Introduction to Transistor Projects
Transistors are the building blocks of modern electronics. These tiny devices have revolutionized the world of technology, enabling the creation of countless electronic devices that we use every day. For beginners in electronics, understanding how transistors work and how to use them in projects can be a exciting and rewarding experience.
In this article, we will explore 10 amazing transistor projects circuits that are perfect for beginners. These projects range from simple LED circuits to more complex audio amplifiers and will help you gain a deeper understanding of how transistors work and how to use them in your own projects.
What are Transistors?
Before we dive into the projects, let’s take a moment to understand what transistors are and how they work.
A transistor is a semiconductor device that consists of three layers of material: an emitter, a base, and a collector. When a small current is applied to the base, it allows a much larger current to flow between the emitter and the collector. This ability to amplify current makes transistors an essential component in many electronic circuits.
There are two main types of transistors: bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs). BJTs are the most common type and are used in many of the projects we will be exploring in this article.
Tools and Materials Needed for Transistor Projects
Before you start building your transistor projects, you will need a few basic tools and materials. Here’s a list of what you’ll need:
- Breadboard
- Jumper wires
- Resistors (various values)
- Capacitors (various values)
- Light-emitting diodes (LEDs)
- Transistors (BJTs and FETs)
- Multimeter
- Power supply (battery or DC power supply)
With these tools and materials, you’ll be ready to start building your transistor projects.

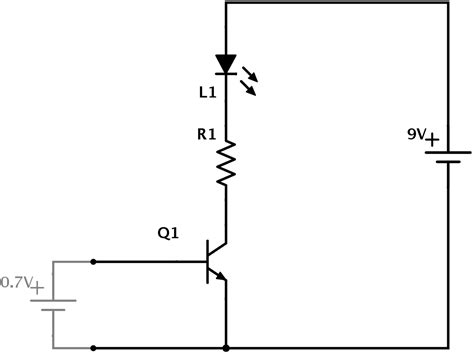
Project 1: Simple LED Circuit
The first project on our list is a simple LED circuit. This project is a great way to get started with transistors and learn how they can be used to control the flow of current in a circuit.
Materials Needed
- 1 x NPN transistor (e.g., 2N2222)
- 1 x LED
- 1 x 1k resistor
- 1 x 10k resistor
- Jumper wires
- Breadboard
Circuit Diagram
+-----+
| |
| |
| |
/ \ |
LED --| |-- 1k
\ / |
| |
| |
| |
+-----+
|
|
|
10k
|
|
|
GND
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Place the NPN transistor on the breadboard.
- Connect the collector of the transistor to the positive rail of the breadboard.
- Connect the emitter of the transistor to one end of the 1k resistor.
- Connect the other end of the 1k resistor to the anode (long leg) of the LED.
- Connect the cathode (short leg) of the LED to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Connect one end of the 10k resistor to the base of the transistor.
- Connect the other end of the 10k resistor to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Apply power to the circuit by connecting the positive and negative rails of the breadboard to your power supply.
When you apply power to the circuit, the LED should light up. This is because the 10k resistor is pulling the base of the transistor low, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter and through the LED.
Project 2: Transistor Switch
The next project on our list is a transistor switch. This project demonstrates how transistors can be used to switch current on and off in a circuit.
Materials Needed
- 1 x NPN transistor (e.g., 2N2222)
- 1 x LED
- 1 x 1k resistor
- 1 x 10k resistor
- 1 x pushbutton switch
- Jumper wires
- Breadboard
Circuit Diagram
+-----+
| |
| |
| |
/ \ |
LED --| |-- 1k
\ / |
| |
| |
| |
+-----+
|
|
|
10k
|
|
|
switch
|
|
|
GND
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Place the NPN transistor on the breadboard.
- Connect the collector of the transistor to the positive rail of the breadboard.
- Connect the emitter of the transistor to one end of the 1k resistor.
- Connect the other end of the 1k resistor to the anode (long leg) of the LED.
