What is PCB Manufacturing?
PCB manufacturing is the process of creating printed circuit boards that are used to connect electronic components in various devices. The process involves several steps, including design, fabrication, assembly, and testing. The goal is to produce a reliable and functional PCB that meets the specific requirements of the intended application.
Design
The first step in PCB manufacturing is the design phase. This involves creating a schematic diagram and a layout of the circuit board using specialized software. The schematic diagram shows the electrical connections between the components, while the layout shows the physical arrangement of the components on the board. The design must take into account factors such as the size and shape of the board, the number and type of components, and the required functionality.
Fabrication
Once the design is finalized, the next step is fabrication. This involves creating the physical circuit board using a variety of processes, including:
- Printing the circuit pattern onto a copper-clad board using a photoresist and a UV light source
- Etching away the unwanted copper to leave only the desired circuit pattern
- Drilling holes for the components and connectors
- Applying a solder mask to protect the copper traces and prevent short circuits
- Applying a silkscreen to label the components and provide other information
The fabrication process can be done using different methods, such as:
- Subtractive method: This involves removing unwanted copper from a copper-clad board using etching or milling.
- Additive method: This involves adding copper to a non-conductive substrate using electroplating or printing.
- Semi-additive method: This involves a combination of subtractive and additive methods, where a thin layer of copper is added to the substrate and then partially removed to create the desired circuit pattern.
Assembly
After the circuit board is fabricated, the next step is assembly. This involves placing and soldering the electronic components onto the board according to the design specifications. The components can be placed manually or using automated equipment, such as pick-and-place machines. The soldering process can be done using different methods, such as:
- Through-hole soldering: This involves inserting the component leads through holes in the board and soldering them on the opposite side.
- Surface-mount soldering: This involves placing the components directly onto pads on the surface of the board and soldering them in place.
- Mixed technology: This involves a combination of through-hole and surface-mount components on the same board.
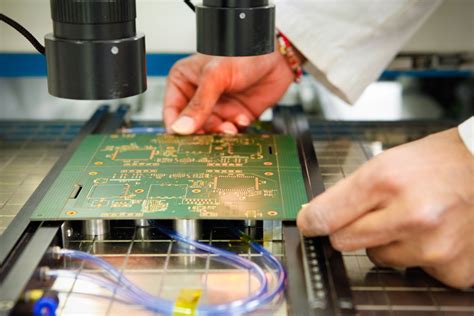
Testing
The final step in PCB manufacturing is testing. This involves verifying that the assembled board functions as intended and meets the required specifications. Testing can be done at various stages of the manufacturing process, including:
- Bare board testing: This involves testing the fabricated board before components are assembled to ensure that there are no defects or short circuits.
- In-circuit testing: This involves testing the assembled board to ensure that each component is functioning correctly and is properly connected.
- Functional testing: This involves testing the complete assembled board to ensure that it performs the intended function and meets the required specifications.
Types of PCBs
There are several types of PCBs that can be manufactured, depending on the specific requirements of the application. Some common types include:
Single-sided PCBs
Single-sided PCBs have conductive traces on only one side of the board. They are the simplest and most cost-effective type of PCB, but they have limited functionality and are not suitable for complex designs.
Double-sided PCBs
Double-sided PCBs have conductive traces on both sides of the board, which allows for more complex designs and higher component density. The two sides are connected using through-holes or vias.
Multi-layer PCBs
Multi-layer PCBs have multiple layers of conductive traces separated by insulating layers. They can have anywhere from four to twenty or more layers, depending on the complexity of the design. Multi-layer PCBs offer the highest level of functionality and density, but they are also the most expensive to manufacture.
Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs are made from flexible materials, such as polyimide or polyester, which allows them to bend and conform to different shapes. They are often used in applications where space is limited or where the board needs to flex during use, such as in wearable devices or aerospace equipment.
