ALL ABOUT FLEX PCB
-
What is a PCB?
Posted by
–
 Read more: What is a PCB?
Read more: What is a PCB?Introduction A printed circuit board (PCB) is a thin board made of fiberglass or other insulating materials that houses the components and interconnects of an electronic circuit. PCBs provide the mechanical structure to mount and electronically connect electronic components using conductive pathways or traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto […]
-
9 Must-Knows for Your Flex PCB Design
Posted by
–
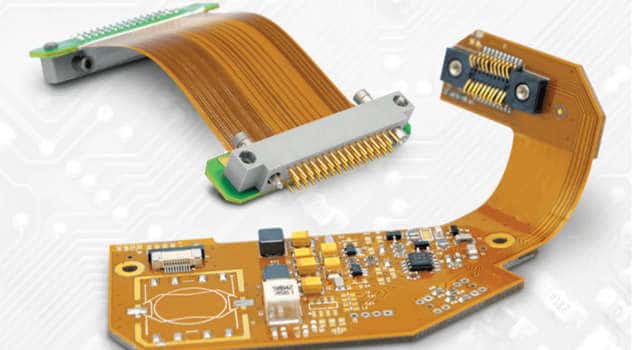
 Read more: 9 Must-Knows for Your Flex PCB Design
Read more: 9 Must-Knows for Your Flex PCB DesignFlexible printed circuit boards (flex PCBs) offer many advantages over traditional rigid PCBs. They can bend and flex to fit into tight spaces, move dynamically in products, and improve reliability in high-vibration environments. However, flex PCBs require some unique design considerations. Follow these key tips when creating your flex PCB […]
-
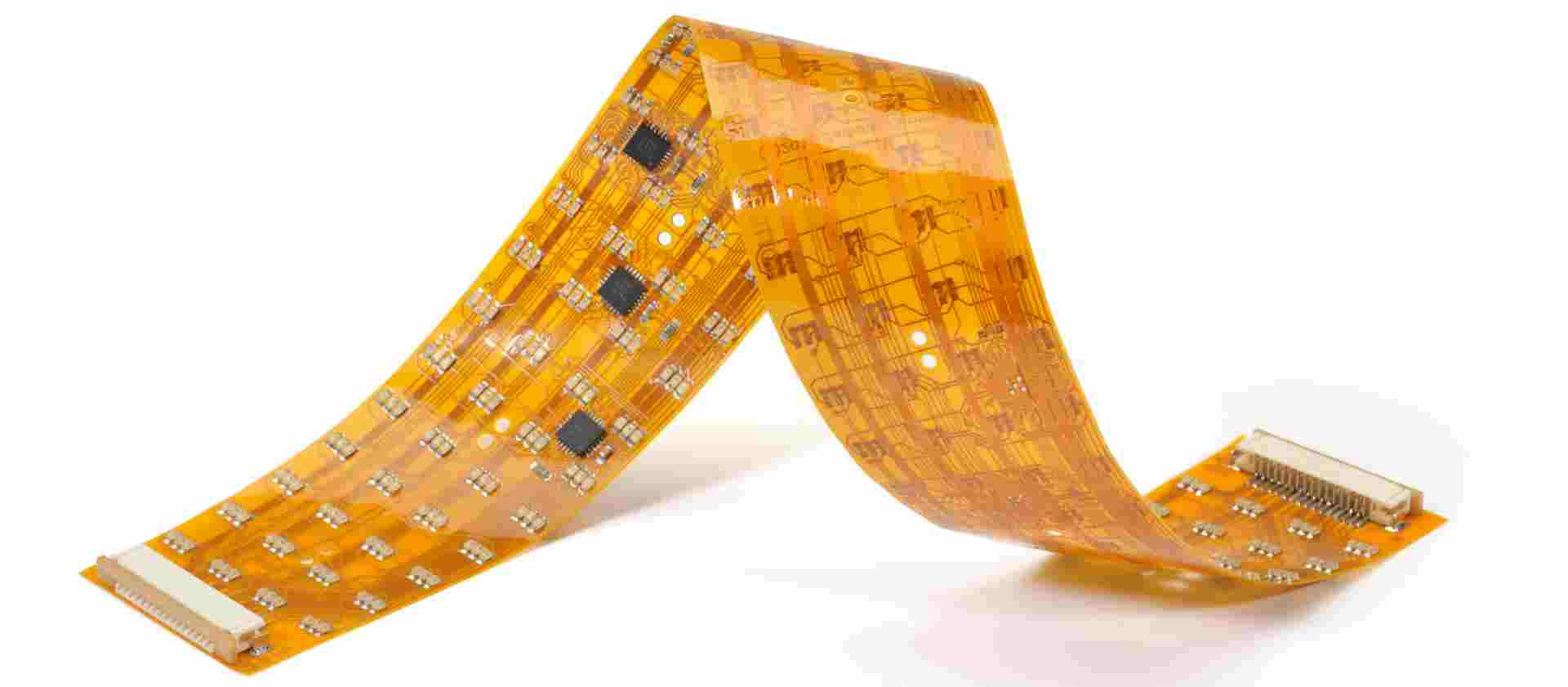
 Read more: An Overview of Flex Circuit Materials and Layer Stacks
Read more: An Overview of Flex Circuit Materials and Layer StacksIntroduction Flexible printed circuits, also known as flex circuits, are made from flexible polymer substrates that allow them to bend and flex. They are commonly used in electronics applications where flexibility is required, like wearables, medical devices, automotive electronics, and consumer electronics. The materials and layer stack-up used in a […]
-
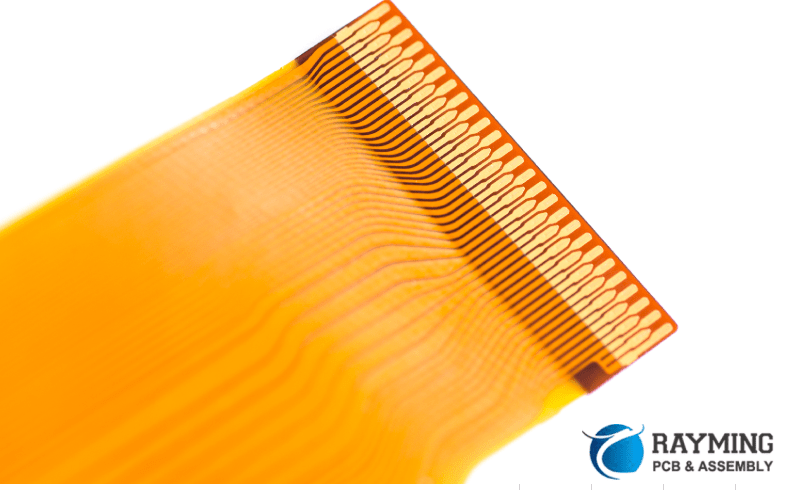
 Read more: Stack-up Design and Analysis for Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs)
Read more: Stack-up Design and Analysis for Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs)Introduction Flexible printed circuits (FPCs) are widely used in modern electronics due to their ability to bend and flex to fit constrained spaces. Proper stack-up design and analysis is critical for FPCs to ensure reliable performance under bending and dynamic stress. This article provides an overview of key considerations and […]
