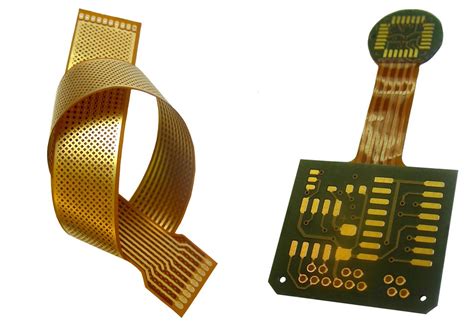
What is a Flex PCB?
A Flex PCB, or Flexible Printed Circuit Board, is a type of printed circuit board that is designed to be flexible and bendable. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, Flex PCBs can conform to various shapes and angles, making them ideal for applications where space is limited or where the PCB needs to fit into a specific form factor.
Flex PCBs are made by printing conductive traces on a flexible substrate material, such as polyimide or polyester. The substrate is then covered with a protective layer, such as a coverlay or soldermask, to protect the traces from damage and environmental factors.
Advantages of Flex PCBs
Flex PCBs offer several advantages over traditional rigid PCBs, including:
Space Savings
Flex PCBs can be bent and folded to fit into tight spaces, making them ideal for applications where space is at a premium. This is particularly useful in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, where every millimeter counts.
Increased Reliability
Flex PCBs are more resistant to vibration and shock than rigid PCBs, making them more reliable in harsh environments. This is because the flexible substrate can absorb some of the mechanical stress, reducing the risk of cracking or breaking.
Reduced Weight
Flex PCBs are typically lighter than rigid PCBs, which can be important in applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace or portable devices.
Improved Signal Integrity
Flex PCBs can provide better signal integrity than rigid PCBs, particularly at high frequencies. This is because the flexible substrate can reduce the amount of crosstalk and electromagnetic interference (EMI) between traces.
Types of Flex PCBs
There are several types of Flex PCBs, each with its own unique characteristics and applications.
Single-Layer Flex PCBs
Single-layer Flex PCBs consist of a single layer of conductive traces on a flexible substrate. They are the simplest and most cost-effective type of Flex PCB, making them ideal for low-complexity applications.
Double-Layer Flex PCBs
Double-layer Flex PCBs have two layers of conductive traces, separated by a flexible substrate. They offer more routing options and higher circuit density than single-layer Flex PCBs, making them suitable for more complex applications.
Multi-Layer Flex PCBs
Multi-layer Flex PCBs have three or more layers of conductive traces, separated by flexible substrates. They offer the highest circuit density and routing options, making them ideal for the most complex applications.
Rigid-Flex PCBs
Rigid-Flex PCBs combine rigid and flexible sections on a single board. The rigid sections provide mechanical support and can accommodate components that require a stable base, while the flexible sections allow the board to bend and fit into tight spaces.

Flex PCB Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process for Flex PCBs is similar to that of rigid PCBs, but with a few key differences.
Substrate Selection
The first step in Flex PCB manufacturing is to select the appropriate substrate material. The most common substrate materials for Flex PCBs are polyimide and polyester, both of which offer excellent flexibility and durability.
Circuit Design
The next step is to design the circuit layout using CAD software. The design must take into account the flexible nature of the substrate, as well as any bending or folding that will be required in the final application.
Printing
Once the circuit design is complete, the conductive traces are printed onto the substrate using a screen printing process. The traces are typically made of copper, although other materials such as silver or carbon can also be used.
Etching
After printing, the unwanted copper is etched away using a chemical process, leaving only the desired circuit traces on the substrate.
Coverlay Application
A coverlay or soldermask is then applied to the surface of the Flex PCB to protect the traces from damage and environmental factors. The coverlay is typically made of a flexible material such as polyimide or acrylic.
Cutting and Drilling
The Flex PCB is then cut to the desired shape and size using a laser or die cutting process. Any necessary holes or vias are also drilled at this stage.
Finishing
Finally, any additional finishing steps such as surface plating, solder mask application, or silkscreen printing are performed to complete the Flex PCB manufacturing process.
Applications of Flex PCBs
Flex PCBs are used in a wide range of applications across various industries, including:
Aerospace
Flex PCBs are commonly used in aerospace applications, where space and weight are at a premium. They can be used in avionics systems, satellite communications, and missile guidance systems, among others.
