Introduction
Electronic manufacturing refers to the process of designing, fabricating, assembling, and testing electronic components and systems. It is a vast global industry encompassing everything from semiconductors and printed circuit boards to finished consumer and industrial products.
This guide will provide an overview of the key sectors that make up the electronics manufacturing landscape. We’ll examine the core technologies, products, and companies across these major segments:
- Semiconductor fabrication
- Passive component manufacturing
- Printed circuit board fabrication
- Electronic contract manufacturing
- Original equipment manufacturing
Understanding these foundational areas provides insight into the complex ecosystem that delivers the electronics enabling modern life. From mobile devices to cars to the internet itself, all rely on firms operating across these manufacturing sectors.
Semiconductor Fabrication
Semiconductor fabrication involves constructing integrated circuits (ICs) onto silicon wafers. This process builds up transistors, interconnects, and other components layer by layer to create complex ICs like microprocessors, memory, and application specific chips.
Some key aspects:
- Utilizes sophisticated fabrication facilities (‘fabs’) with cleanroom environments
- Process steps include oxidation, photolithography, etching, doping, thin film deposition
- Leading companies include Intel, Samsung, TSMC, GlobalFoundries
- Encompasses memory, logic, analog, MEMS devices
- Both mass market and customized ICs for specific applications
Semiconductor fabs require multi-billion dollar investments. The high fixed costs cause consolidation around a handful of companies operating at the leading edge.
Passive Component Manufacturing
Passive components provide basic functions like resistors, capacitors, and inductors rather than active operation. Key aspects:
- Includes resistors, capacitors, inductors, transformers, connectors, wires
- Materials like ceramics, plastics, metals used in fabrication
- High volume manufacturing methods like screen printing
- Provides supporting components for circuit boards
- Major firms include Murata, TDK, Taiyo Yuden, TE Connectivity
While lower complexity than active ICs, high quality passive components are vital for circuit performance. The sector has consolidated as manufacturing of basic discrete devices becomes commoditized.
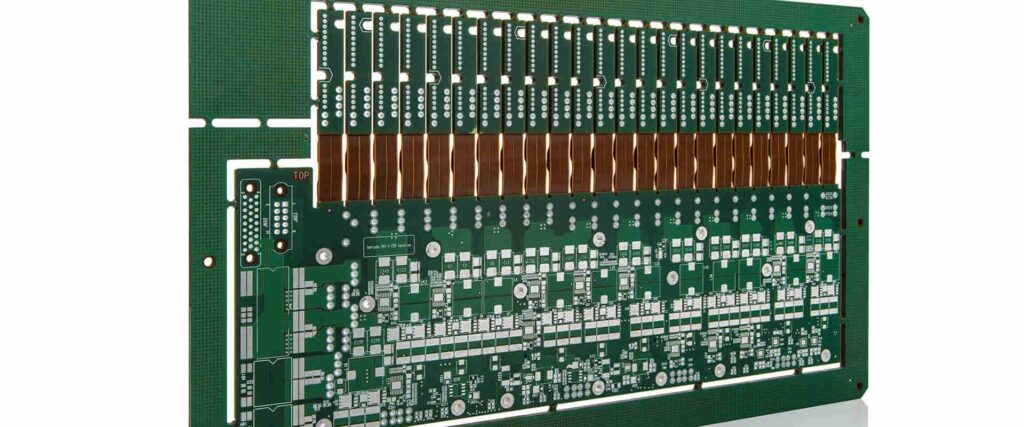
Printed Circuit Board Fabrication
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) form the physical platform onto which ICs, passives, and other components are attached. This sector handles PCB manufacturing:
- PCB fabrication transforms design files into physical boards
- Core capabilities include etching, drilling, plating, solder mask, silkscreen
- Services range from fast prototyping to high volume production
- Leading manufacturers include Ibiden, Tripod, Compeq, Unimicron
- Complexity spans single-sided boards to high density multilayer
PCB fabrication enables creating the interconnect substrates that realize electronic designs. Quality and tolerances are critical for functioning end products.