-
How thick is a 6 layer PCB Stackup?
Posted by
–
 Read more: How thick is a 6 layer PCB Stackup?
Read more: How thick is a 6 layer PCB Stackup?Introduction Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are essential components in nearly all modern electronics. As electronic devices become more complex and packed with features, PCBs must increase in layer count to accommodate all the necessary interconnections and circuitry. One of the most common high layer count PCBs is the 6 layer […]
-
What is the common 2 layer PCB Stackup?
Posted by
–
 Read more: What is the common 2 layer PCB Stackup?
Read more: What is the common 2 layer PCB Stackup?Introduction A printed circuit board (PCB) is the core component of most electronic devices. It provides the mechanical structure and electrical connections between components. The way the layers in a PCB are stacked up is referred to as the PCB stackup. For simple and cost-effective boards, a 2 layer stackup […]
-
How do I choose a PCB Stackup?
Posted by
–
 Read more: How do I choose a PCB Stackup?
Read more: How do I choose a PCB Stackup?Choosing the right printed circuit board (PCB) stackup is critical for ensuring your PCB design meets your electrical, thermal, and mechanical requirements. The stackup refers to the sequence and thicknesses of the conductive copper and insulating dielectric layers in your PCB. Selecting an optimal stackup requires balancing many factors like […]
-
What is PCB layer Stackup?
Posted by
–
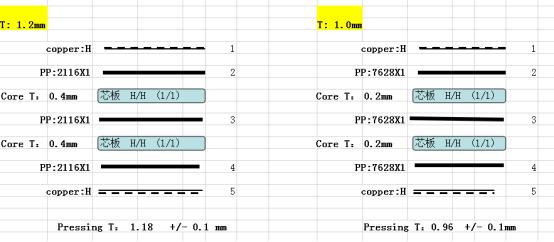 Read more: What is PCB layer Stackup?
Read more: What is PCB layer Stackup?Introduction A printed circuit board (PCB) is made up of layers of conductive and insulating materials stacked on top of each other. The sequence and thickness of these layers is referred to as the PCB layer stackup. The layer stackup defines the electrical, mechanical, and thermal characteristics of the PCB. […]
-
What is rigid flex PCB Stackup?
Posted by
–
 Read more: What is rigid flex PCB Stackup?