Rigid-flex PCBs
Rigid-flex PCBs are a combination of rigid and flexible sections on the same board. The rigid sections provide structural support and stability, while the flexible sections allow for bending and folding. Rigid-flex PCBs are often used in applications where the board needs to fit into a specific shape or where there are space constraints.
PCB Manufacturing Services
PCB manufacturing services are provided by specialized companies that have the expertise, equipment, and resources to produce high-quality PCBs efficiently and cost-effectively. These services can include:
Design services
Many PCB manufacturers offer design services to help customers create the schematic diagram and layout of their circuit board. This can include assistance with component selection, placement, and routing, as well as design for manufacturability (DFM) analysis to ensure that the board can be manufactured efficiently and reliably.
Prototyping services
Prototyping services allow customers to test and validate their design before committing to full-scale production. PCB manufacturers can produce small quantities of boards quickly and cost-effectively, allowing customers to make any necessary changes or improvements before moving to production.
Production services
Production services involve the large-scale manufacturing of PCBs according to the customer’s specifications. PCB manufacturers can produce boards in a variety of quantities, from a few dozen to several thousand or more, depending on the customer’s needs.
Assembly services
Many PCB manufacturers also offer assembly services, which involve placing and soldering the electronic components onto the fabricated board. This can include both through-hole and surface-mount assembly, as well as mixed technology assembly.
Testing services
Testing services ensure that the assembled board functions as intended and meets the required specifications. PCB manufacturers can perform various types of testing, including bare board testing, in-circuit testing, and functional testing, to ensure the quality and reliability of the final product.

Benefits of Using PCB Manufacturing Services
Using PCB manufacturing services offers several benefits for companies and individuals who need to produce circuit boards for their products or projects. Some of the key benefits include:
Expertise and experience
PCB manufacturers have the expertise and experience necessary to produce high-quality circuit boards efficiently and reliably. They have a deep understanding of the various processes and technologies involved in PCB manufacturing, as well as the ability to troubleshoot and solve problems that may arise during production.
Access to advanced equipment and technologies
PCB manufacturers have access to advanced equipment and technologies that may not be available or cost-effective for individual companies to acquire and maintain. This includes specialized software for design and simulation, high-precision fabrication equipment, automated assembly machines, and advanced testing equipment.
Cost-effectiveness
Outsourcing PCB manufacturing to a specialized service provider can be more cost-effective than trying to produce boards in-house, especially for small to medium-sized companies. PCB manufacturers can achieve economies of scale by producing large quantities of boards for multiple customers, which allows them to offer competitive pricing and fast turnaround times.
Quality control
PCB manufacturers have rigorous quality control processes in place to ensure that the boards they produce meet the required specifications and are free from defects. This includes regular inspections and testing at various stages of the manufacturing process, as well as traceability and documentation to ensure that any issues can be quickly identified and resolved.
Flexibility and scalability
PCB manufacturing services offer flexibility and scalability to meet the changing needs of their customers. They can produce boards in a variety of quantities, from small prototypes to large production runs, and can quickly adjust their processes and capacities to accommodate changes in demand or design.
Choosing a PCB Manufacturing Service
When choosing a PCB manufacturing service, there are several factors to consider to ensure that you select a provider that can meet your specific needs and requirements. Some key factors to consider include:
Capabilities and expertise
Look for a PCB manufacturer that has the capabilities and expertise necessary to produce the type of boards you need, whether they are single-sided, double-sided, multi-layer, flexible, or rigid-flex. Make sure they have experience working with the materials, components, and technologies that are relevant to your project.
Quality and reliability
Choose a PCB manufacturer that has a strong reputation for quality and reliability. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, UL, and IPC, which demonstrate a commitment to quality and adherence to industry standards. Ask for references or case studies from previous customers to get a sense of their track record and customer satisfaction.
Turnaround time and delivery
Consider the turnaround time and delivery options offered by the PCB manufacturer. Make sure they can meet your timeline and delivery requirements, whether you need small quantities quickly for prototyping or large volumes for production. Look for manufacturers that offer expedited services or flexible delivery options to accommodate your specific needs.