Automotive
Flex PCBs are used in various automotive applications, such as in-vehicle entertainment systems, dashboard displays, and engine control modules. They offer improved reliability and space savings compared to rigid PCBs.
Medical Devices
Flex PCBs are used in a variety of medical devices, such as wearable monitors, implantable devices, and diagnostic equipment. They offer improved patient comfort and ease of use compared to rigid PCBs.
Consumer Electronics
Flex PCBs are commonly used in consumer electronics, such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. They allow for more compact and lightweight designs, as well as improved durability.
Industrial Equipment
Flex PCBs are used in various industrial equipment, such as robotics, automation systems, and power electronics. They offer improved reliability and flexibility compared to rigid PCBs.
Choosing a Flex PCB Manufacturer
When choosing a Flex PCB manufacturer, there are several key factors to consider:
Experience and Expertise
Look for a manufacturer with extensive experience and expertise in Flex PCB design and manufacturing. They should have a proven track record of delivering high-quality products on time and within budget.
Quality Control
Choose a manufacturer with a robust quality control process in place to ensure that every Flex PCB meets the highest standards of quality and reliability.
Technical Support
Look for a manufacturer that offers comprehensive technical support throughout the design and manufacturing process, as well as after the product is delivered.
Pricing
While price is certainly a factor to consider, it should not be the only one. Look for a manufacturer that offers competitive pricing without sacrificing quality or service.
Flex PCB Design Considerations
When designing a Flex PCB, there are several key considerations to keep in mind:
Bend Radius
The bend radius is the minimum radius that the Flex PCB can be bent without causing damage to the traces or substrate. It is important to design the PCB with the appropriate bend radius in mind to ensure reliability and durability.
Trace Width and Spacing
The trace width and spacing must be carefully designed to ensure adequate current carrying capacity and to minimize the risk of short circuits or crosstalk.
Stiffeners
Stiffeners can be added to the Flex PCB to provide additional support and stability in areas where components will be mounted or where the PCB will be subjected to mechanical stress.
Shielding
In applications where EMI is a concern, shielding can be added to the Flex PCB to reduce interference and improve signal integrity.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between a Flex PCB and a rigid PCB?
A: A Flex PCB is designed to be flexible and bendable, while a rigid PCB is not. Flex PCBs offer several advantages over rigid PCBs, including space savings, increased reliability, reduced weight, and improved signal integrity.
Q: What are the most common substrate materials used in Flex PCBs?
A: The most common substrate materials used in Flex PCBs are polyimide and polyester, both of which offer excellent flexibility and durability.
Q: Can Flex PCBs be used in high-temperature applications?
A: Yes, Flex PCBs can be designed to withstand high temperatures, typically up to 150°C or higher, depending on the materials used.
Q: How do I choose the right Flex PCB manufacturer for my project?
A: When choosing a Flex PCB manufacturer, look for one with extensive experience and expertise, a robust quality control process, comprehensive technical support, and competitive pricing.
Q: What are some common applications for Flex PCBs?
A: Flex PCBs are used in a wide range of applications across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical devices, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment.
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Avionics systems, satellite communications, missile guidance systems |
| Automotive | In-vehicle entertainment systems, dashboard displays, engine control modules |
| Medical Devices | Wearable monitors, implantable devices, diagnostic equipment |
| Consumer Electronics | Smartphones, tablets, wearable devices |
| Industrial Equipment | Robotics, automation systems, power electronics |
Conclusion
Flex PCBs offer a range of advantages over traditional rigid PCBs, including space savings, increased reliability, reduced weight, and improved signal integrity. They are used in a wide range of applications across various industries, from aerospace and automotive to medical devices and consumer electronics.
When designing a Flex PCB, it is important to consider factors such as bend radius, trace width and spacing, stiffeners, and shielding to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Choosing the right Flex PCB manufacturer is also critical, and factors such as experience, quality control, technical support, and pricing should all be taken into account.
Overall, Flex PCBs are a valuable and useful technology that offers significant benefits over traditional rigid PCBs in many applications. As technology continues to advance and new applications emerge, the demand for Flex PCBs is only likely to grow in the years ahead.





Leave a Reply