ALL ABOUT FLEX PCB
-
What is track width (TW)?
Posted by
–
 Read more: What is track width (TW)?
Read more: What is track width (TW)?Importance of Track width The track width of a vehicle has a significant impact on its handling and stability. A wider track width generally provides better stability and handling, especially during cornering and high-speed maneuvers. This is because a wider track width reduces the vehicle’s tendency to roll and increases […]
-
The Optimum PCB Design Flow – Right First Time
Posted by
–
 Read more: The Optimum PCB Design Flow – Right First Time
Read more: The Optimum PCB Design Flow – Right First TimeIntroduction Designing a printed circuit board (PCB) can be a complex and time-consuming process, with many steps and potential pitfalls along the way. Getting the PCB design right the first time is critical to avoid costly redesigns, manufacturing delays, and product failures. In this article, we’ll explore the optimum PCB […]
-
FR4 Quality – What to Expect
Posted by
–
 Read more: FR4 Quality – What to Expect
Read more: FR4 Quality – What to ExpectWhat is FR4? FR4 is a composite material made from woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with an epoxy resin binder. The “FR” stands for “Flame Retardant,” indicating that the material has been treated to resist catching fire and spreading flames. The “4” in FR4 refers to the specific grade of the […]
-
What is a Peelable Soldermask?
Posted by
–
 Read more: What is a Peelable Soldermask?
Read more: What is a Peelable Soldermask?Introduction to Peelable Soldermask A peelable soldermask, also known as a temporary soldermask or removable soldermask, is a protective coating applied to printed circuit boards (PCBs) during the manufacturing process. This special type of soldermask is designed to be easily removed from specific areas of the PCB when needed, allowing […]
-
 Read more: How does the parameter temperature correction work?
Read more: How does the parameter temperature correction work?What is temperature correction? Temperature correction is a method used to compensate for the influence of temperature variations on the measurement of a parameter. It involves adjusting the measured value of a parameter to account for the deviation caused by temperature changes. By applying temperature correction, the true value of […]
-
cEDM – Electronics Design & Manufacturing
Posted by
–
 Read more: cEDM – Electronics Design & Manufacturing
Read more: cEDM – Electronics Design & ManufacturingIntroduction to cEDM cEDM, or Collaborative Electronic Design and Manufacturing, is a groundbreaking approach that combines the power of collaborative design with the efficiency of modern manufacturing techniques. This innovative methodology is transforming the way electronics are designed and produced, enabling companies to bring their products to market faster, more […]
-
Review – Standard and Predefined Build-ups
Posted by
–
 Read more: Review – Standard and Predefined Build-ups
Read more: Review – Standard and Predefined Build-upsWhat are Build-ups? Build-ups, in the context of construction and engineering, refer to the process of gradually increasing the complexity or size of a structure or system. This approach is commonly used in various fields, such as software development, manufacturing, and project management. The main purpose of build-ups is to […]
-
Cross Sections – What is their Purpose ?
Posted by
–
 Read more: Cross Sections – What is their Purpose ?
Read more: Cross Sections – What is their Purpose ?What are Cross Sections? A cross section is a view of an object as if it had been sliced through to reveal its internal structure. Imagine cutting a loaf of bread in half and looking at the exposed surface – this is essentially a cross section. Cross sections can be […]
-
 Read more: EAGLE and DesignLink – Valuable information about components
Read more: EAGLE and DesignLink – Valuable information about componentsWhat is EAGLE? EAGLE (Easily Applicable Graphical Layout Editor) is a powerful PCB (Printed Circuit Board) design software developed by Autodesk. It is widely used by electronic designers, engineers, and hobbyists to create high-quality PCB layouts for various applications. EAGLE offers a user-friendly interface, extensive component libraries, and a wide […]
-
What is the Delivery Term?
Posted by
–
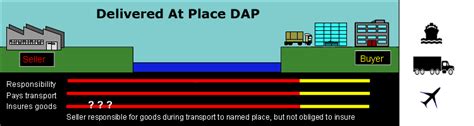 Read more: What is the Delivery Term?
Read more: What is the Delivery Term?Types of Delivery Terms There are two primary sets of delivery terms used in international trade: Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) Terms Incoterms Incoterms, developed by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC), are a set of predefined commercial terms widely used in international trade contracts. They define […]