- Connect the cathode (short leg) of the LED to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Connect one end of the 10k resistor to the base of the transistor.
- Connect the other end of the 10k resistor to one pin of the pushbutton switch.
- Connect the other pin of the pushbutton switch to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Apply power to the circuit by connecting the positive and negative rails of the breadboard to your power supply.
When you press the pushbutton switch, the LED should turn on. This is because pressing the switch pulls the base of the transistor high, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter and through the LED.
Project 3: Adjustable LED Brightness
The third project on our list is an adjustable LED brightness circuit. This project demonstrates how transistors can be used to control the brightness of an LED by adjusting the current flowing through it.
Materials Needed
- 1 x NPN transistor (e.g., 2N2222)
- 1 x LED
- 1 x 1k resistor
- 1 x 10k potentiometer
- Jumper wires
- Breadboard
Circuit Diagram
+-----+
| |
| |
| |
/ \ |
LED --| |-- 1k
\ / |
| |
| |
| |
+-----+
|
|
|
pot
|
|
|
GND
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Place the NPN transistor on the breadboard.
- Connect the collector of the transistor to the positive rail of the breadboard.
- Connect the emitter of the transistor to one end of the 1k resistor.
- Connect the other end of the 1k resistor to the anode (long leg) of the LED.
- Connect the cathode (short leg) of the LED to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Connect the middle pin of the potentiometer to the base of the transistor.
- Connect one of the outer pins of the potentiometer to the positive rail of the breadboard.
- Connect the other outer pin of the potentiometer to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Apply power to the circuit by connecting the positive and negative rails of the breadboard to your power supply.
When you turn the potentiometer, you should see the brightness of the LED change. This is because the potentiometer is adjusting the voltage applied to the base of the transistor, which in turn controls the current flowing through the LED.
Project 4: Transistor Amplifier
The fourth project on our list is a transistor amplifier. This project demonstrates how transistors can be used to amplify small signals, such as audio signals from a microphone.
Materials Needed
- 1 x NPN transistor (e.g., 2N2222)
- 1 x Electret Microphone
- 1 x 10k resistor
- 1 x 100k resistor
- 1 x 100uF capacitor
- 1 x 8-ohm speaker
- Jumper wires
- Breadboard
Circuit Diagram
+-----+
| |
| |
| |
/ \ |
mic -----+---| |-- 10k
| \ / |
| | |
100uF | |
| | |
GND +-----+
|
|
|
100k
|
|
|
speaker
|
|
|
GND
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Place the NPN transistor on the breadboard.
- Connect the collector of the transistor to one end of the 10k resistor.
- Connect the other end of the 10k resistor to the positive rail of the breadboard.
- Connect the emitter of the transistor to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Connect one lead of the electret microphone to the base of the transistor.
- Connect the other lead of the electret microphone to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Connect the positive lead of the 100uF capacitor to the base of the transistor.
- Connect the negative lead of the 100uF capacitor to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Connect one end of the 100k resistor to the collector of the transistor.
- Connect the other end of the 100k resistor to one lead of the speaker.
- Connect the other lead of the speaker to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Apply power to the circuit by connecting the positive and negative rails of the breadboard to your power supply.
When you speak into the microphone, you should hear your voice amplified through the speaker. This is because the transistor is amplifying the small audio signal from the microphone and driving the speaker.
Project 5: Transistor Oscillator
The fifth project on our list is a transistor oscillator. This project demonstrates how transistors can be used to generate periodic waveforms, such as square waves or sine waves.
Materials Needed
- 1 x NPN transistor (e.g., 2N2222)
- 1 x 1k resistor
- 1 x 10k resistor
- 1 x 100nF capacitor
- 1 x 8-ohm speaker
- Jumper wires
- Breadboard
Circuit Diagram
+-----+
| |
| |
| |
/ \ |
spkr --| |-- 1k
\ / |
| |
| |
| |
+-----+
|
|
|
10k
|
|
--- 100nF
|
|
GND
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Place the NPN transistor on the breadboard.
