What is Electrical Phase?
Before we delve into the specifics of single-phase and three-phase systems, let’s first understand what electrical phase means. In simple terms, phase refers to the time-varying nature of alternating current (AC) electricity. AC electricity oscillates between positive and negative values in a sinusoidal pattern, and the phase represents the position of this waveform at any given moment.
The Sinusoidal Waveform
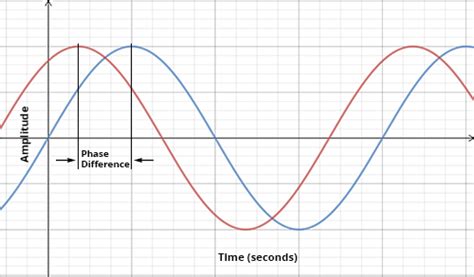
The sinusoidal waveform is a graphical representation of the variation of voltage or current over time in an AC system. It consists of a series of peaks and troughs, with the peaks representing the maximum positive values and the troughs representing the maximum negative values. The distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs is known as the period, and it represents one complete cycle of the waveform.
Phase Angle
The phase angle is a measure of the relative position of the sinusoidal waveform at a specific point in time. It is typically expressed in degrees, with a complete cycle spanning 360 degrees. The phase angle helps determine the timing and synchronization of electrical signals in a system.
Single-Phase Power Systems
Single-phase power systems are the most common type of electrical power supply in residential and small commercial settings. As the name suggests, single-phase systems use a single alternating current to deliver power to the load.
Characteristics of Single-Phase Systems
-
Single Live Wire: In a single-phase system, there is one live wire that carries the alternating current. This wire is typically referred to as the “hot” or “live” wire.
-
Neutral Wire: Along with the live wire, single-phase systems also have a neutral wire. The neutral wire serves as a return path for the current and is connected to the ground at the transformer.
-
Voltage: In most countries, the standard voltage for single-phase systems ranges from 110V to 240V, depending on the specific region and application.
-
Frequency: The frequency of single-phase systems is typically either 50Hz or 60Hz, again varying by country and region.
Applications of Single-Phase Systems
Single-phase power systems are widely used in various applications, including:
-
Residential Homes: Most homes are equipped with single-phase power supply to run household appliances, lighting, and electronics.
-
Small Businesses: Many small commercial establishments, such as offices, shops, and restaurants, rely on single-phase power for their electrical needs.
-
Agricultural Settings: Single-phase power is often used in agricultural settings to operate pumps, lights, and small machinery.
Three-Phase Power Systems
Three-phase power systems are more complex and powerful than single-phase systems. They are commonly used in industrial and commercial settings where high power demand and efficiency are crucial.
Characteristics of Three-Phase Systems
-
Three Live Wires: In a three-phase system, there are three live wires, each carrying an alternating current. These wires are typically referred to as “Phase A,” “Phase B,” and “Phase C.”
-
Neutral Wire: Three-phase systems may or may not include a neutral wire, depending on the specific configuration and grounding requirements.
-
Phase Difference: The key characteristic of three-phase systems is the phase difference between the three live wires. Each phase is separated by 120 degrees, resulting in a balanced and efficient power delivery.
-
Voltage: The voltage in three-phase systems is usually higher than in single-phase systems, typically ranging from 208V to 480V.
-
Frequency: Like single-phase systems, the frequency of three-phase systems is either 50Hz or 60Hz.
Applications of Three-Phase Systems
Three-phase power systems are used in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications, including:
-
Manufacturing Plants: Large manufacturing facilities rely on three-phase power to operate heavy machinery, conveyor systems, and production lines.
-
Data Centers: Three-phase power is essential for powering servers, cooling systems, and backup generators in data centers.
-
Commercial Buildings: Large commercial buildings, such as shopping malls, hospitals, and office complexes, often utilize three-phase power for their electrical infrastructure.
-
Electric Vehicles: Three-phase power is used in charging stations for electric vehicles, enabling faster and more efficient charging.

The Key Differences Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase
Now that we’ve explored the characteristics and applications of single-phase and three-phase systems, let’s summarize the key differences between them:
| Characteristic | Single-Phase | Three-Phase |
|---|---|---|
| Live Wires | One | Three |
| Neutral Wire | Always present | Not always present |
| Phase Difference | N/A | 120 degrees |
| Voltage Range | 110V-240V | 208V-480V |
| Power Delivery | Less efficient | More efficient |
| Load Balancing | Not balanced | Balanced |
| Applications | Residential and small commercial | Industrial and large commercial |
Power Delivery and Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of three-phase systems over single-phase systems is their power delivery and efficiency. In a three-phase system, the power is delivered more consistently and with less fluctuation, resulting in smoother operation of electrical devices. Additionally, three-phase systems can transmit more power over longer distances with less power loss compared to single-phase systems.
Load Balancing
Another key difference between single-phase and three-phase systems is load balancing. In a single-phase system, the load is connected across a single live wire and the neutral wire, which can lead to uneven distribution of power. In contrast, three-phase systems distribute the load evenly across the three live wires, resulting in better load balancing and reduced strain on the electrical components.
FAQ
-
Q: Can I use single-phase appliances in a three-phase system?
A: Yes, you can use single-phase appliances in a three-phase system by connecting them between any one of the live wires and the neutral wire. However, it’s important to ensure that the voltage rating of the appliance matches the voltage of the single phase. -
Q: Can I convert a single-phase system to a three-phase system?
A: Converting a single-phase system to a three-phase system is possible but requires significant modifications to the electrical infrastructure. It involves installing new wiring, transformers, and protective devices. Such conversions should only be carried out by qualified electricians. -
Q: What happens if one phase fails in a three-phase system?
A: If one phase fails in a three-phase system, the remaining two phases will continue to operate, but the overall power capacity will be reduced. This can lead to unbalanced loads and potential damage to electrical equipment. It’s crucial to address phase failures promptly to avoid further issues. -
Q: How do I determine if my building has single-phase or three-phase power?
A: You can determine the type of power supply in your building by inspecting the main electrical panel. Single-phase systems typically have a single live wire and a neutral wire, while three-phase systems have three live wires and may or may not have a neutral wire. If you’re unsure, it’s best to consult a qualified electrician. -
Q: Are there any safety considerations when working with three-phase systems?
A: Yes, working with three-phase systems requires extra caution due to the higher voltages and currents involved. Proper safety measures, such as using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and following lockout/tagout procedures, should be strictly adhered to. Only trained and qualified individuals should work on three-phase systems.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between single-phase and three-phase power systems is essential for anyone working with electrical systems or making decisions about electrical infrastructure. Single-phase systems are simpler and more common in residential and small commercial settings, while three-phase systems offer higher power capacity, efficiency, and load balancing, making them ideal for industrial and large commercial applications.
By grasping the concepts of electrical phase, sinusoidal waveforms, and phase difference, you can make informed choices when designing, installing, or maintaining electrical systems. Always prioritize safety and consult with qualified professionals when working with electrical systems to ensure proper functioning and avoid potential hazards.
As technology advances and electrical demands continue to grow, the importance of understanding single-phase and three-phase power systems will only increase. By staying informed and up-to-date with the latest developments in electrical engineering, you can contribute to the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems in various settings.





Leave a Reply