs and PCBAs are cost-effective, as they can be manufactured in large quantities using automated processes.
-
Customization: PCBs and PCBAs can be customized to meet the specific needs of a particular application, allowing for greater flexibility in design and functionality.
Challenges in PCB and PCBA Manufacturing
While PCB and PCBA manufacturing offer many advantages, there are also several challenges that manufacturers must overcome, including:
-
Complexity: As electronic devices become more complex, so too do the PCBs and PCBAs that power them. This complexity can make the design and manufacturing process more difficult and time-consuming.
-
Material Constraints: PCBs and PCBAs require specific materials, such as copper and fiberglass, which can be subject to supply chain disruptions and price fluctuations.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring the quality and reliability of PCBs and PCBAs requires strict quality control measures, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
-
Environmental Concerns: The manufacturing process for PCBs and PCBAs can generate hazardous waste, which must be properly disposed of to avoid environmental contamination.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the main difference between a PCB and a PCBA?
The main difference between a PCB and a PCBA is that a PCB is a bare board with no components, while a PCBA is a board that has been populated with components and is ready to be installed in an electronic device. -
What are the steps involved in the PCB manufacturing process?
The PCB manufacturing process involves several steps, including design, printing, etching, drilling, plating, solder masking, and silkscreening. -
What are the steps involved in the PCBA manufacturing process?
The PCBA manufacturing process involves several additional steps beyond those required for PCB manufacturing, including component placement, soldering, inspection, testing, coating, and packaging. -
What are some common applications of PCBs and PCBAs?
PCBs and PCBAs are used in a wide range of applications, including consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and military and defense systems. -
What are some challenges in PCB and PCBA manufacturing?
Some challenges in PCB and PCBA manufacturing include complexity, material constraints, quality control, and environmental concerns.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while PCB and PCBA are often used interchangeably, there is a significant difference between the two. A PCB is a bare board with no components, while a PCBA is a board that has been populated with components and is ready to be installed in an electronic device. Understanding the differences between PCB and PCBA, as well as their manufacturing processes and applications, is crucial for anyone involved in the electronics industry. By overcoming the challenges associated with PCB and PCBA manufacturing, manufacturers can create reliable, cost-effective, and customizable electronic devices that meet the needs of a wide range of industries and applications.





Leave a Reply