Pricing and value
Compare pricing and value among different PCB manufacturers to ensure that you are getting a competitive price for the quality and service you require. Keep in mind that the lowest price may not always be the best value, especially if it comes at the expense of quality or reliability. Look for manufacturers that offer transparent pricing and can provide a detailed breakdown of costs.
Customer service and support
Choose a PCB manufacturer that offers excellent customer service and support throughout the entire manufacturing process. Look for manufacturers that have dedicated account managers or support teams that can answer your questions, provide updates on your project status, and help troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
PCB Manufacturing Process
The PCB manufacturing process involves several steps, each of which is critical to ensuring the quality and reliability of the final product. Here is an overview of the typical steps involved in PCB manufacturing:
Design and layout
The first step in PCB manufacturing is to create the schematic diagram and layout of the circuit board using specialized software. This involves selecting and placing the components, routing the connections between them, and ensuring that the board meets the required specifications and standards.
Fabrication
Once the design is finalized, the next step is to fabricate the physical circuit board. This typically involves the following sub-steps:
- Printing the circuit pattern onto a copper-clad board using a photoresist and a UV light source
- Etching away the unwanted copper to leave only the desired circuit pattern
- Drilling holes for the components and connectors
- Applying a solder mask to protect the copper traces and prevent short circuits
- Applying a silkscreen to label the components and provide other information
Assembly
After the circuit board is fabricated, the next step is to assemble the electronic components onto the board. This typically involves the following sub-steps:
- Placing the components onto the board according to the design specifications, either manually or using automated equipment such as pick-and-place machines
- Soldering the components onto the board using either through-hole or surface-mount soldering methods
- Cleaning the board to remove any flux residue or other contaminants
Testing and inspection
Once the board is assembled, it must be tested and inspected to ensure that it functions as intended and meets the required specifications. This typically involves the following sub-steps:
- Bare board testing to ensure that there are no defects or short circuits in the fabricated board
- In-circuit testing to ensure that each component is functioning correctly and is properly connected
- Functional testing to ensure that the complete assembled board performs the intended function and meets the required specifications
- Visual inspection to check for any defects or anomalies in the assembly or soldering
Packing and shipping
After the board has passed all necessary tests and inspections, it is packaged and shipped to the customer according to their specifications. This may involve special packaging or handling requirements to ensure that the boards arrive safely and in good condition.
Common PCB Manufacturing Challenges and Solutions
PCB manufacturing can be a complex and challenging process, with many potential issues that can arise at various stages of production. Here are some common PCB manufacturing challenges and solutions:
Design issues
Design issues can arise when the schematic diagram or layout of the board is not optimized for manufacturability or does not meet the required specifications. Some common design issues include:
- Incorrect component placement or orientation
- Insufficient clearance between components or traces
- Incorrect hole sizes or locations
- Incompatible materials or finishes
To avoid design issues, it is important to work closely with the PCB manufacturer during the design phase to ensure that the board is optimized for manufacturability and meets all necessary specifications. Many PCB manufacturers offer design services or design for manufacturability (DFM) analysis to help identify and correct potential issues before production begins.
Fabrication issues
Fabrication issues can arise during the physical manufacturing of the circuit board, such as:
- Incorrect etching or drilling
- Contamination or defects in the copper or insulating layers
- Incorrect solder mask or silkscreen application
- Warping or delamination of the board
To avoid fabrication issues, PCB manufacturers must maintain strict process controls and quality assurance procedures. This includes regular maintenance and calibration of equipment, use of high-quality materials and chemicals, and thorough inspection and testing at various stages of production.