Electronic Contract Manufacturing
Contract manufacturing provides production and assembly services for electronics companies. Key characteristics:
- Assembles PCBs by soldering components onto boards
- Manages procurement of required components
- Offers turnkey manufacturing services
- Significant labor component for manual assembly
- Leading firms include Foxconn, Flex, Jabil, Sanmina-SCI
- Often clustered around low labor cost regions
By outsourcing production, brands can focus on design and innovation while reducing manufacturing costs. Contract manufacturing enables rapid scaling.
Original Equipment Manufacturing
Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) design and produce finished electronic goods. Important elements:
- Engages in product design, engineering, manufacturing
- Leverages contractors for manufacturing
- Markets and sells products under own brand
- Spans consumer electronics, appliances, automotive, medical, etc
- Leading companies include Samsung, Sony, LG, Bosch
OEMs handle end-to-end delivery of branded electronic goods by coordinating the value chain. They determine product planning and definition.
Relationship Between Sectors
These sectors form a value chain:
- Semiconductor fabs build ICs and die
- Passive component makers fabricate supporting parts
- PCB companies transform designs into circuit boards
- Contract manufacturers assemble boards and systems
- OEMs design and market finished products
This flow from components to finished goods outlines the supply chain that brings electronics to life through specialized companies focused on each layer of value add.
Geographic Breakdown
Geographic clusters have formed around manufacturing expertise:
- Semiconductors – USA, Taiwan, South Korea, Japan
- Passives – Japan, China
- PCB Fabrication – China, Japan, Taiwan, USA
- Contract Manufacturing – China, Taiwan, Southeast Asia
- OEMs – Japan, Korea, USA, China, Europe
This outlines the global distribution, though many companies now operate across multiple geographies.
Industry Trends and Outlook
Key trends shaping electronics manufacturing:
- Consolidation around mega suppliers like Foxconn enables economies of scale
- Automation is reducing labor content and increasing precision
- Growth of electronics content in products supports expansion
- Developing specialized process capabilities wins business
- Leveraging software/IT for design, supply chain agility
The industry continues to evolve, but the core sectors powering electronics manufacturing remain. Gaining expertise within these domains drives success.
Conclusion
This overview covered the major segments composing the electronics manufacturing landscape:
- Semiconductor fabrication producing integrated circuits
- Passive component manufacturing
- PCB fabrication transforming designs into circuit boards
- Contract manufacturing providing assembly services
- OEMs delivering finished electronic products
Each sector focuses on specialized capabilities while linking together to enable complex end products. Understanding this ecosystem helps identify where opportunities exist across the entire value chain.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 5 main segments of electronic manufacturing?
The 5 main segments are semiconductor fabrication, passive component manufacturing, PCB fabrication, electronic contract manufacturing, and original equipment manufacturing.
What are the 4 types of electronic manufacturing?
The 4 major types are semiconductors, passives, electromechanical components, and PCBs. Semiconductors and passives provide active and passive functionality. Electromechanical parts enable physical interface. PCBs interconnect everything.
What are the main manufacturing processes in electronics?
Core electronics manufacturing processes include wafer fabrication for ICs, surface mount technology for PCB assembly, 3D printing, CNC machining, injection molding, sheet metal fabrication, die casting, and extrusion.
What are the key products in electronic manufacturing?
Major electronic products include semiconductors, sensors, PCBs, passive components, displays, memory, batteries, connectors, wiring, power supplies, cases, and much more. The diversity of parts enables complex systems.
What regions lead in electronic manufacturing?
Major regions with focused electronics manufacturing expertise include the United States, China, Japan, Taiwan, South Korea, Singapore, Malaysia, Europe, and India. Different specializations exist across these areas.





Leave a Reply