Read more: What is rigid flex PCB Stackup?Introduction Rigid-flex printed circuit boards (PCBs) combine rigid and flexible circuitry into a single integrated assembly. They provide solutions for applications where flexible and dynamic interconnections are required between multiple rigid PCBs. Rigid-flex PCBs allow three-dimensional wiring to interconnect rigid PCBs and components. This enables more efficient use of space […]
-
What is the adhesive in Flex PCB?
Posted by
–
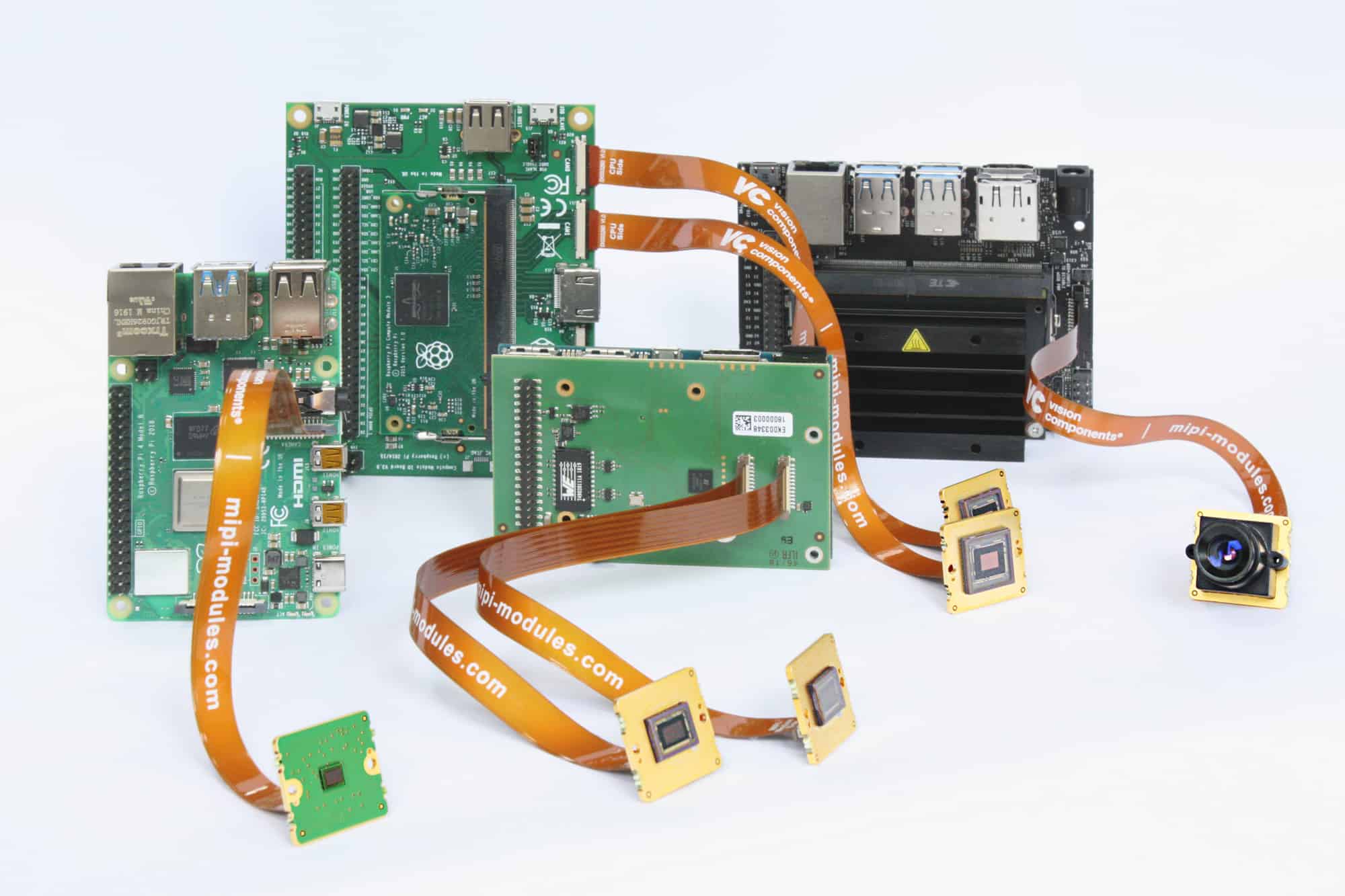 Read more: What is the adhesive in Flex PCB?
Read more: What is the adhesive in Flex PCB?Introduction A flexible printed circuit board (Flex PCB) is a type of printed circuit board that is thin, bendable and flexible. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, flex PCBs can be bent, folded and shaped to fit into tight or moving spaces in electronic devices. One of the key components that allows […]