- Connect the collector of the transistor to one end of the 1k resistor.
- Connect the other end of the 1k resistor to one lead of the speaker.
- Connect the other lead of the speaker to the positive rail of the breadboard.
- Connect the emitter of the transistor to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Connect one end of the 10k resistor to the base of the transistor.
- Connect the other end of the 10k resistor to one lead of the 100nF capacitor.
- Connect the other lead of the 100nF capacitor to the collector of the transistor.
- Apply power to the circuit by connecting the positive and negative rails of the breadboard to your power supply.
When you apply power to the circuit, you should hear a tone coming from the speaker. This is because the transistor is oscillating and generating a periodic waveform that is driving the speaker.
Project 6: Transistor Timer
The sixth project on our list is a transistor timer. This project demonstrates how transistors can be used to create a timed delay in a circuit.
Materials Needed
- 1 x NPN transistor (e.g., 2N2222)
- 1 x LED
- 1 x 1k resistor
- 1 x 10k resistor
- 1 x 100uF capacitor
- Jumper wires
- Breadboard
Circuit Diagram
+-----+
| |
| |
| |
/ \ |
LED --| |-- 1k
\ / |
| |
| |
| |
+-----+
|
|
|
10k
|
|
--- 100uF
|
|
GND
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Place the NPN transistor on the breadboard.
- Connect the collector of the transistor to the positive rail of the breadboard.
- Connect the emitter of the transistor to one end of the 1k resistor.
- Connect the other end of the 1k resistor to the anode (long leg) of the LED.
- Connect the cathode (short leg) of the LED to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Connect one end of the 10k resistor to the base of the transistor.
- Connect the other end of the 10k resistor to the positive lead of the 100uF capacitor.
- Connect the negative lead of the 100uF capacitor to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Apply power to the circuit by connecting the positive and negative rails of the breadboard to your power supply.
When you apply power to the circuit, the LED should turn on for a short period of time and then turn off. This is because the capacitor is charging through the 10k resistor, and when it reaches a certain voltage, it turns on the transistor, which allows current to flow through the LED. Once the capacitor is fully charged, the transistor turns off, and the LED turns off.
Project 7: Transistor Latch
The seventh project on our list is a transistor latch. This project demonstrates how transistors can be used to create a simple memory circuit that can store a binary value.
Materials Needed
- 2 x NPN transistors (e.g., 2N2222)
- 2 x 1k resistors
- 2 x 10k resistors
- 2 x LEDs
- 2 x pushbutton switches
- Jumper wires
- Breadboard
Circuit Diagram
+-----+ +-----+
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
/ \ 1k / \ 1k
LED1 --| |--+--+--| |--+--+-- LED2
\ / | | \ / | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
+----+ | +----+ |
| | | |
| 10k | 10k
| | | |
sw1 | sw2 |
| | | |
| | | |
GND GND GND GND
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Place the two NPN transistors on the breadboard.
- Connect the collector of the first transistor to one end of a 1k resistor.
- Connect the other end of the 1k resistor to the anode (long leg) of the first LED.
- Connect the cathode (short leg) of the first LED to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Connect the emitter of the first transistor to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Repeat steps 2-5 for the second transistor and LED.
- Connect one end of a 10k resistor to the base of the first transistor.
- Connect the other end of the 10k resistor to one pin of the first pushbutton switch.
- Connect the other pin of the first pushbutton switch to the negative rail of the breadboard.
- Repeat steps 7-9 for the second transistor and pushbutton switch.
- Connect the collector of the first transistor to the base of the second transistor.
- Connect the collector of the second transistor to the base of the first transistor.
- Apply power to the circuit by connecting the positive and negative rails of the breadboard to your power supply.
When you press one of the pushbutton switches, the corresponding LED should turn on and stay on, even after you release the switch. This is because the transistors are latched in a stable state, with one transistor turned on an





Leave a Reply