Introduction to Piezo and Magnetic Buzzers
Buzzers are small but essential components in many electronic devices, providing audible feedback, alerts, and notifications. Two common types of buzzers are piezo buzzers and magnetic buzzers. Both convert electrical energy into sound, but they differ in their operating principles, characteristics, and applications. Understanding the differences between piezo and magnetic buzzers can help you choose the right type for your specific needs.
What is a Piezo Buzzer?
A piezo buzzer, also known as a piezoelectric buzzer, uses the piezoelectric effect to generate sound. It consists of a piezoelectric element, usually a ceramic disc, that vibrates when an alternating current is applied. The vibrations create pressure waves in the air, which we perceive as sound.
Piezo buzzers are compact, lightweight, and have a simple construction. They typically produce high-frequency sounds and have a wide operating voltage range. Piezo buzzers are commonly used in devices such as alarm systems, timers, and electronic toys.
What is a Magnetic Buzzer?
A magnetic buzzer, also called an electromagnetic buzzer, generates sound using the principle of electromagnetism. It consists of a coil of wire wound around a magnetic core, with a flexible diaphragm attached. When an alternating current passes through the coil, it creates a magnetic field that attracts and repels the diaphragm, causing it to vibrate and produce sound.
Magnetic buzzers are generally larger and heavier than piezo buzzers. They produce lower-frequency sounds and have a narrower operating voltage range. Magnetic buzzers are often used in applications that require louder and deeper tones, such as industrial alarms, automotive horns, and large appliances.
Comparing Piezo and Magnetic Buzzers
To better understand the differences between piezo and magnetic buzzers, let’s compare their key characteristics:
Operating Principle
| Buzzer Type | Operating Principle |
|---|---|
| Piezo | Piezoelectric effect: vibration of a piezoelectric element |
| Magnetic | Electromagnetism: vibration of a diaphragm due to a magnetic field |
Sound Characteristics
| Buzzer Type | Frequency Range | Sound Pressure Level (SPL) | Tone Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piezo | High (1-20 kHz) | Moderate (70-90 dB) | Clear, sharp |
| Magnetic | Low (100-5 kHz) | High (80-100 dB) | Loud, deep |
Physical Properties
| Buzzer Type | Size | Weight | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piezo | Compact | Lightweight | High |
| Magnetic | Larger | Heavier | Moderate |
Electrical Characteristics
| Buzzer Type | Operating Voltage Range | Current Consumption |
|---|---|---|
| Piezo | Wide (3-30V) | Low (1-10 mA) |
| Magnetic | Narrow (1.5-12V) | High (10-100 mA) |
Cost and Availability
Both piezo and magnetic buzzers are relatively inexpensive and widely available. However, piezo buzzers are generally cheaper due to their simpler construction and more abundant raw materials.
Applications of Piezo and Magnetic Buzzers
Piezo Buzzer Applications
- Alarm systems (smoke detectors, security systems)
- Timers and clocks
- Electronic toys and games
- Medical devices (insulin pumps, heart rate monitors)
- Home appliances (microwaves, washing machines)
- Automotive electronics (parking sensors, seatbelt reminders)
Magnetic Buzzer Applications
- Industrial alarms and sirens
- Automotive horns and backup alarms
- Large appliances (refrigerators, dishwashers)
- Fire alarms and emergency notification systems
- Public address systems
- Musical instruments (electronic drums, synthesizers)

Choosing Between Piezo and Magnetic Buzzers
When selecting a buzzer for your application, consider the following factors:
-
Sound requirements: If you need high-frequency, clear tones, a piezo buzzer may be the better choice. For louder, lower-frequency sounds, a magnetic buzzer is more suitable.
-
Size and weight constraints: Piezo buzzers are more compact and lightweight, making them ideal for portable and space-constrained devices. Magnetic buzzers are larger and heavier, but can be used when size and weight are less critical.
-
Power consumption: Piezo buzzers have lower current consumption, making them more energy-efficient and suitable for battery-powered devices. Magnetic buzzers require more power but can produce louder sounds.
-
Durability: Piezo buzzers are generally more durable and have a longer lifespan due to their simple construction. Magnetic buzzers have moving parts that may wear out over time, but they can still provide reliable performance in most applications.
-
Cost: Both types of buzzers are affordable, but piezo buzzers are typically cheaper. However, the cost difference may be negligible in the context of the overall device cost.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Can piezo and magnetic buzzers be used interchangeably?
In some cases, yes, but it depends on the specific requirements of your application. Consider the sound characteristics, size, power consumption, and durability when making a decision. -
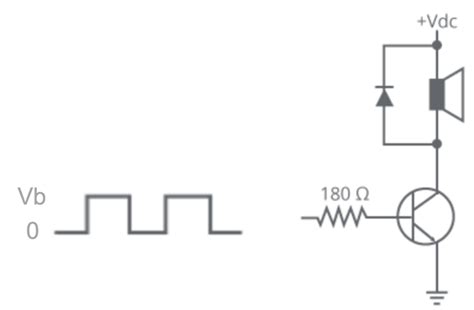
How do I drive a piezo or magnetic buzzer?
Piezo buzzers can be driven directly by an AC voltage or a square wave signal from a microcontroller. Magnetic buzzers require a driver circuit, such as a transistor or an IC, to control the current through the coil. -
What is the lifespan of a piezo or magnetic buzzer?
Piezo buzzers typically have a longer lifespan, often exceeding 1000 hours of continuous use. Magnetic buzzers have a shorter lifespan due to the wear of moving parts, but they can still last for several hundred hours under normal operating conditions. -
Can I adjust the volume of a piezo or magnetic buzzer?
Yes, the volume can be adjusted by varying the driving voltage or pulse width. However, keep in mind that operating the buzzer outside its specified voltage range may damage the component or affect its performance. -
Are there any environmental factors to consider when using piezo or magnetic buzzers?
Both types of buzzers can be affected by extreme temperatures, humidity, and vibrations. Ensure that the buzzer is rated for the intended operating environment and consider protective measures such as enclosures or conformal coatings if necessary.
Conclusion
Piezo and magnetic buzzers are essential components in many electronic devices, providing audible feedback and alerts. While both types of buzzers serve similar purposes, they differ in their operating principles, sound characteristics, physical properties, and electrical requirements.
Piezo buzzers are compact, lightweight, and energy-efficient, making them suitable for portable and battery-powered devices. They produce high-frequency, clear tones and are commonly used in alarms, timers, and electronic toys. Magnetic buzzers, on the other hand, are larger and consume more power but can generate louder, lower-frequency sounds. They are often used in industrial alarms, automotive applications, and large appliances.
When choosing between piezo and magnetic buzzers, consider your application’s specific requirements, such as desired sound characteristics, size constraints, power consumption, and durability. Both types of buzzers are affordable and widely available, making them accessible for a wide range of projects and products.
By understanding the differences between piezo and magnetic buzzers, you can make an informed decision and select the most suitable type for your application, ensuring reliable and high-quality sound output while keeping costs low.





Leave a Reply