Assembly issues
Assembly issues can arise during the placement and soldering of components onto the board, such as:
- Incorrect component placement or orientation
- Insufficient or excessive solder
- Bridging or short circuits between components or traces
- Damage to components or the board during handling or soldering
To avoid assembly issues, PCB manufacturers must use appropriate equipment and techniques for the specific type of components and soldering method being used. This may include automated pick-and-place machines, specialized soldering equipment, and proper handling and storage procedures.
Testing and inspection issues
Testing and inspection issues can arise when the assembled board does not function as intended or does not meet the required specifications. Some common testing and inspection issues include:
- False positive or false negative test results
- Inadequate or incomplete testing coverage
- Missed or overlooked defects or anomalies
- Inconsistent or unreliable test equipment or methods
To avoid testing and inspection issues, PCB manufacturers must use appropriate and reliable test equipment and methods for the specific type of board and components being tested. This may include automated test equipment (ATE), flying probe testers, X-ray inspection, or other specialized tools and techniques.
Supply chain issues
Supply chain issues can arise when there are disruptions or delays in the availability of materials, components, or equipment needed for PCB manufacturing. Some common supply chain issues include:
- Shortages or delays in the supply of raw materials such as copper, laminates, or chemicals
- Obsolescence or discontinuation of specific components or technologies
- Shipping or logistics delays or disruptions
- Quality or compatibility issues with third-party suppliers or vendors
To avoid supply chain issues, PCB manufacturers must maintain strong relationships with reliable suppliers and vendors, and have contingency plans in place for potential disruptions or delays. This may include maintaining adequate inventory levels, diversifying suppliers, or establishing backup or alternative sourcing options.
Future Trends in PCB Manufacturing
PCB manufacturing is a constantly evolving field, with new technologies and trends emerging all the time. Here are some of the key trends and developments that are shaping the future of PCB manufacturing:
Miniaturization and increased density
As electronic devices continue to get smaller and more complex, there is a growing demand for PCBs with higher component density and smaller feature sizes. This is driving the development of new materials, processes, and technologies for PCB manufacturing, such as:
- High-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs with microvias and fine pitch components
- Embedded components and 3D packaging technologies
- Advanced materials such as high-frequency laminates and low-loss dielectrics
Automation and digitalization
PCB manufacturing is increasingly relying on automation and digitalization to improve efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. This includes the use of:
- Automated design and simulation tools for optimizing board layout and performance
- Automated equipment for fabrication, assembly, and testing, such as robotic pick-and-place machines and flying probe testers
- Digital twin technologies for real-time monitoring and optimization of production processes
- Cloud-based platforms for data management, traceability, and collaboration
Sustainability and environmental responsibility
There is growing awareness of the environmental impact of PCB manufacturing, and a push towards more sustainable and responsible practices. This includes:
- Use of renewable energy sources and energy-efficient equipment
- Reduction of waste and emissions through process optimization and material recycling
- Adoption of green chemistry principles and elimination of hazardous substances
- Design for sustainability and circular economy, such as design for disassembly and recyclability
Advanced materials and technologies
PCB manufacturing is benefiting from the development of new materials and technologies that offer improved performance, reliability, and functionality. Some examples include:
- Flexible and stretchable electronics for wearables and IoT applications
- High-speed and high-frequency materials for 5G and millimeter-wave applications
- Additive manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing and inkjet printing for rapid prototyping and customization
- Graphene and other nanomaterials for enhanced electrical and thermal properties
FAQ
What is the typical turnaround time for PCB manufacturing?
The turnaround time for PCB manufacturing can vary depending on the complexity of the design, the quantity of boards required, and the specific manufacturing processes and services needed. Typical turnaround times can range from a few days for simple prototypes to several weeks for large production runs. Many PCB manufacturers offer expedited services for faster turnaround times, but this may come at an additional cost.
What are the most common PCB materials and finishes?
The most common PCB materials are FR-4, a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate, and polyimide, a flexible and high-temperature resistant material. Other common materials include ceramic, metal-core, and high-frequency laminates. The most common PCB finishes are





Leave a Reply