What is a 1N4002 Diode?
A 1N4002 diode is a general-purpose rectifier diode that belongs to the 1N400x series. It is designed to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) and protect circuits from reverse voltage spikes. The 1N4002 diode has a maximum reverse voltage of 100 volts and a forward current rating of 1 ampere.
Key Features of the 1N4002 Diode
- Maximum Repetitive Peak Reverse Voltage (VRRM): 100 V
- Maximum RMS Voltage (VRMS): 70 V
- Maximum DC Blocking Voltage (VDC): 100 V
- Maximum Average Forward Rectified Current (IF(AV)): 1 A
- Peak Forward Surge Current (IFSM): 30 A
- Maximum Instantaneous Forward Voltage Drop (VF) at 1 A: 1.1 V
- Maximum Reverse Current (IR) at 100 V: 5 μA
- Maximum Junction Temperature (TJ): 175°C
- Operating Temperature Range: -65°C to +175°C
How Does a 1N4002 Diode Work?
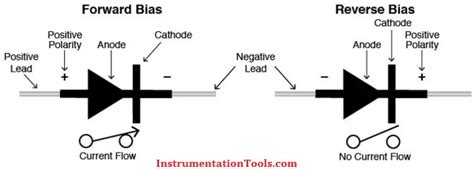
A 1N4002 diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in only one direction, from its anode to its cathode. When the voltage at the anode is higher than the voltage at the cathode by a certain amount (forward voltage drop), the diode becomes forward-biased, and current flows through it. When the voltage at the cathode is higher than the voltage at the anode, the diode becomes reverse-biased, and current flow is blocked.
Forward Bias Characteristics
When the 1N4002 diode is forward-biased, it exhibits the following characteristics:
- Low forward voltage drop (VF): Typically around 0.7 V to 1.1 V at 1 A
- High forward current capability: Up to 1 A of average forward rectified current
- Low forward resistance: Allowing efficient current flow
Reverse Bias Characteristics
When the 1N4002 diode is reverse-biased, it exhibits the following characteristics:
- High reverse voltage capability: Up to 100 V of peak reverse voltage
- Low reverse current leakage: Typically less than 5 μA at the maximum reverse voltage
- High reverse resistance: Preventing significant current flow in the reverse direction
Applications of the 1N4002 Diode
The 1N4002 diode finds applications in a wide range of electronic circuits, including:
- Power Supply Rectification
- Half-wave rectifiers
- Full-wave rectifiers
-
Bridge rectifiers
-
Reverse Polarity Protection
-
Preventing damage to circuits due to incorrect power supply connections
-
Voltage Clamping
-
Limiting voltage spikes in circuits
-
Voltage Multipliers
-
Generating higher voltages from a lower voltage source
-
Switching Applications
-
Isolating signals in switching circuits
-
Freewheel Diodes
- Providing a path for inductive currents in switching circuits

Selecting the Right 1N4002 Diode
When choosing a 1N4002 diode for your application, consider the following factors:
- Voltage Rating
-
Ensure that the diode’s maximum reverse voltage rating is sufficient for your application.
-
Current Rating
-
Verify that the diode can handle the expected forward current in your circuit.
-
Package Type
-
1N4002 diodes are available in various packages, such as DO-41, DO-15, and SMA. Choose the package that suits your space constraints and PCB layout.
-
Temperature Range
-
Consider the operating temperature range of your application and ensure that the 1N4002 diode’s temperature rating is adequate.
-
Reverse Recovery Time
- In high-speed switching applications, the reverse recovery time of the diode may be critical. The 1N4002 diode has a relatively slow reverse recovery time compared to fast-recovery diodes.
Comparing the 1N4002 Diode with Other Rectifier Diodes
The 1N400x series includes several rectifier diodes with different voltage and current ratings. The following table compares the 1N4002 diode with other common rectifier diodes in the series:
| Diode | Maximum Reverse Voltage (VRRM) | Maximum Average Forward Current (IF(AV)) |
|---|---|---|
| 1N4001 | 50 V | 1 A |
| 1N4002 | 100 V | 1 A |
| 1N4003 | 200 V | 1 A |
| 1N4004 | 400 V | 1 A |
| 1N4005 | 600 V | 1 A |
| 1N4006 | 800 V | 1 A |
| 1N4007 | 1000 V | 1 A |
When selecting a rectifier diode, consider the maximum reverse voltage and average forward current requirements of your application to choose the most suitable diode.
FAQs
-
Q: Can I use a 1N4002 diode for high-frequency applications?
A: The 1N4002 diode is not designed for high-frequency applications due to its relatively slow reverse recovery time. For high-frequency applications, fast-recovery diodes or Schottky diodes are more suitable. -
Q: Is the 1N4002 diode polarized?
A: Yes, the 1N4002 diode is a polarized component. The cathode is marked with a band on the diode’s body, while the unmarked end is the anode. -
Q: Can I parallel multiple 1N4002 diodes to increase the current capacity?
A: Yes, you can parallel multiple 1N4002 diodes to increase the current capacity. However, ensure that the diodes have similar forward voltage drops and that the current is evenly distributed among them. Using diodes with closely matched characteristics is recommended. -
Q: What happens if I exceed the maximum reverse voltage of a 1N4002 diode?
A: Exceeding the maximum reverse voltage of a 1N4002 diode can lead to breakdown and permanent damage to the diode. Always ensure that the reverse voltage in your application does not exceed the diode’s maximum rating. -
Q: Can I use a 1N4002 diode for voltage regulation?
A: While the 1N4002 diode can be used in simple voltage regulation circuits, such as zener diode regulators, it is not designed specifically for voltage regulation. Zener diodes or dedicated voltage regulator ICs are more suitable for precise voltage regulation applications.
Conclusion
The 1N4002 diode is a reliable and versatile rectifier diode that finds applications in various electronic circuits. Its key features, such as a high reverse voltage rating and a reasonable forward current capability, make it a popular choice for power supply rectification, reverse polarity protection, and voltage clamping.
When selecting a 1N4002 diode for your application, consider factors such as voltage and current ratings, package type, temperature range, and reverse recovery time. By understanding the characteristics and specifications of the 1N4002 diode, you can effectively incorporate it into your designs and ensure optimal performance.
Remember to handle the 1N4002 diode with care, observing proper electrostatic discharge (ESD) precautions and avoiding excessive heat during soldering. With its robust construction and reliable performance, the 1N4002 diode is a valuable component in any electronics enthusiast’s toolkit.





Leave a Reply